Ontology Wasm 自從上線測試網以來便受到了社區開發人員的極大關注。Ontology Wasm 的上線將使得業務邏輯復雜的 dApp 合約上鏈成本降低,極大豐富 dApp 生態。在進行 Ontology Wasm 合約開發時,開發者不僅可以使用 Rust,還可以使用 C++ 作為合約開發語言。
一、Hello World
按照慣例,我們還是從一個 Hello world 開始
#include《ontiolib/ontio.hpp》#include《stdio.h》
using namespace ontio;class hello:public contract {
public:
using contract::contract:
void sayHello(){
printf(“hello world!”);
}
};
ONTIO_DISPATCH(hello, (sayHello));
1.1 合約入口
Ontology Wasm CDT 編譯器已經對入口和參數解析進行了封裝,所以開發者不需要重新定義入口方法。接下來是定義合約的對外接口,這是智能合約對外提供服務的方法。
ONTIO_DISPATCH(hello, (sayHello));
在上面的例子中, 我們暫時只支持 sayHello 這個方法:
printf(“hello world!”);
這個“Hello world!”會在節點的日志中以調試信息打印出來。在實際的應用中, printf 只能用作調試的目的, 一個實際的智能合約,需要實現更多更復雜的功能。
1.2 智能合約 API
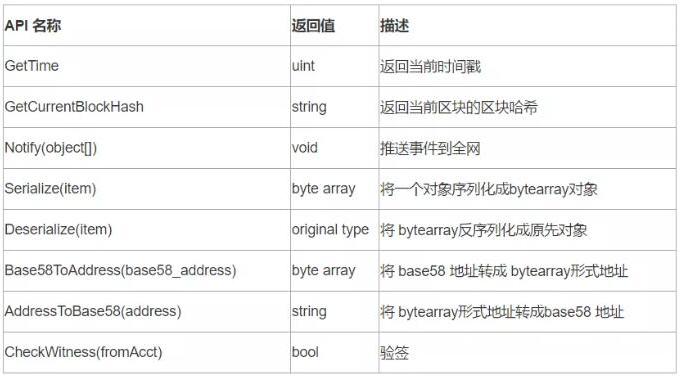
Ontology Wasm 提供如下 API 與區塊鏈的底層進行交互:
二、紅包合約
下面我們通過一個更加復雜的例子來演示如何通過這些 API 來開發一個完整的 Wasm 智能合約。
很多情況下我們都會通過各種 App,如微信等聊天工具發紅包。我們可以給朋友發送紅包,也可以搶其他人發送的紅包,收到的錢會記入到個人微信賬戶中。
類似于微信的流程,我們將嘗試創建一個智能合約。用戶使用該合約,可以發送 ONT,ONG 或者是標準的 OEP-4的 Token 資產紅包給他的朋友們,而朋友們搶到的紅包可以直接轉入到他們的錢包賬戶中。
2.1 創建合約
首先,我們需要新建合約的源文件,暫且命名為 redEnvelope.cpp。這個合約我們需要三個接口:
· createRedEnvelope: 創建紅包
· queryEnvelope: 查詢紅包信息
· claimEnvelope: 搶紅包
#include《ontiolib/ontio.hpp》
using namespace ontio;
class redEnvelope: public contract{
}
ONTIO_DISPATCH(redEnvelope, (createRedEnvelope)(queryEnvelope)(claimEnvelope));
我們需要在存儲中保存一些關鍵的數據。在智能合約中, 數據以 KV 的形式保存在該合約的上下文空間中,這些數據的 KEY 需要設置前綴以便于后面的查詢。下面定義了三個不同的前綴供使用:
std::string rePrefix = “RE_PREFIX_”;
std::string sentPrefix = “SENT_COUNT_”;
std::string claimPrefix = “CLAIM_PREFIX_”;
因為我們的合約支持 ONT 和 ONG 這兩種 Ontology 的原生資產, 我們可以預先定義好這兩種資產的合約地址。不同于標準的智能合約, Ontology 原生合約(native contract)的合約地址是固定的,而不是根據合約代碼的 hash 計算而來的。
address ONTAddress = {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1};
address ONGAddress = {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,2};
我們需要在合約中保存紅包的信息, 如紅包的資產信息(token 的合約地址, 紅包的總金額, 紅包的個數等等)。
struct receiveRecord{
address account; //用戶地址
asset amount; //搶到的金額
ONTLIB_SERIALIZE(receiveRecord,(account)(amount))
};
struct EnvelopeStruct{
address tokenAddress; //資產token的地址
asset totalAmount; //紅包總金額
asset totalPackageCount; //紅包總數
asset remainAmount; //當前剩余的金額
asset remainPackageCount; //當前剩余的紅包數
std::vector《struct receiveRecord》 records; //已經搶完的記錄
ONTLIB_SERIALIZE( EnvelopeStruct, (tokenAddress)(totalAmount)(totalPackageCount)(remainAmount)(remainPackageCount)(records) )
};
其中,
ONTLIB_SERIALIZE(receiveRecord,(account)(amount))
是由 Ontology Wasm CDT 定義的宏操作,用于在將 struct 存儲前進行序列化的操作。
2.2 創建紅包
準備工作差不多了,下面我們開始開發具體的接口邏輯。
1. 創建紅包需要指定創建者地址, 紅包數量, 紅包金額和資產的合約地址:
bool createRedEnvelope(address owner,asset packcount, asset amount,address tokenAddr ){
return true;
}
2. 檢查是否有創建者的簽名, 否則交易回滾退出:
ontio_assert(check_witness(owner),“checkwitness failed”);
