一、磁盤分區
(一)概述
原始磁盤需要經過那些操作才能存取數據?
原始磁盤的形態是一個光滑的盤體;
需要將盤體劃分出柱面和磁道,然后將磁道劃分為多個扇區,稱為“低級格式化”;
為了有效組織磁盤和提高I\\O效率,還需要進行“分區”;
此時,磁盤還不能存儲數據,還需要對每一分區中的扇區進行邏輯編號,并建立數據結構和磁盤數據的管理方式,稱為“高級格式化”,本質上是在分區上確定了文件系統,便可以進行數據存儲了。
如果把原始磁盤比作待開發的地塊
那么,
“低級格式化”相當于在該地塊上修建了道路和房屋;
“分區”相當于根據地理區域劃分不同的小區;
“高級格式化”相當于將小區內的房屋進行標記。
Windows操作系統,分區、格式化之后,就可以建目錄存儲文件了。
而Linux操作系統則與Windows相反,需要先虛擬一個根目錄,再將磁盤掛載到根目錄。
(二)實踐
1. 查看當前分區情況:
工具fdisk:用于Linux的磁盤分區表操作
root@linux:~# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/vda: 40 GiB, 42949672960 bytes, 83886080 sectors
# 磁盤大小為 40G
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: gpt
Disk identifier: EC404E4B-BF45-4DEE-8D63-3D59FBB9C44E
Device Start End Sectors Size Type
/dev/vda1 227328 41943006 41715679 19.9G Linux filesystem
/dev/vda14 2048 10239 8192 4M BIOS boot
/dev/vda15 10240 227327 217088 106M EFI System
# 磁盤分區約為20G,還有20G的空間未使用
Partition table entries are not in disk order.
2. 創建新分區
root@linux:~# fdisk /dev/vda
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.31.1).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Command (m for help): p # 列出磁盤分區表
Disk /dev/vda: 40 GiB, 42949672960 bytes, 83886080 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: gpt
Disk identifier: EC404E4B-BF45-4DEE-8D63-3D59FBB9C44E
Device Start End Sectors Size Type
/dev/vda1 227328 41943006 41715679 19.9G Linux filesystem
/dev/vda14 2048 10239 8192 4M BIOS boot
/dev/vda15 10240 227327 217088 106M EFI System
Partition table entries are not in disk order.
Command (m for help): n # 創建新分區
Partition number (2-13,16-128, default 2): # 默認回車
First sector (41943007-83886046, default 41943040): # 默認回車
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G,T,P} (41943040-83886046, default 83886046): +10G # 使用size方式定義10G大小
Created a new partition 2 of type 'Linux filesystem' and of size 10 GiB.
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/vda: 40 GiB, 42949672960 bytes, 83886080 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: gpt
Disk identifier: EC404E4B-BF45-4DEE-8D63-3D59FBB9C44E
Device Start End Sectors Size Type
/dev/vda1 227328 41943006 41715679 19.9G Linux filesystem
/dev/vda2 41943040 62914559 20971520 10G Linux filesystem
/dev/vda14 2048 10239 8192 4M BIOS boot
/dev/vda15 10240 227327 217088 106M EFI System
Partition table entries are not in disk order.
Command (m for help): w # 保存、退出
The partition table has been altered.
Syncing disks.
