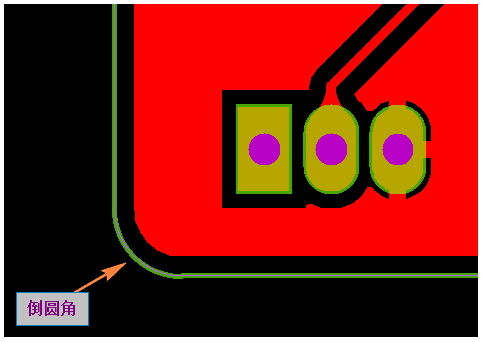
當 PCB 外形是直角時, 通常工程制作外形 (鑼帶) 時, 會將直角或尖角的地方倒成圓角, 主要是為了防止板邊容易劃傷板且容易扎傷人
所以當客戶沒有特殊要求時, PCB 外形是直角一般會默認倒角 0.5mm 圓角(如下圖所示)
一。 PCB 板邊倒圓角點分析
原 PCB 外形 如下圖圖示: 看了這個 PCB 外形, 產(chǎn)生有 2 個問題點。
1. 外形中哪些點需倒圓角?
2. 如何怎么倒圓角?
1. 外形中哪些點需倒圓角?
看下圖: PCB 外形倒圓角的點, 剛好就是我們凸包需求出的點, 接下來我們將玩轉(zhuǎn)凸包了, 只要求出凸包, 那么就可以實現(xiàn) PCB 板邊倒圓角啦。
求凸包的算法: 我們可以借鑒算法導論中的查找凸包的算法(加以改進得到新的求凸包方法, 詳見[方法一] 與[方法二] )
2. 如何怎么倒圓角?
在下面有說明倒角方法。
二。 求凸點
方法一求凸點:[采用多輪遍歷, 一遍一遍將凹點踢除, 剩于的即是凸點]
方法一求凸點: 代碼
/// 《summary》
/// 求最大多邊形最大凸包 1 [采用多輪遍歷將凹點踢除, 剩于的即是凸點]
/// 《/summary》
/// 《param name=“gSur_Point_list”》《/param》
/// 《returns》《/returns》
public List《gSur_Point》 s_convex_polyon1(List《gSur_Point》 gSur_Point_list)
{
bool isOK = true;
List《gSur_Point》 PointList = new List《gSur_Point》();
var isCCW = s_isCCW(gSur_Point_list);
int sum = gSur_Point_list.Count() - 1;
int n = gSur_Point_list.Count();
for (int i = 0; i 《n; i++)
{
int IndexPre = (i - 1) % sum;
if (IndexPre == -1) IndexPre = sum - 1;
int IndexCurrent = i % sum;
int IndexNext = (i + 1) % sum;
if (gSur_Point_list[IndexPre].type_point》 0) continue;
if (gSur_Point_list[IndexCurrent].type_point》 0) continue;
var multiVal = multi(gSur_Point_list[IndexPre].p, gSur_Point_list[IndexCurrent].p, gSur_Point_list[IndexNext].p);
if ((isCCW && multiVal》 0) || (!isCCW && multiVal 《0))
PointList.Add(gSur_Point_list[IndexCurrent]);
else
isOK = false;
}
List《gSur_Point》 Point2List = new List《gSur_Point》(PointList);
while (!isOK)
{
isOK = true;
PointList.Clear();
PointList.AddRange(Point2List);
Point2List.Clear();
sum = PointList.Count() - 1;
n = PointList.Count();
for (int i = 0; i 《n; i++)
{
int IndexPre = (i - 1) % sum;
if (IndexPre == -1) IndexPre = sum - 1;
int IndexCurrent = i % sum;
int IndexNext = (i + 1) % sum;
var multiVal = multi(PointList[IndexPre].p, PointList[IndexCurrent].p, PointList[IndexNext].p);
if ((isCCW && multiVal》 0) || (!isCCW && multiVal 《0))
Point2List.Add(PointList[IndexCurrent]);
else
isOK = false;
}
}
return Point2List;
}
方法二求凸包:[采用一邊遍歷找出凸點并加入隊列, 并同時將隊列中的凸點隊列中找出凹點踢除]
方法二求凸包代碼:
/// 《summary》
/// 求最大多邊形最大凸包 2 [采用一邊遍歷找出凸點并加入隊列, 并同時將隊列中的凸點隊列中找出凹點踢除]
/// 《/summary》
/// 《param name=“gSur_Point_list”》《/param》
/// 《returns》《/returns》
public List《gSur_Point》 s_convex_polyon2(List《gSur_Point》 gSur_Point_list)
{
Stack《gSur_Point》 StackPoint = new Stack《gSur_Point》();
var isCCW = s_isCCW(gSur_Point_list);
int sum = gSur_Point_list.Count() - 1;
int n = gSur_Point_list.Count();
for (int i = 0; i 《n; i++)
{
int IndexPre = (i - 1) % sum;
if (IndexPre == -1) IndexPre = sum - 1;
int IndexCurrent = i % sum;
int IndexNext = (i + 1) % sum;
if (gSur_Point_list[IndexPre].type_point》 0) continue;
if (gSur_Point_list[IndexCurrent].type_point》 0) continue;
var multiVal = multi(gSur_Point_list[IndexPre].p, gSur_Point_list[IndexCurrent].p, gSur_Point_list[IndexNext].p);
if ((isCCW && multiVal》 0) || (!isCCW && multiVal 《0))
{
L1:
if (StackPoint.Count》 1)
