寫在前面的話:只是對(duì)兩種路徑優(yōu)化算法進(jìn)行簡單的理解和嘗試,為后續(xù)使用做準(zhǔn)備。如果用到,請(qǐng)?jiān)俅魏煤美斫庠砗?a href="http://www.nxhydt.com/tags/matlab/" target="_blank">Matlab源碼。
首先給出Matlab下的三個(gè)腳本文件:
TestScript.m
% % TestScript for Assignment 1 % %% Define a small map % map = false(10); map = ans; % Add an obstacle % map (1:5, 6) = true; map = logical(map); start_coords = [1, 1]; dest_coords = [40, 20]; %% close all; % [route, numExpanded] = DijkstraGrid (map, start_coords, dest_coords); % Uncomment following line to run Astar [route, numExpanded] = AStarGrid (map, start_coords, dest_coords); %HINT: With default start and destination coordinates defined above, numExpanded for Dijkstras should be 76, numExpanded for Astar should be 23.
AStarGrid.m
function [route,numExpanded] = AStarGrid (input_map, start_coords, dest_coords) % Run A* algorithm on a grid. % Inputs : % input_map : a logical array where the freespace cells are false or 0 and % the obstacles are true or 1 % start_coords and dest_coords : Coordinates of the start and end cell % respectively, the first entry is the row and the second the column. % Output : % route : An array containing the linear indices of the cells along the % shortest route from start to dest or an empty array if there is no % route. This is a single dimensional vector % numExpanded: Remember to also return the total number of nodes % expanded during your search. Do not count the goal node as an expanded node. % set up color map for display用一個(gè)map矩陣來表示每個(gè)點(diǎn)的狀態(tài) % 1 - white - clear cell % 2 - black - obstacle % 3 - red = visited 相當(dāng)于CLOSED列表的作用 % 4 - blue - on list 相當(dāng)于OPEN列表的作用 % 5 - green - start % 6 - yellow - destination cmap = [1 1 1; ... 0 0 0; ... 1 0 0; ... 0 0 1; ... 0 1 0; ... 1 1 0; ... 0.5 0.5 0.5]; colormap(cmap); % variable to control if the map is being visualized on every % iteration drawMapEveryTime = true; [nrows, ncols] = size(input_map); % map - a table that keeps track of the state of each grid cell用來上色的 map = zeros(nrows,ncols); map(~input_map) = 1; % Mark free cells map(input_map) = 2; % Mark obstacle cells % Generate linear indices of start and dest nodes將下標(biāo)轉(zhuǎn)換為線性的索引值 start_node = sub2ind(size(map), start_coords(1), start_coords(2)); dest_node = sub2ind(size(map), dest_coords(1), dest_coords(2)); map(start_node) = 5; map(dest_node) = 6; % meshgrid will `replicate grid vectors' nrows and ncols to produce % a full grid % type `help meshgrid' in the Matlab command prompt for more information parent = zeros(nrows,ncols);%用來記錄每個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)的父節(jié)點(diǎn) % [X, Y] = meshgrid (1:ncols, 1:nrows); xd = dest_coords(1); yd = dest_coords(2); % Evaluate Heuristic function, H, for each grid cell % Manhattan distance用曼哈頓距離作為啟發(fā)式函數(shù) H = abs(X - xd) + abs(Y - yd); H = H'; % Initialize cost arrays f = Inf(nrows,ncols); g = Inf(nrows,ncols); g(start_node) = 0; f(start_node) = H(start_node); % keep track of the number of nodes that are expanded numExpanded = 0; % Main Loop while true % Draw current map map(start_node) = 5; map(dest_node) = 6; % make drawMapEveryTime = true if you want to see how the % nodes are expanded on the grid. if (drawMapEveryTime) image(1.5, 1.5, map); grid on; axis image; drawnow; end % Find the node with the minimum f value,其中的current是index值,需要轉(zhuǎn)換 [min_f, current] = min(f(:)); if ((current == dest_node) || isinf(min_f)) break; end; % Update input_map map(current) = 3; f(current) = Inf; % remove this node from further consideration numExpanded=numExpanded+1; % Compute row, column coordinates of current node [i, j] = ind2sub(size(f), current); % ********************************************************************* % ALL YOUR CODE BETWEEN THESE LINES OF STARS % Visit all of the neighbors around the current node and update the % entries in the map, f, g and parent arrays % action=[-1 0; 1 0; 0 -1; 0 1];%上,下,左,右 for a=1:4 expand=[i,j]+action(a,:); expand1=expand(1,1); expand2=expand(1,2); %不超出邊界,不穿越障礙,不在CLOSED列表里,也不是起點(diǎn),則進(jìn)行擴(kuò)展 if ( expand1>=1 && expand1<=nrows && expand2>=1 && expand2<=nrows && map(expand1,expand2)~=2 && map(expand1,expand2)~=3 && map(expand1,expand2)~=5) ? ? ? ? ? ?if ( g(expand1,expand2)> g(i,j)+1 ) g(expand1,expand2)= g(i,j)+1; f(expand1,expand2)= g(expand1,expand2)+H(expand1,expand2); parent(expand1,expand2)=current; map(expand1,expand2)=4; end end end %********************************************************************* end %% Construct route from start to dest by following the parent links if (isinf(f(dest_node))) route = []; else route = [dest_node]; while (parent(route(1)) ~= 0) route = [parent(route(1)), route]; end % Snippet of code used to visualize the map and the path for k = 2:length(route) - 1 map(route(k)) = 7; pause(0.1); image(1.5, 1.5, map); grid on; axis image; end end end
DijkstraGrid.m
function [route,numExpanded] = DijkstraGrid (input_map, start_coords, dest_coords)
% Run Dijkstra's algorithm on a grid.
