道路車道檢測系統(tǒng):
自動駕駛汽車是現(xiàn)代世界的新趨勢之一。他們使用非常復雜的控制系統(tǒng)和工程技術來操縱車輛。道路車道檢測是車輛導航中的重要內容之一。在這里,我描述了一個使用 Raspberry pi 3 和計算機視覺技術的簡單快速的車道檢測。為了快速計算,我只是避免使用線性回歸方法。這種方法在低噪聲環(huán)境下效果很好,但對于復雜的場景,需要先進的統(tǒng)計和圖像處理技術。
硬件設置:
將相機與您的 Pi 連接

攝像頭配置:
按照此鏈接進行相機設置https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/configuration/camera.md
軟件設置:
為 python 安裝 OpenCV。按照這些說明安裝 OpenCV。這些說明是從https://raspberrypi.stackexchange.com復制的。
通用:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
sudo rpi-update
sudo reboot
sudo apt-get install build-essential git cmake pkg-config
sudo apt-get install libjpeg-dev libtiff5-dev libjasper-dev libpng12-dev
sudo apt-get install libavcodec-dev libavformat-dev libswscale-dev libv4l-dev
sudo apt-get install libxvidcore-dev libx264-dev
sudo apt-get install libgtk2.0-dev
sudo apt-get install libatlas-base-dev gfortran
cd ~
git clone
cd opencv
git checkout 3.1.0
cd ~
git clone
cd opencv_contrib
git checkout 3.1.0
如果您想將 OpenCV 與 python 2.7 一起使用:
sudo apt-get install python2.7-dev
wget
sudo python
pip install numpy
cd ~/opencv
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -D CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE \
-D INSTALL_C_EXAMPLES=OFF \
-D INSTALL_PYTHON_EXAMPLES=ON \
-D OPENCV_EXTRA_MODULES_PATH=~/opencv_contrib/modules \
-D BUILD_EXAMPLES=ON ..
make -j4
sudo make install
sudo ldconfig
如果您想在 Python 3 中使用 OpenCV:
sudo apt-get install python3-dev
wget
sudo python3
pip install numpy
cd ~/opencv
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -D CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE \
-D CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local \
-D INSTALL_C_EXAMPLES=OFF \
-D INSTALL_PYTHON_EXAMPLES=ON \
-D OPENCV_EXTRA_MODULES_PATH=~/opencv_contrib/modules \
-D BUILD_EXAMPLES=ON ..
make -j4
sudo make install
sudo ldconfig
將以上配置完成大約需要 2 個小時。在此期間,我們可以了解一下 Hough-Transform,這項技術是大多數(shù)實用車道檢測算法背后的關鍵。
Python代碼:
from picamera.array import PiRGBArray
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
from picamera import PiCamera
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
import math
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD)
GPIO.setup(7, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(8, GPIO.OUT)
theta=0
minLineLength = 5
maxLineGap = 10
camera = PiCamera()
camera.resolution = (640, 480)
camera.framerate = 30
rawCapture = PiRGBArray(camera, size=(640, 480))
time.sleep(0.1)
for frame in camera.capture_continuous(rawCapture, format="bgr", use_video_port=True):
image = frame.array
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0)
edged = cv2.Canny(blurred, 85, 85)
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(edged,1,np.pi/180,10,minLineLength,maxLineGap)
if(lines !=None):
for x in range(0, len(lines)):
for x1,y1,x2,y2 in lines[x]:
cv2.line(image,(x1,y1),(x2,y2),(0,255,0),2)
theta=theta+math.atan2((y2-y1),(x2-x1))
#print(theta)GPIO pins were connected to arduino for servo steering control
threshold=6
if(theta>threshold):
GPIO.output(7,True)
GPIO.output(8,False)
print("left")
if(theta<-threshold):
GPIO.output(8,True)
GPIO.output(7,False)
print("right")
if(abs(theta) GPIO.output(8,False)
GPIO.output(7,False)
print "straight"
theta=0
cv2.imshow("Frame",image)
key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
rawCapture.truncate(0)
if key == ord("q"):
break):
示例輸出結果:
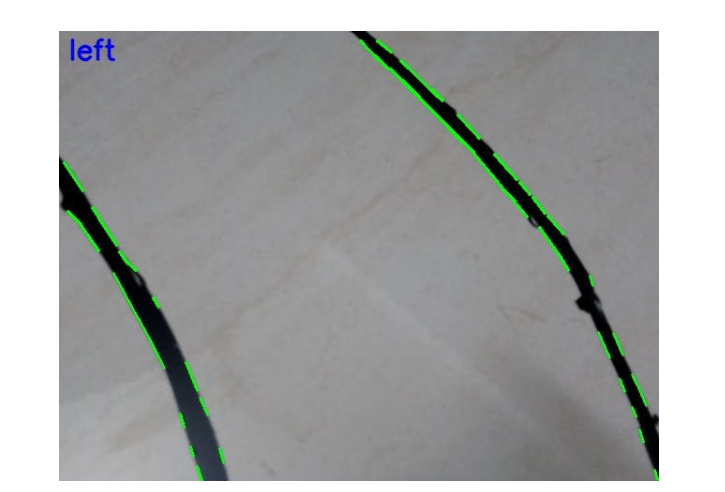
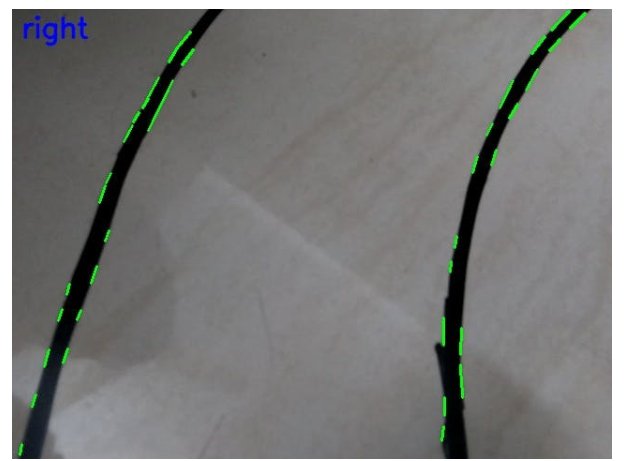
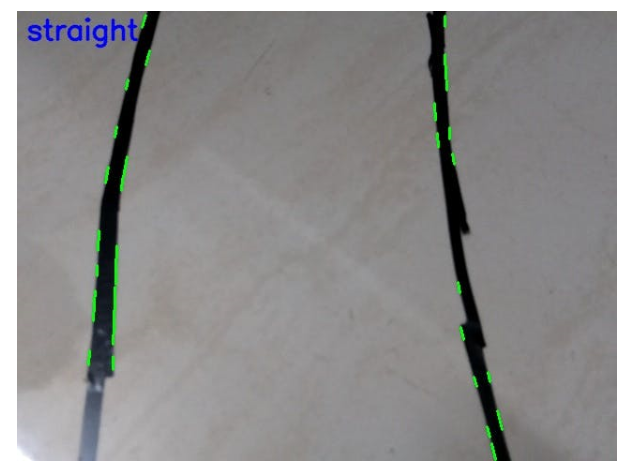



