字符串數(shù)據(jù)類型是一個有序的字符集合。
字符串變量的長度是集合中的字符數(shù)。
字符串類型的變量是動態(tài)的,因為它們的長度在仿真過程中可能會變化。
字符串中的單個字符變量的類型為byte。
Syntax:
string variable_name [= initial_value];
如果在聲明中未指定初始值,則將變量初始化為" ",一個空字符串。空字符串的長度為零。下面是一個字符串數(shù)據(jù)類型的示例:
module datatype1; string s1 = "hello"; string s2 = "hello world"; string s3 = "helloworld"; // is ignored string s4, s5, s6; initial begin s4 = "later"; s5 = ""; //empty string s6 = {"hi", s5}; //concatenation #10; $display ("s1=%s s2=%s s3=%s s4=%s s5=%s s6=%s", s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6); #100 $fnish; end endmodule
在本例中,我們聲明了6個字符串,從s1到s6。s1、s2和s3分別進行了初始化。其中字符串s3中的轉(zhuǎn)義字符()被轉(zhuǎn)義為空字符。
然后在“initial”語句塊中,將s4賦值為字符串“l(fā)ater”,將s5賦值為空字符串,并連接s5與" hi ",賦值給字符串s6。下面是仿真log:
ncsim> run s1=hello s2=hello world s3=helloworld s4=later s5= s6=hi
String Operators
字符串數(shù)據(jù)類型還提供了處理字符串的操作符,如下表所示:
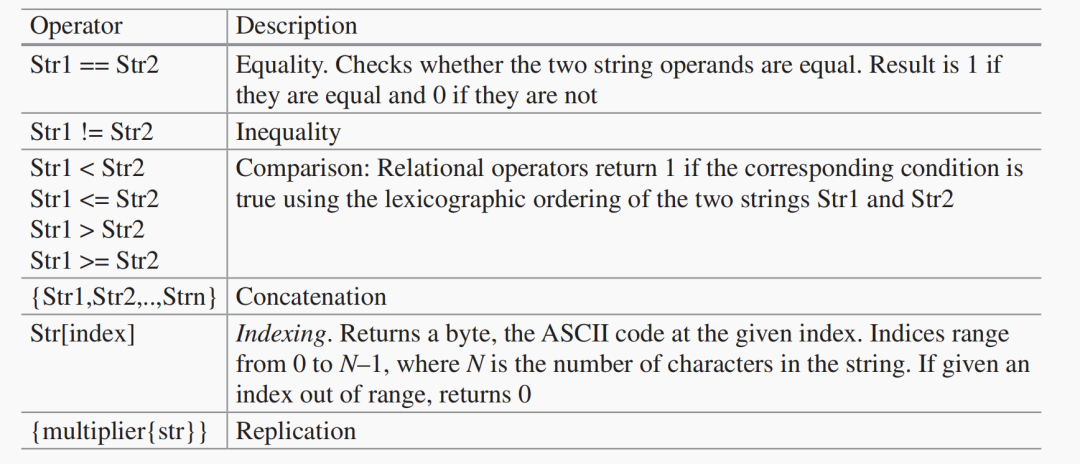
module datatype1;
string s2 = "hello world";
string s3 = "helloworld";
string s4, s5;
string s6 = "compare";
string s7 = "compare";
string s8;
integer s2len, s3len, s2c;
initial begin
#10; $display ("s2=%s s3=%s",s2,s3);
#100 $fnish;
end
initial begin
#15;
s2len = s2.len( ); $display("String Length s2 =
%0d",s2len);
s3len = s3.len( ); $display("String Length s3 =
%0d",s3len);
if (s2 == s3) $display("s2 = s3"); else $display("s2
!= s3");
if (s6 == s7) $display("s6 = s7"); else $display("s6
!= s7");
s4 = s2.substr(1,6);
$display("s4 = %s",s4);
s5 = "later ";
s8 = {3{s5}};
$display("s8 = %s",s8);
S2c = s2[0];
$display("s2c = %s",s2c);
end
endmodule
在上面的例子中,聲明了字符串s2到s8并初始化為各種字符串。
將字符串長度(.len())賦值給整數(shù)類型s2len和s3len。
比較字符串s2和s3以及字符串s6和
s7。
提取s2的部分字符串并將其賦值給s4。
復制s5三次,賦值給s8。
下面是仿真的log:
s2=hello world s3=helloworld String Length s2 = 11 String Length s3 = 10 s2 != s3 s6 = s7 s4 = ello w s8 = later later later s2c = h $fnish at simulation time 110 V C S S i m u l a t i o n R e p o r t
String Methods
還有幾種方法可用于處理字符串,如下表所示:
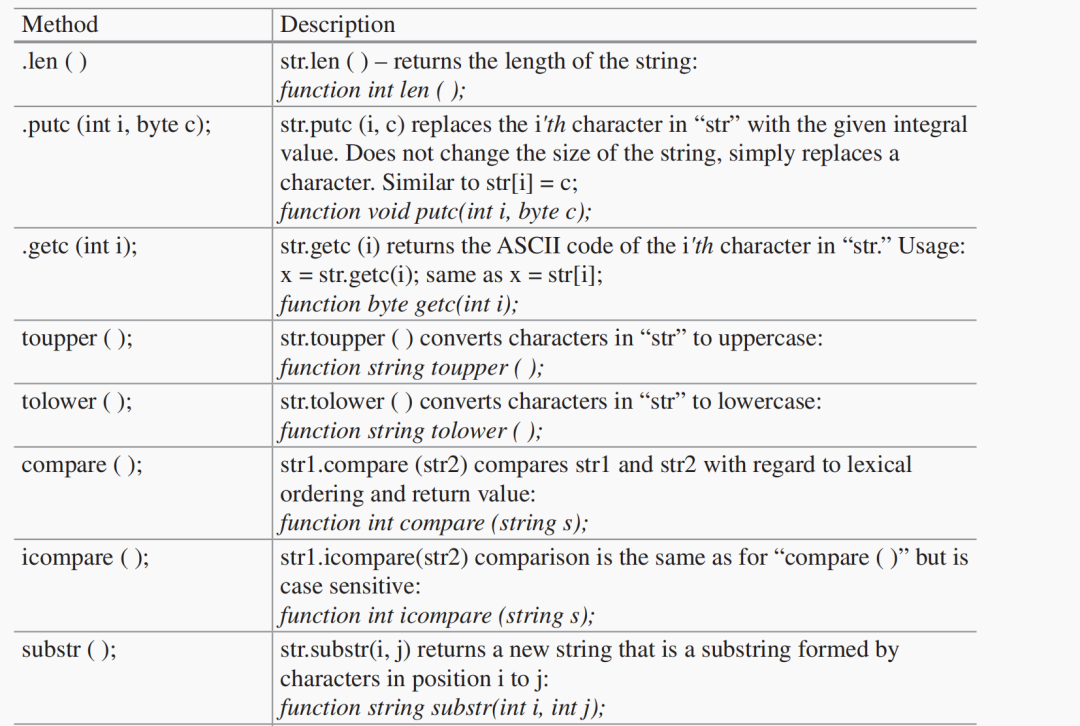