% Inputs :
% input_map : a logical array where the freespace cells are false or 0 and
% the obstacles are true or 1
% start_coords and dest_coords : Coordinates of the start and end cell
% respectively, the first entry is the row and the second the column.
% Output :
% route : An array containing the linear indices of the cells along the
% shortest route from start to dest or an empty array if there is no
% route. This is a single dimensional vector
% numExpanded: Remember to also return the total number of nodes
% expanded during your search. Do not count the goal node as an expanded node.
% set up color map for display
% 1 - white - clear cell
% 2 - black - obstacle
% 3 - red = visited
% 4 - blue - on list
% 5 - green - start
% 6 - yellow - destination
cmap = [1 1 1; ...
0 0 0; ...
1 0 0; ...
0 0 1; ...
0 1 0; ...
1 1 0; ...
0.5 0.5 0.5];
colormap(cmap);
% variable to control if the map is being visualized on every
% iteration
drawMapEveryTime = true;
[nrows, ncols] = size(input_map);
% map - a table that keeps track of the state of each grid cell
map = zeros(nrows,ncols);
map(~input_map) = 1; % Mark free cells
map(input_map) = 2; % Mark obstacle cells
% Generate linear indices of start and dest nodes
start_node = sub2ind(size(map), start_coords(1), start_coords(2));
dest_node = sub2ind(size(map), dest_coords(1), dest_coords(2));
map(start_node) = 5;
map(dest_node) = 6;
% Initialize distance array
distanceFromStart = Inf(nrows,ncols);
% For each grid cell this array holds the index of its parent
parent = zeros(nrows,ncols);
distanceFromStart(start_node) = 0;
% keep track of number of nodes expanded
numExpanded = 0;
% Main Loop
while true
% Draw current map
map(start_node) = 5;
map(dest_node) = 6;
% make drawMapEveryTime = true if you want to see how the
% nodes are expanded on the grid.
if (drawMapEveryTime)
image(1.5, 1.5, map);
grid on;
axis image;
drawnow;
end
% Find the node with the minimum distance
[min_dist, current] = min(distanceFromStart(:));
if ((current == dest_node) || isinf(min_dist))
break;
end;
% Update map
map(current) = 3; % mark current node as visited
numExpanded=numExpanded+1;
% Compute row, column coordinates of current node
[i, j] = ind2sub(size(distanceFromStart), current);
% *********************************************************************
% YOUR CODE BETWEEN THESE LINES OF STARS
% Visit each neighbor of the current node and update the map, distances
% and parent tables appropriately.