NOTE: ontio_assert(expr, errormsg):當 expr 為 false 時, 拋出異常并退出。
3. 如果紅包資產是 ONT,由于 ONT 的不可分割性(最小為1個 ONT), 紅包的金額要大于或等于紅包的數量,保證每個紅包最少有1個 ONT:
if (isONTToken(tokenAddr)){
ontio_assert(amount 》= packcount,“ont amount should greater than packcount”);
}
4. 對于每個紅包的創建者,我們需要記錄一下他發送紅包的總數量:
key sentkey = make_key(sentPrefix,owner.tohexstring());
asset sentcount = 0;
storage_get(sentkey,sentcount);
sentcount += 1;
storage_put(sentkey,sentcount);
5. 生成紅包 hash, 這個 hash 就是之后標識這個紅包的唯一 ID:
H256 hash ;
hash256(make_key(owner,sentcount),hash) ;
key rekey = make_key(rePrefix,hash256ToHexstring(hash));
6. 根據 token 資產的類型,將資產轉入合約中,self_address()可以取得當前執行的合約地址, 我們根據用戶輸入的 token 類型,將指定數量的 token 轉入合約:
address selfaddr = self_address();
if (isONTToken(tokenAddr)){
bool result = ont::transfer(owner,selfaddr ,amount);
ontio_assert(result,“transfer native token failed!”);
}else if (isONGToken(tokenAddr)){
bool result = ong::transfer(owner,selfaddr ,amount);
ontio_assert(result,“transfer native token failed!”);
}else{
std::vector《char》 params = pack(std::string(“transfer”),owner,selfaddr,amount);
bool res;
call_contract(tokenAddr,params, res );
ontio_assert(res,“transfer oep4 token failed!”);
}
NOTE 1:對于 ONT 和 ONG 這兩種原生資產, Ontology Wasm CDT 提供了ont::transfer API 進行轉賬操作;而 OEP-4類的資產,需要按照普通的跨合約調用方法來轉賬。
NOTE 2:和普通的錢包地址一樣, 合約地址也可以接受任意類型的資產。但是合約地址是由合約編譯后的二進制代碼 hash 產生的,所以沒有對應的私鑰,也就無法隨意操作合約中的資產,如果你沒有在合約中設置對資產的操作,就意味著你將無法控制這部分資產。
7. 將合約的信息保存在存儲中:
struct EnvelopeStruct es ;
es.tokenAddress = tokenAddr;
es.totalAmount = amount;
es.totalPackageCount = packcount;
es.remainAmount = amount;
es.remainPackageCount = packcount;
es.records = {};
storage_put(rekey, es);
8. 發送創建紅包的事件。對于智能合約的調用是一個異步的過程,合約會在執行成功后發送一個事件來通知客戶端執行結果,這個事件的格式可以由合約的編寫者來指定。
char buffer [100];
sprintf(buffer, “{”states“:[”%s“, ”%s“, ”%s“]}”,“createEnvelope”,owner.tohexstring().c_str(),hash256ToHexstring(hash).c_str());
notify(buffer);
return true;
一個簡單的紅包就創建完成了, 下一步我們需要實現如何查詢這個紅包的信息。
2.3 查詢紅包
查詢紅包的邏輯非常簡單, 只需要將存儲中的紅包信息取出并格式化返回即可:
std::string queryEnvelope(std::string hash){
key rekey = make_key(rePrefix, hash);
struct EnvelopeStruct es;
storage_get(rekey, es);
return formatEnvelope(es);
}
NOTE:對于智能合約的只讀操作(例如查詢), 可以通過預執行(pre-exec)來讀取結果。不同于普通的合約調用,預執行不需要錢包的簽名,同時也就無需花費 ONG。最后,其他用戶可以根據 hash(紅包的 ID)來領取(搶)這個紅包了。
2.4 領取紅包
我們已經把資產成功地轉入到智能合約中了, 接下來就可以把這個紅包的 ID 發送給你的朋友們讓他們去搶紅包了。
1. 領取紅包需要輸入領取人的賬戶和紅包的hash:
bool claimEnvelope(address account, std::string hash){
return true;
}
2. 同樣, 我們需要驗證領取賬戶的簽名, 不允許替其他人搶紅包, 而且每個賬戶每個紅包只能搶一次:
ontio_assert(check_witness(account),“checkwitness failed”);
key claimkey = make_key(claimPrefix,hash,account);
asset claimed = 0 ;
storage_get(claimkey,claimed);
