一個完整的醫療影像推理流程一般包含數據的前處理、AI 推理以及數據后處理這幾部分。通常情況下,我們可以通過 TensorRT, TensorFlow 或者 PyTorch 這些框架來實現 GPU 加速的 AI 推理部分,然而數據前后處理部分往往是放在 CPU 上執行的。對于一些比較大的數據,比如 CT 或者 MR 這種 3D 圖像,CPU 上的數據前后處理會成為整個推理流程的瓶頸,導致推理的時延變長,GPU 使用效率不高。醫療影像推理的另一個需要考慮的問題是如何實現高效的部署。我們往往需要部署多個醫療影像 AI 應用,那么如何去調度多個模型,如何并發處理多個請求,并充分利用 GPU 資源成為挑戰。
什么是 MONAI
MONAI 是一個專門針對醫療圖像的深度學習開源框架。MONAI 致力于:
-
發展一個學術界、工業界和臨床研究人員共同合作的社區;
-
為醫療圖像創建最先進的端到端工作流;
-
為研究人員提供創建和評估深度學習模型的優化和標準化的方法。
MONAI 中包含一系列的 transforms 對醫療圖像數據進行前后處理。在 MONAI 0.7 中,我們在 transforms 中引入基于 PyTorch Tensor 的計算,許多 transforms 既支持 NumPy array,也支持 PyTorch Tensor 作為輸入類型和計算后端。當以 PyTorch Tensor 作為輸入數據時,我們可以使用 GPU 來加速數據前后處理的計算。
什么是 NVIDIA Triton 推理服務器
Triton 推理服務器是一個開源的 AI 模型部署軟件,可以簡化深度學習推理的大規模部署。它能夠對多種框架(TensorFlow、TensorRT、PyTorch、ONNX Runtime 或自定義框架),在任何基于 GPU 或 CPU 的環境上(云、數據中心、邊緣)大規模部署經過訓練的 AI 模型。Triton 可提供高吞吐量推理,以實現 GPU 使用率的最大化。
在較新的版本中,Triton 增加了 Python backend 這一新特性,Python backend 的目標是讓使用者可以更加容易的部署 Python 寫的模型,無需再去編寫任何 C++ 代碼。在一些場景下,我們的推理流程中可能會出現循環、條件判斷、依賴于運行時數據的控制流和其他自定義邏輯與模型混合執行。使用 Triton Python backend,開發人員可以更加容易地在自己的推理流程中實現這些控制流,并且在 Python 模型中調用 Triton 部署的其他模型。
使用 MONAI 和 Triton 高效搭建和部署 GPU 加速的醫療影像推理流程
在本文介紹的例子中,我們將使用 MONAI 中 GPU 加速的數據處理以及 Triton 的 Python backend 來構建一個 GPU 加速的醫療影像推理流程。通過這個例子,讀者可以了解到,在 GPU 上進行數據處理所帶來的性能增益,以及如何使用 Triton 進行高效的推理部署。
整個推理流程如下圖所示,包含數據預處理,AI 模型推理,和數據后處理三部分。
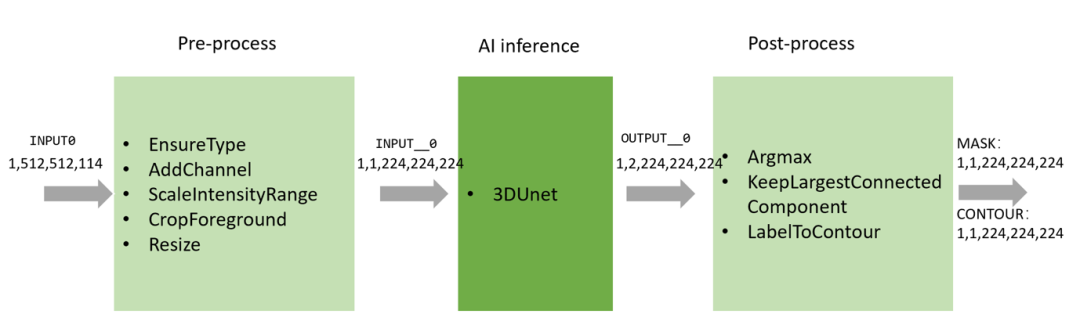
通過 EnsureType 這個 transform,我們將輸入數據轉換成 PyTorch Tensor 并放到 GPU 上,這樣之后的數據預處理操作都會在 GPU 上進行。我們使用 Triton 的 Torch backend 來作為 3DUnet 的推理后端,輸出的結果為 GPU 上的 Torch Tensor,并作為后處理模塊的輸入,在 GPU 上進行后處理計算。
使用 Triton 的 Python backend,我們可以非常容易的將整個流程串聯起來,即:按照 Triton Python backend 要求的模型結構構建前后處理的 Python 代碼,并在其中調用 3DUnet 的推理。以下是我們例子中的代碼片段。完整的代碼及復現步驟請見 Github:
https://github.com/Project-MONAI/tutorials/tree/master/full_gpu_inference_pipeline