action=[-1 0; 1 0; 0 -1; 0 1];%上,下,左,右
for a=1:4
expand=[i,j]+action(a,:);
expand1=expand(1,1);
expand2=expand(1,2);
%不超出邊界,不穿越障礙,不在CLOSED列表里,則進(jìn)行擴(kuò)展
if ( expand1>=1 && expand1<=nrows && expand2>=1 && expand2<=ncols && map(expand1,expand2)~=2 && map(expand1,expand2)~=3 && map(expand1,expand2)~=5 )
% ? ? ? ? ? if ( expand1>=1 && expand1<=nrows && expand2>=1 && expand2<=ncols && map(expand1,expand2)~=2 && map(expand1,expand2)~=3 && map(expand1,expand2)~=5)
if ( distanceFromStart(expand1,expand2)> distanceFromStart(i,j)+1 )
distanceFromStart(expand1,expand2)= distanceFromStart(i,j)+1;
parent(expand1,expand2)=current;
map(expand1,expand2)=4;
end
end
end
distanceFromStart(current) = Inf; % remove this node from further consideration
%*********************************************************************
end
%% Construct route from start to dest by following the parent links
if (isinf(distanceFromStart(dest_node)))
route = [];
else
route = [dest_node];
while (parent(route(1)) ~= 0)
route = [parent(route(1)), route];
end
% Snippet of code used to visualize the map and the path
for k = 2:length(route) - 1
map(route(k)) = 7;
pause(0.1);
image(1.5, 1.5, map);
grid on;
axis image;
end
end
end
注:運(yùn)行環(huán)境,Matlab 2019a 版本,安裝 RTB(Robotic Tool Box)工具包,鏈接地址為,RTB安裝鏈接。
該工具包中可以運(yùn)行作者大佬寫到的matlab/simulink四軸歷程,只需要使用指令 sl_quadrotor 即可。
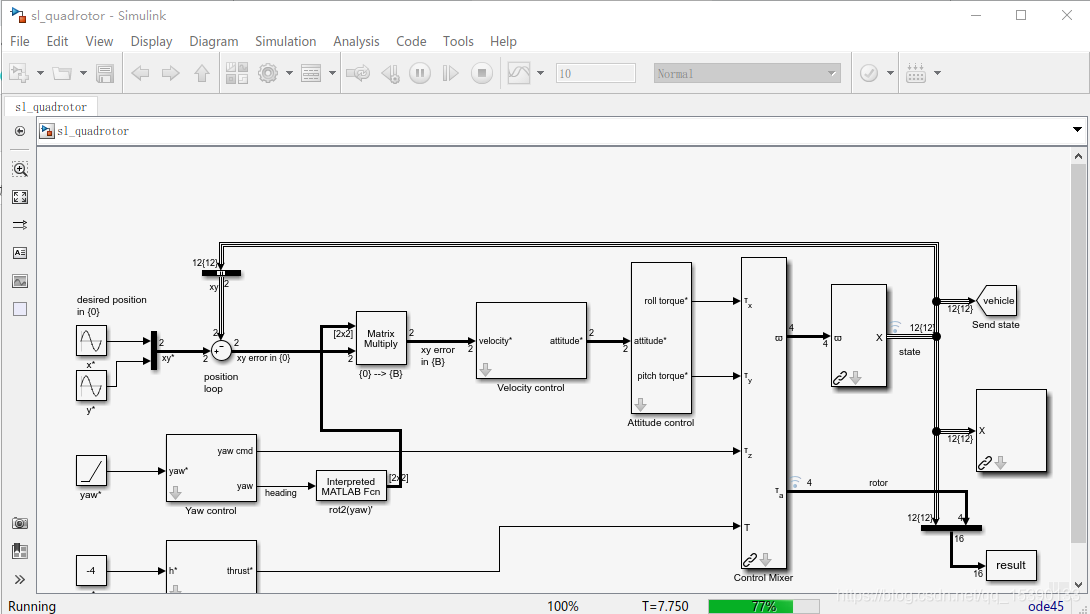
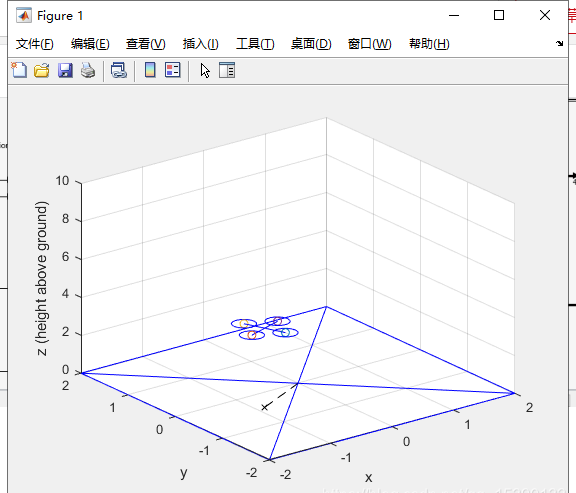
使用方法
在Matlab 中,使用 makemap(30) 來生成地圖,通過鼠標(biāo)來設(shè)置障礙形狀。該例子生成了一個(gè)30*30的方陣,然后直接運(yùn)行TestScript.m即可。
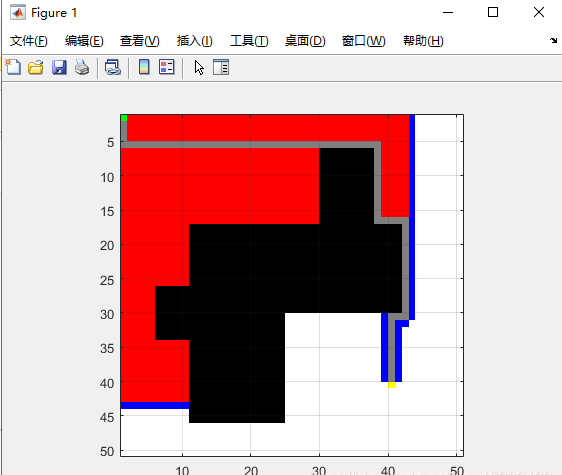
