以太坊區塊鏈使用修改后的Merkle Patricia樹進行狀態認證。這使區塊鏈節點在每個區塊的整個區塊鏈狀態上達成共識,并使輕客戶端可以為任何狀態信息創建Merkle證明。
但是自以太坊初期以來就可以進行狀態Merkle證明驗證,但直到最近才將其添加到JSON RPC API中,因此很高興看到更多應用程序利用此功能。
存儲Merkle證明僅對特定的trie root(即特定狀態)有效。因此用戶或輕客戶端應用程序應該通過運行輕客戶端或信任由多個證明方進行多重簽名的狀態根來信任該狀態根:更安全。
賬戶和合約變量查詢
在本例中,我們將使用web3.py構建一個merkle證明,證明指定的狀態根中包含鍵的某些值。
Web3.py尚不支持eth_getProof,因為在撰寫本文時并未合并PR。因此可以改用web3.py的這個fork:https://github.com/paouvrard/web3.py/tree/EIP-1186-eth_getProof
編輯(2019年10月):eth_getProof現在在web3.py和web3.js中可用,但在Metamask提供程序中不可用。
Web3.py連接到以太坊節點,并通過JSON RPC或IPC API eth_getProof進行狀態查詢并提供證明。
合約狀態變量查詢
簡單的Solidity合約,我們要在其中證明映射鍵的價值:
contract Proof {
string public greeting;
mapping (address =》 uint) public my_map;
constructor() public {
greeting = ‘Hello’;
my_map[msg.sender] = 33333;
}
}
驗證“ greeting”和“ my_map”的存儲證明:
from web3 import Web3, IPCProvider
from web3.middleware import geth_poa_middleware
from web3._utils.proof import verify_eth_getProof, storage_position
w3 = Web3(IPCProvider(。..))
w3.middleware_stack.inject(geth_poa_middleware, layer=0)
w3.eth.defaultAccount = Web3.toChecksumAddress(‘0x.。.’)
block = w3.eth.getBlock(‘latest’)
greeting = “0x0”
my_map_sender = storage_position(w3.eth.defaultAccount, “0x1”)
proof = w3.eth.getProof(contract_addr, [greeting, my_map_sender], block.number)
is_valid_proof = verify_eth_getProof(proof, block.stateRoot)
通過上面的腳本,我們現在可以構建和驗證帳戶和合約變量的狀態Merkle證明。 請注意,verify_eth_getProof(…)僅驗證包含證明,并且如果包含排除證明,則將返回False。 可以通過eth.getProof(。..)返回的“proof”對象來驗證排除情況。
合約變量如何存儲在Patricia trie中?
為了存儲變量,EVM根據合約中定義變量的位置使用key:keccack(LeftPad32(key,0),LeftPad32(map position,0))。 此處有更多詳細信息:https://github.com/ethereum/wiki/wiki/JSON-RPC#eth_getstorageat。
web3.py分叉提供了方便的storage_position(),它返回所請求的映射密鑰的Patricia樹存儲密鑰。
作為比較,Aergo Lua VM在trie中使用key存儲變量狀態信息:hash(bytes(“ __ sv __” + variable_name + [“-”,var_index],‘utf-8’)),其中var_u index是可選的,用于映射的鍵或數組的索引。
證明驗證碼
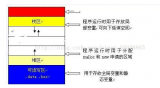
這是一個很好的圖表,解釋了patricia樹中不同類型的節點:
來源:https://ethereum.stackexchange.com/questions/6415/eli5-how-does-a-merkle-patricia-trie-tree-work

下面的代碼通過迭代驗證節點(上圖中的extension、branch、leaf…)來驗證key值和expected_value。 如果Expected_value等于證明中包含的值,則返回true。
def _verify(expected_root, key, proof, key_index, proof_index, expected_value):
‘’‘ Iterate the proof following the key.
Return True if the value at the leaf is equal to the expected value.
@param expected_root is the expected root of the current proof node.
@param key is the key for which we are proving the value.
@param proof is the proof the key nibbles as path.
@param key_index keeps track of the index while stepping through
the key nibbles.
@param proof_index keeps track of the index while stepping through
the proof nodes.
@param expected_value is the key’s value expected to be stored in
the last node (leaf node) of the proof.
‘’‘
node = proof[proof_index]
dec = rlp.decode(node)
if key_index == 0:
# trie root is always a hash
assert keccak(node) == expected_root
elif len(node) 《 32:
# if rlp 《 32 bytes, then it is not hashed
assert dec == expected_root
else:
assert keccak(node) == expected_root
if len(dec) == 17:
# branch node
if key_index 》= len(key):
if dec[-1] == expected_value:
# value stored in the branch
return True
else:
new_expected_root = dec[nibble_to_number[key[key_index]]]
if new_expected_root != b’‘:
return _verify(new_expected_root, key, proof, key_index + 1, proof_index + 1,
expected_value)
elif len(dec) == 2:
# leaf or extension node
# get prefix and optional nibble from the first byte
(prefix, nibble) = dec[0][:1].hex()
if prefix == ’2‘:
# even leaf node
key_end = dec[0][1:].hex()
if key_end == key[key_index:] and expected_value == dec[1]:
return True
elif prefix == ’3‘:
# odd leaf node
key_end = nibble + dec[0][1:].hex()
if key_end == key[key_index:] and expected_value == dec[1]:
return True
elif prefix == ’0‘:
# even extension node
shared_nibbles = dec[0][1:].hex()
extension_length = len(shared_nibbles)
if shared_nibbles == key[key_index:key_index + extension_length]:
new_expected_root = dec[1]
return _verify(new_expected_root, key, proof,
key_index + extension_length, proof_index + 1,
expected_value)
elif prefix == ’1‘:
# odd extension node
shared_nibbles = nibble + dec[0][1:].hex()
extension_length = len(shared_nibbles)
if shared_nibbles == key[key_index:key_index + extension_length]:
new_expected_root = dec[1]
return _verify(new_expected_root, key, proof,
key_index + extension_length, proof_index + 1,
expected_value)
else:
# This should not be reached if the proof has the correct format
assert False
return True if expected_value == b’‘ else False
Solidity:TODO
結論
這是一個關于如何使用包含/排除證明(inclusion/exclusion)來查詢Solidity合約變量的快速概述。 eth_getStorageAt和eth_getProof實際上消除了在合約代碼中定義getter的需要,因為getProof API直接查詢了trie狀態數據庫(獲取另一個合約變量的合約仍然需要getter)。
責任編輯;zl
 電子發燒友App
電子發燒友App






























評論