3. 查看新創建分區
root@linux:~# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
vda 252:0 0 40G 0 disk
├─vda1 252:1 0 19.9G 0 part /
├─vda2 252:2 0 10G 0 part
├─vda14 252:14 0 4M 0 part
└─vda15 252:15 0 106M 0 part /boot/efi
4. 格式化
命令mkfs(make file system):在特定的分區上建立linux文件系統。
root@linux:~# mkfs # 兩次鍵入Tab,則可展示支持的文件類型
mkfs mkfs.btrfs mkfs.ext2 mkfs.ext4 mkfs.minix mkfs.ntfs mkfs.xfs
mkfs.bfs mkfs.cramfs mkfs.ext3 mkfs.fat mkfs.msdos mkfs.vfat
root@linux:~# mkfs.ext3 /dev/vda2 # 在新分區創建ext3的文件系統
mke2fs 1.44.1 (24-Mar-2018)
Creating filesystem with 2621440 4k blocks and 655360 inodes
Filesystem UUID: 0e6a8449-acbf-4428-a5d7-b67b4535b844
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (16384 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
5. 掛載
命令mount:用來掛載文件系統。
root@linux:~# mkdir /test2
root@linux:~# mount /dev/vda2 /test2/
root@linux:~# ls /test2/
lost+found
6. 查看分區掛載點及文件類型
root@linux:~# df -T
Filesystem Type 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
udev devtmpfs 1007416 0 1007416 0% /dev
tmpfs tmpfs 204092 776 203316 1% /run
/dev/vda1 ext4 20145724 3279936 16849404 17% /
tmpfs tmpfs 1020448 0 1020448 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs tmpfs 5120 0 5120 0% /run/lock
tmpfs tmpfs 1020448 0 1020448 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/vda15 vfat 106858 3668 103190 4% /boot/efi
tmpfs tmpfs 204088 8 204080 1% /run/user/1001
/dev/vda2 ext3 10255672 23096 9708288 1% /test2
二、邏輯卷管理
(一)概述
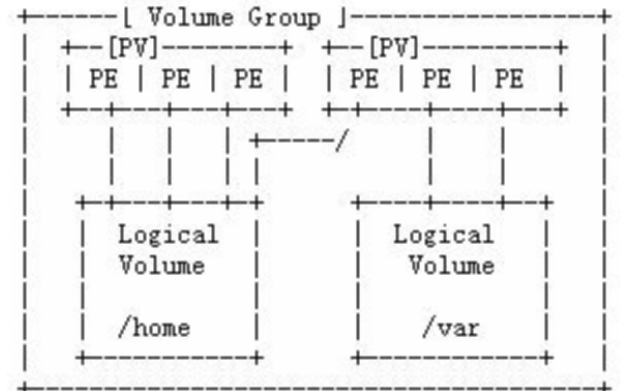
邏輯卷管理也就是LVM(Logical Volume Manager),位于磁盤和操作系統之間,將一個或多個磁盤分區(PV)虛擬為一個卷組(VG),并在VG上面劃分一些邏輯卷(LV)。邏輯卷可再進行格式化、掛載,并且邏輯卷可以動態伸縮。
也就是從物理磁盤或分區開始,經過PV--VG--LV(形成邏輯卷)之后,將邏輯卷看成新的磁盤進行分區、格式化并掛載,供主機使用。
(二)實踐
使用lsblk命令查看系統的磁盤使用情況(lsblk--list block);
使用fdisk命令進行分區;
使用pvcreate創建物理卷,
使用vgcreate創建卷組;
使用lvcreate創建邏輯卷。
1. 創建新分區vda3
root@linux:~# fdisk /dev/vda
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.31.1).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Command (m for help): n
Partition number (3-13,16-128, default 3):
First sector (62914560-83886046, default 62914560):
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G,T,P} (62914560-83886046, default 83886046): +8G
Created a new partition 3 of type 'Linux filesystem' and of size 8 GiB.
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/vda: 40 GiB, 42949672960 bytes, 83886080 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: gpt
Disk identifier: EC404E4B-BF45-4DEE-8D63-3D59FBB9C44E
Device Start End Sectors Size Type
/dev/vda1 227328 41943006 41715679 19.9G Linux filesystem
/dev/vda2 41943040 62914559 20971520 10G Linux filesystem
/dev/vda3 62914560 79691775 16777216 8G Linux filesystem
/dev/vda14 2048 10239 8192 4M BIOS boot
/dev/vda15 10240 227327 217088 106M EFI System
Partition table entries are not in disk order.
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered.
Syncing disks.
2. 創建物理卷
命令pvcreate:用于將物理硬盤分區初始化為物理卷。
root@linux:~# pvcreate /dev/vda3
Physical volume "/dev/vda3" successfully created.
root@linux:~# pvdisplay /dev/vda3
"/dev/vda3" is a new physical volume of "8.00 GiB"
--- NEW Physical volume ---
PV Name /dev/vda3
VG Name
PV Size 8.00 GiB
Allocatable NO
PE Size 0
Total PE 0
Free PE 0
Allocated PE 0
PV UUID ke8k0X-RgZL-Fejo-1AVO-fPPO-hhEP-WVb79K
3. 創建卷組
命令vgcreate:用于創建LVM卷組(Volume Group),將多個物理卷組織成一個整體,屏蔽底層物理卷細節。
root@linux:~# vgcreate vgtest /dev/vda3
Volume group "vgtest" successfully created
root@linux:~# vgdisplay vg0
Volume group "vg0" not found
Cannot process volume group vg0
root@linux:~# vgdisplay vgtest
--- Volume group ---
VG Name vgtest
System ID
Format lvm2
Metadata Areas 1
Metadata Sequence No 1
VG Access read/write
VG Status resizable
MAX LV 0
Cur LV 0
Open LV 0
Max PV 0
Cur PV 1
Act PV 1
VG Size <8.00 GiB
PE Size 4.00 MiB
Total PE 2047
Alloc PE / Size 0 / 0
Free PE / Size 2047 / <8.00 GiB
VG UUID 2TM5qM-9fUR-xTTU-55Nq-nYZE-ATYg-SjQQ6y
4. 創建邏輯卷
命令lvcreate:創建LVM的邏輯卷。
root@linux:~# lvcreate -L 200M -n lv0 vgtest
Logical volume "lv0" created.