其中要在TestScript.m中選擇是采用A算法,還是Dijkstra算法。同時(shí)設(shè)置起始點(diǎn)和終點(diǎn)在哪。下圖顯示得到的A算法路徑優(yōu)化結(jié)果。
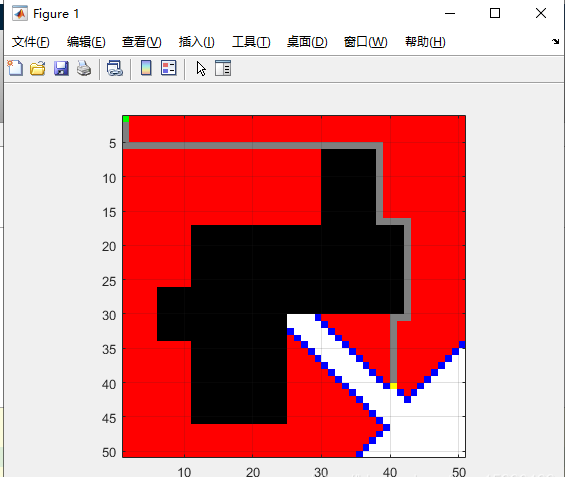
其中綠色點(diǎn)為起點(diǎn),黃色點(diǎn)為終點(diǎn),黑色表示障礙,白色表示空閑,紅色表示搜尋過,灰色表示最后規(guī)劃的路徑。
下圖顯示Dijkstra算法的路徑優(yōu)化結(jié)果:
對(duì)應(yīng)的動(dòng)態(tài)效果已經(jīng)錄屏,下面給出傳送門(錄屏水印廣告請(qǐng)忽略):
通過對(duì)比可以看出:A* 算法搜索速度較快,畢竟里面有貪心算法。
這在地圖較大的場景應(yīng)用較好。但是A*算法只能得到局部最優(yōu)解,并不能保證全局最優(yōu)解。
相比之下,Dijkstra算法盡管搜索速度慢,但是是全局最優(yōu)解。不知道兩種方法結(jié)合gmapping,hector或者cartographer生成的柵格地圖會(huì)是什么樣的效果。后面期待嘗試一下。
審核編輯:湯梓紅
-
matlab
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
182文章
2963瀏覽量
230192 -
算法
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
23文章
4601瀏覽量
92671 -
源碼
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
8文章
633瀏覽量
29146 -
Dijkstra
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
13瀏覽量
8432
原文標(biāo)題:Dijkstra和A*算法及其Matlab實(shí)現(xiàn)
文章出處:【微信號(hào):3D視覺工坊,微信公眾號(hào):3D視覺工坊】歡迎添加關(guān)注!文章轉(zhuǎn)載請(qǐng)注明出處。
發(fā)布評(píng)論請(qǐng)先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
使用dijkstra算法的準(zhǔn)備工作
數(shù)字信號(hào)處理及其MATLAB實(shí)現(xiàn)
數(shù)字信號(hào)處理及其MATLAB實(shí)現(xiàn)
SOFM網(wǎng)絡(luò)及其在MATLAB中的實(shí)現(xiàn)
基于有向非負(fù)極圖數(shù)據(jù)DIJKSTRA算法
基于Dijkstra最短路徑的抽樣算法
《圖論算法及其MATLAB實(shí)現(xiàn)》電子教材和函數(shù)及函數(shù)功能列表概述
遺傳算法原理及其MATLAB實(shí)現(xiàn)的詳細(xì)資料說明
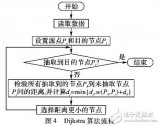
基于STM32的A*(A星)尋路算法實(shí)現(xiàn)

Dijkstra算法和A*算法

路徑規(guī)劃算法實(shí)現(xiàn)原理
中國鐵路網(wǎng)的Dijkstra算法實(shí)現(xiàn)案例




 Dijkstra和A*算法及其Matlab實(shí)現(xiàn)
Dijkstra和A*算法及其Matlab實(shí)現(xiàn)










評(píng)論