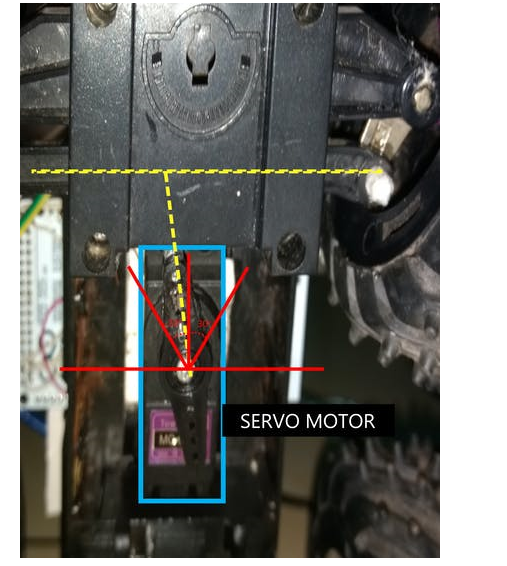
GPIO 引腳連接到 Arduino mega 用于伺服電機控制。
#include
Servo myservo;
void setup() {
myservo.attach(10);//attach servo motor PWM(orange) wire to pin 10
pinMode(0, INPUT);//attach GPIO 7&8 pins to arduino pin 0&1
pinMode(1,INPUT);
void loop() {
if(digitalRead(0)==HIGH && digitalRead(1)==LOW)
{
myservo.write(118);
}
if(digitalRead(1)==HIGH && digitalRead(0)==LOW)
{
myservo.write(62);
}
if(digitalRead(1)==LOW && digitalRead(0)==LOW)
{
myservo.write(90);
}
}
-
自動駕駛汽車
+關注
關注
4文章
376瀏覽量
40815 -
樹莓派
+關注
關注
116文章
1699瀏覽量
105527
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
基于樹莓派設計的RFID門禁系統(tǒng)
樹莓派防占位系統(tǒng)
樹莓派的種類_樹莓派安裝教程
樹莓派3wifi配置_樹莓派3開啟wifi熱點_樹莓派3的wifi使用教程
樹莓派3硬件配置_樹莓派3都能裝什么系統(tǒng)_樹莓派3系統(tǒng)安裝教程
樹莓派3系統(tǒng)安裝介紹_Noobs進行樹莓派3系統(tǒng)安裝_Noobs進行樹莓派3系統(tǒng)恢復
樹莓派3系統(tǒng)配置詳解_樹莓派3如何配置config.txt文件_樹莓派3如何設置分辨率

樹莓派入門教程之新手使用樹莓派做系統(tǒng)的教程資料說明

【樹莓派】樹莓派4B新手篇:安裝官網(wǎng)Raspbian Buster系統(tǒng)及基礎配置





 基于樹莓派設計的道路車道檢測系統(tǒng)
基于樹莓派設計的道路車道檢測系統(tǒng)











評論