{
var Top1Point = StackPoint.Pop();
var Top2Point = StackPoint.Peek();
multiVal = multi(Top2Point.p, Top1Point.p, gSur_Point_list[IndexCurrent].p);
if ((isCCW && multiVal》 0) || (!isCCW && multiVal 《0))
StackPoint.Push(Top1Point);
else
goto L1;
}
StackPoint.Push(gSur_Point_list[IndexCurrent]);
}
}
return StackPoint.Reverse().ToList();
}
方法三求凸包:[按算法導論 Graham 掃描法 各節(jié)點按方位角 + 距離 逆時針排序 依次檢查, 當不屬凸點于則彈出]
方法三求凸包代碼
/// 《summary》
/// 求最大多邊形最大凸包 5 [按算法導論 Graham 掃描法 各節(jié)點按方位角 + 距離 逆時針排序 依次檢查, 當不屬凸點于則彈出]
/// 由于把各點的排列順序重新排序了, 只支持折線節(jié)點(當存在弧節(jié)點時會出異常 !!!)
/// 《/summary》
/// 《param name=“gSur_Point_list”》《/param》
/// 《returns》《/returns》
public List《gSur_Point》 s_convex_polyon3(List《gSur_Point》 gSur_Point_list)
{
var LeftBottomPoint = gSur_Point_list.OrderBy(tt =》 tt.p.y).ThenBy(tt =》 tt.p.x).FirstOrDefault();
gSur_Point_list.RemoveAt(gSur_Point_list.Count - 1);
gSur_Point_list.ForEach(tt =》
{
tt.Value = p2p_di(LeftBottomPoint.p, tt.p);
tt.Angle = p_ang(LeftBottomPoint.p, tt.p);
}
);
gSur_Point_list = gSur_Point_list.OrderBy(tt =》 tt.Angle).ThenBy(tt =》 tt.Value).ToList();
gSur_Point_list.Add(gSur_Point_list[0]);
Stack《gSur_Point》 StackPoint = new Stack《gSur_Point》();
var isCCW = true;
int sum = gSur_Point_list.Count() - 1;
int n = gSur_Point_list.Count();
for (int i = 0; i 《n; i++)
{
int IndexPre = (i - 1) % sum;
if (IndexPre == -1) IndexPre = sum - 1;
int IndexCurrent = i % sum;
int IndexNext = (i + 1) % sum;
var multiVal = multi(gSur_Point_list[IndexPre].p, gSur_Point_list[IndexCurrent].p, gSur_Point_list[IndexNext].p);
if (isCCW && multiVal》 0)
{
L1:
if (StackPoint.Count》 1)
{
var Top1Point = StackPoint.Pop();
var Top2Point = StackPoint.Peek();
multiVal = multi(Top2Point.p, Top1Point.p, gSur_Point_list[IndexCurrent].p);
if (isCCW && multiVal》 0)
StackPoint.Push(Top1Point);
else
goto L1;
}
StackPoint.Push(gSur_Point_list[IndexCurrent]);
}
}
return StackPoint.Reverse().ToList();
}
公共方法與數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)
/// 《summary》
/// Surface 坐標泛型集類 1
/// 《/summary》
public class gSur_Point
{
public gSur_Point()
{ }
public gSur_Point(double x_val, double y_val, byte type_point_)
{
this.p.x = x_val;
this.p.y = y_val;
this.type_point = type_point_;
}
public gSur_Point(gPoint p, byte type_point_)
{
this.p = p;
this.type_point = type_point_;
}
public gPoint p;
/// 《summary》
/// 0 為折點 1 為順時針 2 為逆時針
/// 《/summary》
public byte type_point { get; set; } = 0;
/// 《summary》
/// 值
/// 《/summary》
public double Value { get; set; } = 0;
/// 《summary》
/// 角度
/// 《/summary》
public double Angle { get; set; } = 0;
/// 《summary》
/// 標記
/// 《/summary》
public bool isFalg { get; set; }
}
/// 《summary》
/// 點 數(shù)據(jù)類型 (XY)
/// 《/summary》
public struct gPoint
{
public gPoint(gPoint p_)
{
this.x = p_.x;
this.y = p_.y;
}
public gPoint(double x_val, double y_val)
{
this.x = x_val;
this.y = y_val;
}
public double x;
public double y;
public static gPoint operator +(gPoint p1, gPoint p2)