ontio_assert(claimed == 0,“you have claimed this Envelope!”);
3. 按照 hash 從存儲中取出紅包的信息, 判斷這個紅包是否沒有被搶完:
key rekey = make_key(rePrefix,hash);
struct EnvelopeStruct es;
storage_get(rekey,es);
ontio_assert(es.remainAmount 》 0, “the Envelope has been claimed over!”);
ontio_assert(es.remainPackageCount 》 0, “the Envelope has been claimed over!”);
4. 新建一條領取的記錄:
struct receiveRecord record ;
record.account = account;
asset claimAmount = 0;
5. 計算本次領取紅包的資產數量。如果是最后一個紅包, 數量為剩余的金額, 否則根據當前區塊 hash 計算隨機數,確定本次領取的數量, 并更新紅包信息:
if (es.remainPackageCount == 1){
claimAmount = es.remainAmount;
record.amount = claimAmount;
}else{
H256 random = current_blockhash() ;
char part[8];
memcpy(part,&random,8);
uint64_t random_num = *(uint64_t*)part;
uint32_t percent = random_num % 100 + 1;
claimAmount = es.remainAmount * percent / 100;
//ont case
if (claimAmount == 0){
claimAmount = 1;
}else if(isONTToken(es.tokenAddress)){
if ( (es.remainAmount - claimAmount) 《 (es.remainPackageCount - 1)){
claimAmount = es.remainAmount - es.remainPackageCount + 1;
}
}
record.amount = claimAmount;
}
es.remainAmount -= claimAmount;
es.remainPackageCount -= 1;
es.records.push_back(record);
6. 根據計算結果, 將對應資產從合約中轉到領取的賬戶:
address selfaddr = self_address();
if (isONTToken(es.tokenAddress)){
bool result = ont::transfer(selfaddr,account ,claimAmount);
ontio_assert(result,“transfer ont token failed!”);
} else if (isONGToken(es.tokenAddress)){
bool result = ong::transfer(selfaddr,account ,claimAmount);
ontio_assert(result,“transfer ong token failed!”);
} else{
std::vector《char》 params = pack(std::string(“transfer”),selfaddr,account,claimAmount);
bool res = false;
call_contract(es.tokenAddress,params, res );
ontio_assert(res,“transfer oep4 token failed!”);
}
7. 記錄領取的信息, 將更新后的紅包信息寫回存儲并發送通知事件:
storage_put(claimkey,claimAmount);
storage_put(rekey,es);
char buffer [100];
std::sprintf(buffer, “{”states“:[”%s“,”%s“,”%s“,”%lld“]}”,“claimEnvelope”,hash.c_str(),account.tohexstring().c_str(),claimAmount);
notify(buffer);
return true;
如前面所說,這個合約只能通過 claimEnvelope 這個接口將資產轉出合約。所以,合約中的資產是安全的,任何人都無法隨意的取走里面的資產。至此, 一個簡單的紅包合約邏輯完成, 完整的合約代碼如下: https://github.com/JasonZhouPW/pubdocs/blob/master/redEnvelope.cpp
2.5 合約測試
合約測試可以有兩種方法:
1. 使用 CLI
請參考:https://github.com/ontio/ontology-wasm-cdt-cpp/blob/master/How_To_Run_ontologywasm_node.md
2. 使用 Golang SDK
請參考:https://github.com/ontio/ontology-wasm-cdt-cpp/blob/master/example/other/main.go
三、總結
本示例只是為了展示如何編寫一個完整的 Ontology Wasm 智能合約, 如何通過調用 API 和底層的區塊鏈進行交互。如果要作為正式的產品, 還需要解決紅包的隱私問題: 所有人都可以通過監控合約的事件來取得紅包的 hash, 意味著每個人都可以搶這個紅包。一種比較簡單的解決方法,就是在創建紅包時指定哪些賬戶能夠領取。如果有興趣, 您也可以嘗試修改測試一下。
Ontology 作為領先公鏈,率先支持 Wasm 合約,為 Wasm 技術的成熟貢獻自己的一份力量。我們歡迎更多的 Wasm 技術愛好者加入本體開發社區,共同打造技術生態。
 電子發燒友App
電子發燒友App





















評論