5. 管理邏輯卷
# 查看物理卷信息
root@linux:~# pvs
PV VG Fmt Attr PSize PFree
/dev/vda3 vgtest lvm2 a-- <8.00g 7.80g
# 查看卷組信息
root@linux:~# vgs
VG #PV #LV #SN Attr VSize VFree
vgtest 1 1 0 wz--n- <8.00g 7.80g
# 增加邏輯卷空間
root@linux:~# lvextend -L +100M /dev/vgtest/lv0
Size of logical volume vgtest/lv0 changed from 200.00 MiB (50 extents) to 300.00 MiB (75 extents).
Logical volume vgtest/lv0 successfully resized.
# 查詢邏輯卷大小
root@linux:~# lvs /dev/vgtest/lv0
LV VG Attr LSize Pool Origin Data% Meta% Move Log Cpy%Sync Convert
lv0 vgtest -wi-a----- 300.00m
root@linux:~#
聲明:本文內容及配圖由入駐作者撰寫或者入駐合作網站授權轉載。文章觀點僅代表作者本人,不代表電子發燒友網立場。文章及其配圖僅供工程師學習之用,如有內容侵權或者其他違規問題,請聯系本站處理。
舉報投訴
-
格式化
+關注
關注
2文章
38瀏覽量
9103 -
磁盤
+關注
關注
1文章
367瀏覽量
25177
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
LVM邏輯卷管理器簡介和參考實例
LVM(Logical Volume Manager,邏輯卷管理器)是Linux系統用于對硬盤分區進行管理的一種機制,其創建初衷是為了解決硬
【雨林木風系統下載教程】利用XP系統磁盤分區來提升讀寫...
與合并磁盤分區 如果硬盤中最好了的xp系統的某個分區容量過大,可將其拆分為兩個分區。首先將該磁盤分區中的所有文件保存到其它分區中。之后在“
發表于 07-19 10:44
Linux環境下對磁盤分區進行管理的一種機制
物理卷就是指硬盤分區或從邏輯上與磁盤分區具有同樣功能的設備(如RAID),是LVM的基本存儲邏輯塊,但和基本的物理存儲介質(如
Linux磁盤如何劃分 淺談邏輯卷管理(LVM)相關知識
邏輯卷管理LVM是一個多才多藝的硬盤系統工具。無論在Linux或者其他類似的系統,都是非常的好用。傳統分區使用固定大小分區,重新調整大小十分
Linux系統教程之磁盤分區和LVM系統的詳細資料概述
本文檔的主要內容詳細介紹的是Linux系統教程之磁盤分區和LVM系統的詳細資料概述主要內容包括了:1.磁盤相關概念2.磁盤分區工具3.創建 LVM 系統4.維護 LVM 系統
發表于 10-30 16:11
?14次下載
微軟Windows 10研究新的方法管理現代磁盤分區
如果要刪除舊磁盤并創建新分區或擴展特定磁盤的空間,則需要依賴Windows 10的磁盤管理工具。在Windows 10上
Linux磁盤分區和掛載
1.Linux 來說 wulun 有幾個分區,分給哪一目錄使用,他歸根結底只有一個根目錄,一個獨立且唯一的文件結構,Linux 中每個分區都是用來組成整個文件系統的一部分。
linux系統如何進行磁盤分區?
linux系統如何進行磁盤分區? 磁盤分區是在Linux系統中進行硬盤劃分的一種方法,它可以將一個物理硬盤劃分為多個邏輯分區,每個分區可獨立




 什么是磁盤分區與邏輯卷管理
什么是磁盤分區與邏輯卷管理










評論