本文將向你展示如何使用 Arduino 和兩個按鈕對大型線性執(zhí)行器進(jìn)行基本的手動控制。在第一組代碼中,第一個按鈕伸出執(zhí)行器,第二個按鈕縮回執(zhí)行器。在第二組代碼中,兩個按鈕將線性執(zhí)行器移動到預(yù)設(shè)位置。
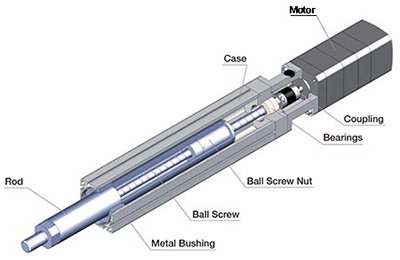
大型線性致動器傳統(tǒng)上具有五根導(dǎo)線。兩根線用于為電機供電,三根線連接到內(nèi)部電位計以讀取位置。這兩個繼電器用于切換電機的正負(fù)電源,以確定活塞的行進(jìn)方向。代碼的第一位不使用這個,第二個使用這個來達(dá)到目標(biāo)??位置。讓我們開始吧。
第 1 步:接線
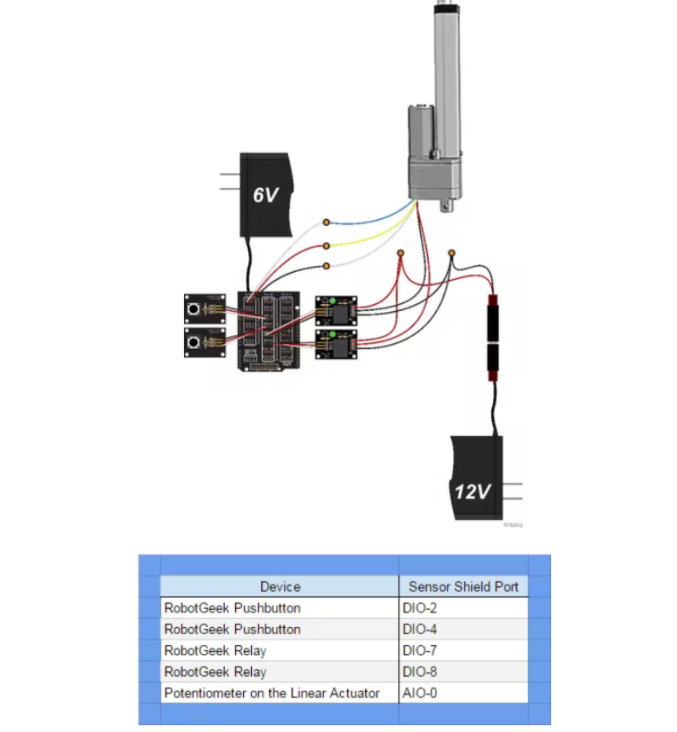
第 2 步:代碼 1 - 手動控制
此部分代碼顯示了如何使用 Arduino 和兩個按鈕對大型線性執(zhí)行器進(jìn)行基本手動控制。第一個按鈕伸出致動器,第二個按鈕縮回致動器。
const int button1Pin = 2; // the number of the pushbutton1 pin
const int button2Pin = 4; // the number of the pushbutton2 pin
const int relay1Pin = 7; // the number of the Realy1 pin
const int relay2Pin = 8; // the number of the Relay2 pin
// variables will change:
int button1State = 0; // variable for reading the pushbutton status
int button2State = 0; // variable for reading the pushbutton status
const int sensorPin = 0; // select the input pin for the potentiometer
int sensorValue = 0; // variable to store the value coming from the sensor
void setup() {
//start serial connection
Serial.begin(9600);
// initialize the pushbutton pin as an input:
pinMode(button1Pin, INPUT);
pinMode(button2Pin, INPUT);
// initialize the relay pin as an output:
pinMode(relay1Pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(relay2Pin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop(){
// read the value from the sensor:
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
//print out the value of the pushbutton
Serial.println(sensorValue);
// read the state of the pushbutton values:
button1State = digitalRead(button1Pin);
button2State = digitalRead(button2Pin);
// check if the pushbutton1 is pressed.
// if it is, the buttonState is HIGH:
// we also ensure tha the other button is not pushed to avoid conflict
if (button1State == HIGH && button2State == LOW) {
// turn relay1 on:
digitalWrite(relay1Pin, HIGH);
}
// When we let go of the button, turn off the relay
else if (digitalRead(relay1Pin) == HIGH) {
// turn relay1 off:
digitalWrite(relay1Pin, LOW);
}
// repeat the same procedure for the second pushbutton
if (button1State == LOW && button2State == HIGH) {
// turn relay2 on:
digitalWrite(relay2Pin, HIGH);
}
// When we let go of the button, turn off the relay
else if (digitalRead(relay2Pin) == HIGH) {
// turn relay2 off:
digitalWrite(relay2Pin, LOW);
}
}
第 3 步:代碼 2 - 使用位置反饋預(yù)設(shè)位置
此部分代碼顯示了如何使用 Arduino 和兩個按鈕對大型線性執(zhí)行器進(jìn)行基本控制,每個按鈕預(yù)設(shè)到一個位置。
const int button1Pin = 2; // the number of the pushbutton1 pin
const int button2Pin = 4; // the number of the pushbutton2 pin
const int relay1Pin = 7; // the number of the Realy1 pin
const int relay2Pin = 8; // the number of the Relay2 pin
const int sensorPin = 0; // select the input pin for the potentiometer
// variables will change:
int button1State = 0; // variable for reading the pushbutton status
int button2State = 0; // variable for reading the pushbutton status
int sensorValue = 0; // variable to store the value coming from the sensor