module sMethods;
string s1 = "hello";
string s2 = "hello world";
string s4;
string s5 = "GOODBYE";
byte x;
integer s2len, s3len, i1, i2;
initial
begin
#15;
s2len = s2.len( );
$display("String Length s2 = %0d",s2len);
s1.putc(0,"C"); //replace 0'th character with 'C'
$display("String s1 = %s",s1);
x = s1.getc(0); //get 0'th character of string s1.
$display("0'th character of string 'Cello' = %s",x);
s4 = s2.toupper( ); //convert string 's2' to upper case
$display("Upper Case of 'hello world' = %s",s4);
s4 = s5.tolower ( );
$display("Lower case of 'GOODBYE' = %s",s4);
end
endmodule
以及仿真log:
String Length s2 = 11 String s1 = Cello 0'th character of string 'Cello' = C Upper Case of 'hello world' = HELLO WORLD Lower case of 'GOODBYE' = goodbye V C S S i m u l a t i o n R e p o r t
在上面的例子中,
聲明一些字符串變量。在“initial”語句塊中,我們首先得到字符串(s2 = " hello world ";)的長度11。
然后使用" putc "方法給字符串" s1 "的第0個字符加上字符" C ":
s1.putc(0,“C”);
由于s1字符串是“hello”,它現(xiàn)在變成“Cello”。然后,得到字符串s1的第0個字符(現(xiàn)在是“Cello”):
x = s1.getc (0);
我們使用.toupper方法將" s2 "字符串(s2 = " hello world ")轉(zhuǎn)換為全大寫,并將結(jié)果存儲在字符串" s4 "中:
s4 = s2.toupper ();
將" s5 "字符串(s5 = " GOODBYE ")轉(zhuǎn)換為全小寫(.tolower方法)
s4 = s5.tolower ( );
審核編輯:湯梓紅
-
Verilog
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
28文章
1345瀏覽量
109996 -
System
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
165瀏覽量
36887 -
字符串
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1文章
577瀏覽量
20488 -
數(shù)據(jù)類型
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
236瀏覽量
13610
原文標題:SystemVerilog中的字符串數(shù)據(jù)類型
文章出處:【微信號:芯片驗證工程師,微信公眾號:芯片驗證工程師】歡迎添加關(guān)注!文章轉(zhuǎn)載請注明出處。
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
Redis數(shù)據(jù)類型介紹
鴻蒙原生應(yīng)用元服務(wù)開發(fā)-倉頡基礎(chǔ)數(shù)據(jù)類型字符串類型
字符串的表示
c#數(shù)據(jù)類型轉(zhuǎn)換-數(shù)值字符串和數(shù)值之間的轉(zhuǎn)換
2.2 python字符串類型
C語言_字符串與指針的練習
Python字符串的數(shù)據(jù)類型與拼接





 關(guān)于字符串數(shù)據(jù)類型的示例
關(guān)于字符串數(shù)據(jù)類型的示例











評論