class TritonPythonModel:"""Your Python model must use the same class name. Every Python modelthat is created must have "TritonPythonModel" as the class name."""def initialize(self, args):"""`initialize` is called only once when the model is being loaded.Implementing `initialize` function is optional. This function allowsthe model to intialize any state associated with this model."""self.inference_device_id = args.get("model_instance_device_id", "0")infer_transforms = []infer_transforms.append(EnsureType(device=torch.device(f"cuda:{self.inference_device_id}")))infer_transforms.append(AddChannel())infer_transforms.append(ScaleIntensityRange(a_min=-57, a_max=164, b_min=0.0, b_max=1.0, clip=True))infer_transforms.append(CropForeground())infer_transforms.append(Resize(spatial_size=(224, 224, 224)))self.pre_transforms = Compose(infer_transforms)def execute(self, requests):"""`execute` must be implemented in every Python model. `execute`function receives a list of pb_utils.InferenceRequest as the onlyargument. This function is called when an inference is requestedfor this model. Depending on the batching configuration (e.g. DynamicBatching) used, `requests` may contain multiple requests. EveryPython model, must create one pb_utils.InferenceResponse for everypb_utils.InferenceRequest in `requests`. If there is an error, you canset the error argument when creating a pb_utils.InferenceResponse."""responses = []for request in requests:# get the input by name (as configured in config.pbtxt)input_triton_tensor = pb_utils.get_input_tensor_by_name(request, "INPUT0")# convert the triton tensor to torch tensorinput_torch_tensor = from_dlpack(input_triton_tensor.to_dlpack())transform_output = self.pre_transforms(input_torch_tensor[0])transform_output_batched = transform_output.unsqueeze(0)# convert the torch tensor to triton tensortransform_tensor = pb_utils.Tensor.from_dlpack("INPUT__0", to_dlpack(transform_output_batched))# send inference request to 3DUnet served by Triton. The name of the model is "segmentation_3d"inference_request = pb_utils.InferenceRequest(model_name="3dunet", requested_output_names=["OUTPUT__0"], inputs=[transform_tensor])infer_response = inference_request.exec()output1 = pb_utils.get_output_tensor_by_name(infer_response, "OUTPUT__0")# convert the triton tensor to torch tensoroutput_tensor = from_dlpack(output1.to_dlpack())# do the post