{
p1.x += p2.x;
p1.y += p2.y;
return p1;
}
public static gPoint operator -(gPoint p1, gPoint p2)
{
p1.x -= p2.x;
p1.y -= p2.y;
return p1;
}
public static gPoint operator +(gPoint p1, double val)
{
p1.x += val;
p1.y += val;
return p1;
}
public static bool operator ==(gPoint p1, gPoint p2)
{
return (p1.x == p2.x && p1.y == p2.y);
}
public static bool operator !=(gPoint p1, gPoint p2)
{
return !(p1.x == p2.x && p1.y == p2.y);
}
}
/// 《summary》
/// 求叉積 判斷[點 P 與線 L] 位置關(guān)系[小于 0] 在右邊 [大于 0] 在左邊 [等于 0] 共線
/// 《/summary》
/// 《param name=“ps”》《/param》
/// 《param name=“pe”》《/param》
/// 《param name=“p”》《/param》
/// 《returns》[小于 0] 在右邊 [大于 0] 在左邊 [等于 0] 共線《/returns》
public double multi(gPoint ps, gPoint pe, gPoint p)
{
return ((ps.x - p.x) * (pe.y - p.y) - (pe.x - p.x) * (ps.y - p.y));
}
/// 《summary》
/// 檢測 Surface 是否逆時針
/// 《/summary》
/// 《param name=“gSur_Point_list”》《/param》
/// 《returns》《/returns》
public bool s_isCCW(List《gSur_Point》 gSur_Point_list)
{
double d = 0;
int n = gSur_Point_list.Count() - 1;
for (int i = 0; i 《n; i++)
{
if (gSur_Point_list.type_point》 0) continue;
int NextI = i + 1 + (gSur_Point_list[i + 1].type_point》 0 ? 1 : 0);
d += -0.5 * (gSur_Point_list[NextI].p.y + gSur_Point_list.p.y) * (gSur_Point_list[NextI].p.x - gSur_Point_list.p.x);
}
return d》 0;
}
/// 《summary》
/// 返回兩點之間歐氏距離
/// 《/summary》
/// 《param name=“p1”》《/param》
/// 《param name=“p2”》《/param》
/// 《returns》《/returns》
public double p2p_di(gPoint p1, gPoint p2)
{
return Math.Sqrt((p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x) + (p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y));
}
/// 《summary》
/// 求方位角
/// 《/summary》
/// 《param name=“ps”》《/param》
/// 《param name=“pe”》《/param》
/// 《returns》《/returns》
public double p_ang(gPoint ps, gPoint pe)
{
double a_ang = Math.Atan((pe.y - ps.y) / (pe.x - ps.x)) / Math.PI * 180;
// 象限角 轉(zhuǎn)方位角 計算所屬象限 并求得方位角
if (pe.x》= ps.x && pe.y》= ps.y) //↗ 第一象限
{
return a_ang;
}
else if (!(pe.x》= ps.x) && pe.y》= ps.y) // ↖ 第二象限
{
return a_ang + 180;
}
else if (!(pe.x》= ps.x) && !(pe.y》= ps.y)) //↙ 第三象限
{
return a_ang + 180;
}
else if (pe.x》= ps.x && !(pe.y》= ps.y)) // ↘ 第四象限
{
return a_ang + 360;
}
else
{
return a_ang;
}
}
View Code
三。 板邊凸點倒圓角方法
方法一。 也最簡單的倒角方法, 我們將 PCB 板邊凸點找出來后, 可以直接借助 genesis 倒角功能就可以實現(xiàn)了
當然但偶爾會報錯的, 且當 N 個小線段組成的尖角倒角會出錯(要實現(xiàn)完美效果只有自己寫倒角算法啦)
方法二: 自己寫倒角算法, 這個算法和加內(nèi)角孔算法類似 (這里只是介紹簡單的倒角) 考慮特殊的需要擴展
四。 凸點加倒圓角實現(xiàn)效果
編輯:hfy
-
pcb
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
4318文章
23017瀏覽量
396394
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
了解雙面和多層pcb板的優(yōu)缺點
中低頻pcb板與高頻pcb板區(qū)別
pcb沒有工藝邊怎么貼片
PCB設計與PCB制板的緊密關(guān)系
PCB抄板如何收費?pcb抄板收費標準
邊OTG邊充電芯片如何實現(xiàn)充電與數(shù)據(jù)傳輸并行?
PCB天線設計原理解析

PCBA為什么要設計工藝邊?設計工藝邊有什么好處嗎?
PCB抄板基礎(chǔ)知識詳細解析
詳解PCB抄板過程
很好的實現(xiàn)PCB板邊倒圓角
PCB高速設計信號完整性五個經(jīng)驗分享
PCB生產(chǎn)過程:為什么PCB內(nèi)外層蝕刻方法不一樣





 基于PCB 板的邊倒圓角實現(xiàn)方案解析
基于PCB 板的邊倒圓角實現(xiàn)方案解析










評論