int goalPosition = 350;
int CurrentPosition = 0;
boolean Extending = false;
boolean Retracting = false;
void setup() {
//start serial connection
Serial.begin(9600);
// initialize the pushbutton pin as an input:
pinMode(button1Pin, INPUT);
pinMode(button2Pin, INPUT);
// initialize the relay pin as an output:
pinMode(relay1Pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(relay2Pin, OUTPUT);
//preset the relays to LOW
digitalWrite(relay1Pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(relay2Pin, LOW);
}
void loop(){
// read the value from the sensor:
CurrentPosition = analogRead(sensorPin);
// print the results to the serial monitor:
Serial.print(“Current = ” );
Serial.print(CurrentPosition);
Serial.print(“\t Goal = ”);
Serial.println(goalPosition);
// read the state of the pushbutton values:
button1State = digitalRead(button1Pin);
button2State = digitalRead(button2Pin);
if (button1State == HIGH) {
// set new goal position
goalPosition = 300;
if (goalPosition 》 CurrentPosition) {
Retracting = false;
Extending = true;
digitalWrite(relay1Pin, HIGH);
digitalWrite(relay2Pin, LOW);
Serial.println(“Extending”);
}
else if (goalPosition 《 CurrentPosition) {
Retracting = true;
Extending = false;
digitalWrite(relay1Pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(relay2Pin, HIGH);
Serial.println(“Retracting”);
}
}
if (button2State == HIGH) {
// set new goal position
goalPosition = 500;
if (goalPosition 》 CurrentPosition) {
Retracting = false;
Extending = true;
digitalWrite(relay1Pin, HIGH);
digitalWrite(relay2Pin, LOW);
Serial.println(“Extending”);
}
else if (goalPosition 《 CurrentPosition) {
Retracting = true;
Extending = false;
digitalWrite(relay1Pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(relay2Pin, HIGH);
Serial.println(“Retracting”);
}
}
if (Extending = true && CurrentPosition 》 goalPosition) {
//we have reached our goal, shut the relay off
digitalWrite(relay1Pin, LOW);
boolean Extending = false;
Serial.println(“IDLE”);
}
if (Retracting = true && CurrentPosition 《 goalPosition){
//we have reached our goal, shut the relay off
digitalWrite(relay2Pin, LOW);
boolean Retracting = false;
Serial.println(“IDLE”);
}
}
以上就是該項目所需的全部功能代碼,到這一步就可以驗收了。
第4步:拓展
在可以控制大型線性執(zhí)行器之后,你打算用它做什么?您可以制作一張可以變形的桌子,以變換坐姿或站姿。同時你還可以使用一些光傳感器,制作一個跟蹤太陽的太陽能電池板。
-
執(zhí)行器
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
5文章
375瀏覽量
19326 -
Arduino
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
187文章
6464瀏覽量
186679
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
如何使用Arduino和光學(xué)系列線性致動器來實現(xiàn)同步控制
具有執(zhí)行器飽和與隨機非線性擾動的離散系統(tǒng)模型預(yù)測控制_石宇靜
帶觸覺反饋的壓電執(zhí)行器(低電壓/薄型)PiezoHapt?執(zhí)行器的開發(fā)
安華高科技:大型家電控制電機和執(zhí)行器的解決者!
汽車控制系統(tǒng)中的電子控制單元和傳感器以及執(zhí)行器
執(zhí)行器由什么組成_執(zhí)行器的工作原理
氣動執(zhí)行器的組成_氣動執(zhí)行器選型
電動執(zhí)行器和風(fēng)門執(zhí)行器之間的差別是什么
推動線性執(zhí)行器設(shè)計的多項因素
從單個Arduino輸出引腳控制多個繼電器或其他執(zhí)行器

用Arduino控制小型線性執(zhí)行器

BeagleBone Black Wireless、MotorCape和線性執(zhí)行器





 如何使用Arduino控制大型線性執(zhí)行器
如何使用Arduino控制大型線性執(zhí)行器










評論