processargmax = AsDiscrete(argmax=True)(output_tensor[0])largest = KeepLargestConnectedComponent(applied_labels=1)(argmax)contour = LabelToContour()(largest)out_tensor_0 = pb_utils.Tensor.from_dlpack("MASK", to_dlpack(largest.unsqueeze(0)))out_tensor_1 = pb_utils.Tensor.from_dlpack("CONTOUR", to_dlpack(contour.unsqueeze(0)))inference_response = pb_utils.InferenceResponse(output_tensors=[out_tensor_0, out_tensor_1])responses.append(inference_response)return responsesdef finalize(self):"""`finalize` is called only once when the model is being unloaded.Implementing `finalize` function is optional. This function allowsthe model to perform any necessary clean ups before exit."""pass
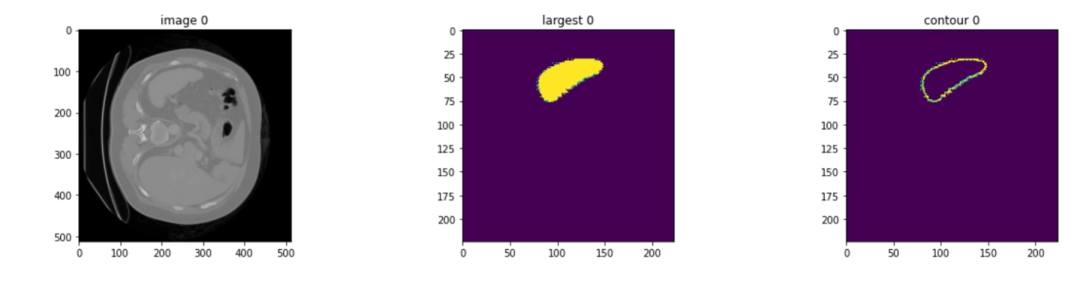
以 MSD Spleen 3D 數據作為輸入,經過整個推理流程,將得到分割后的脾臟區域以及其輪廓。
性能測試
我們在 RTX 8000 上對整個推理流程進行了性能測試,以了解 Triton 及 MONAI 不同特性對性能的影響。
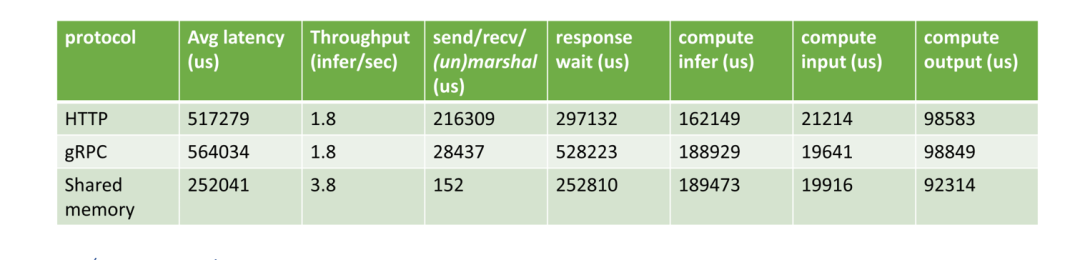
HTTP vs. gRPC vs. shared memory
目前 Triton 支持 HTTP, gRPC 和共享內存等方式進行數據通信。由于三維醫學圖像通常很大,通信帶來的開銷不容忽視。對于許多常見的醫學圖像人工智能應用,客戶端與服務器位于同一臺機器上,因此使用共享內存是減少發送/接收開銷的一種可行方法。在測試中,我們比較了客戶端和服務器之間使用不同通信方式對性能的影響。所有過程(前/后處理和AI推理)都在 GPU 上。我們可以得出結論,當數據傳輸量很大時,使用共享內存將大大減少延遲。
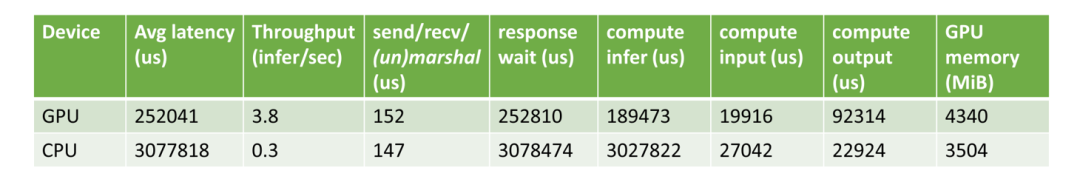
Pre/Post-processing on GPU vs. CPU
接著我們測試了分別在 GPU 和 CPU 進行前后數據處理時,整個推理流程的速度。可以看到,當使用 GPU 進行數據處理時,可以實現 12 倍的加速。
想要了解更多 Triton 和 MONAI 的特性與使用方法,請關注以下鏈接。同時,Triton 和 MONAI 均已在 Github 開源,歡迎開發者踴躍參與開源社區建設。
原文標題:使用 MONAI 和 Triton 高效構建和部署 GPU 加速的醫療影像推理流程
文章出處:【微信公眾號:NVIDIA英偉達企業解決方案】歡迎添加關注!文章轉載請注明出處。
-
NVIDIA
+關注
關注
14文章
4939瀏覽量
102814 -
gpu
+關注
關注
28文章
4700瀏覽量
128699 -
醫療
+關注
關注
8文章
1800瀏覽量
58660
原文標題:使用 MONAI 和 Triton 高效構建和部署 GPU 加速的醫療影像推理流程
文章出處:【微信號:NVIDIA-Enterprise,微信公眾號:NVIDIA英偉達企業解決方案】歡迎添加關注!文章轉載請注明出處。
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
高效大模型的推理綜述
YOLOv6在LabVIEW中的推理部署(含源碼)

凱茉銳電子 SDI編碼板與SONY模組:高效集成的影像處理新紀元
使用OpenVINO Model Server在哪吒開發板上部署模型
英特爾?至強?可擴展處理器助力智慧醫療的數字化轉型

高清醫療影像解決方案:索尼FCB-EW9500H模組引領醫療進步

簡單兩步使用OpenVINO?搞定Qwen2的量化與部署任務

戴爾科技數據存儲方案助力麗水市中心醫院醫療存儲影像系統升級
簡單三步使用OpenVINO?搞定ChatGLM3的本地部署

人工智能在影像升級中的關鍵作用
基于OpenCV DNN實現YOLOv8的模型部署與推理演示




 如何實現高效的部署醫療影像推理
如何實現高效的部署醫療影像推理











評論