1.sort排序算法
sort(const _RanIt _First, const _RanIt _Last, _Pr _Pred) --默認為升序排序
形參:_First、_Last --容器的起始和結束迭代器
_Pred --排序規則,默認為從小到大
示例:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Print
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout vtr;
vtr.push_back(rand()%50);
vtr.push_back(rand() % 50);
vtr.push_back(rand() % 50);
vtr.push_back(rand() % 50);
vtr.push_back(rand() % 50);
vtr.push_back(rand() % 50);
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Print());
cout ());
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Print());
cout
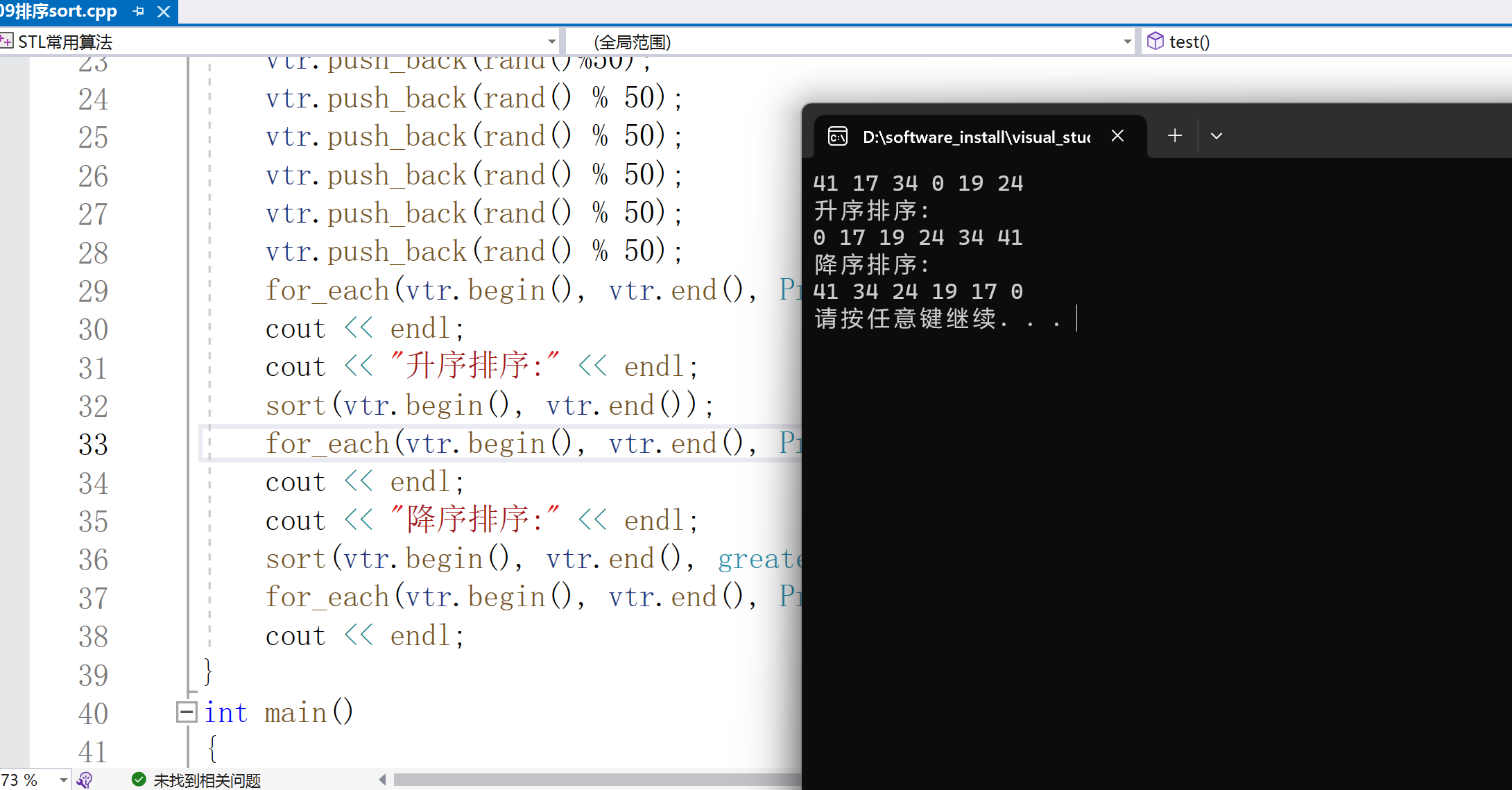
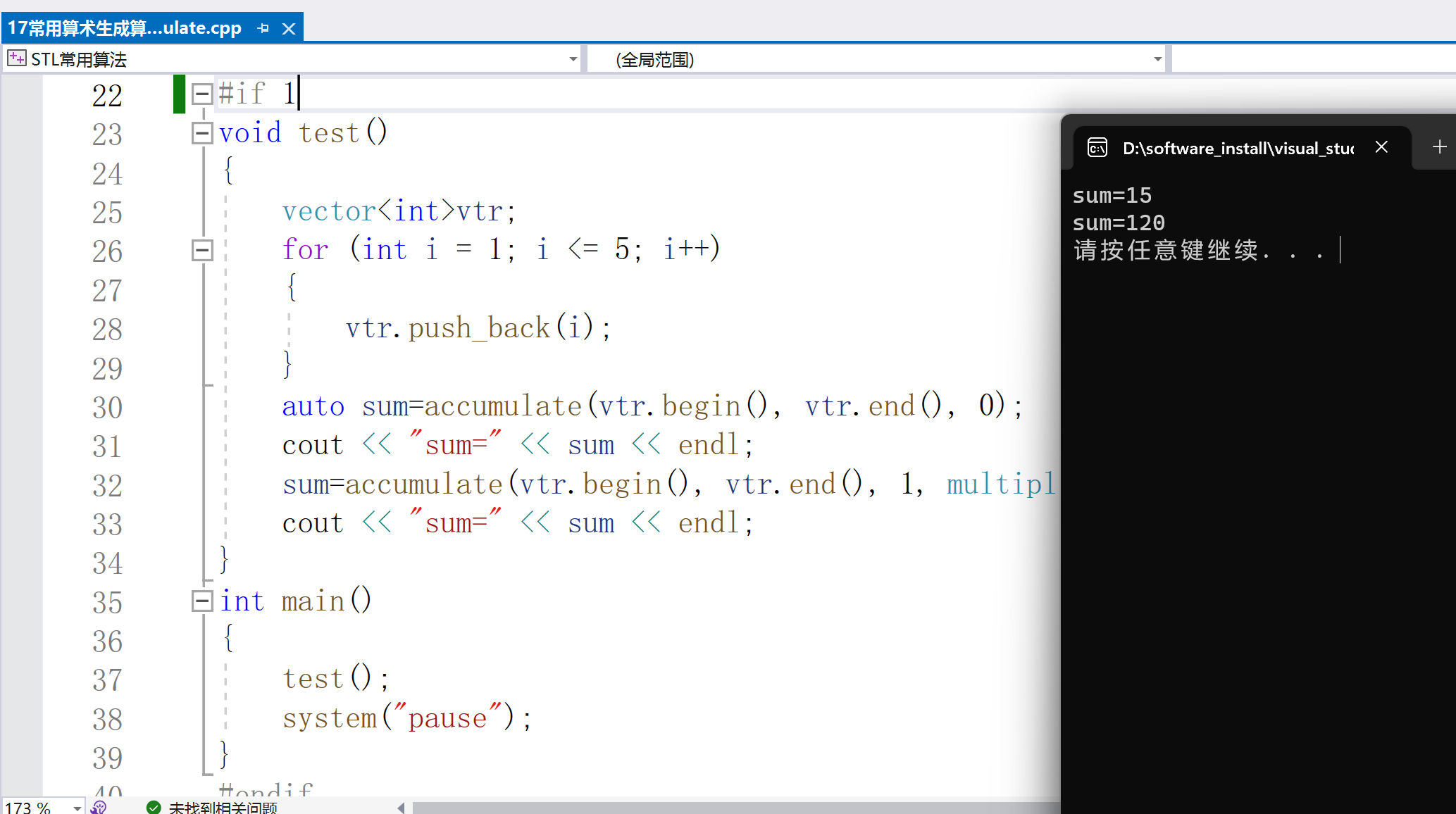
2.random_shuffle打亂順序(洗牌)
打亂有序數列,重新洗牌:
void random_shuffle(_RanIt _First, _RanIt _Last);
形參:_First、_Last --起始和結束迭代器
#include
using namespace std;
#include
#include
#include
#include
class Person
{
friend class Print;
public:
Person() {}
Person(string name, int age) :name(name), age(age) {
}
bool operatorvtr;
vtr.resize(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
vtr[i] = i;
}
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Print());
cout vtr;
vtr.push_back(Person("小王", 1));
vtr.push_back(Person("小王", 2));
vtr.push_back(Person("小王", 3));
vtr.push_back(Person("小李", 1));
vtr.push_back(Person("小李", 2));
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Print());
cout p)
{
cout
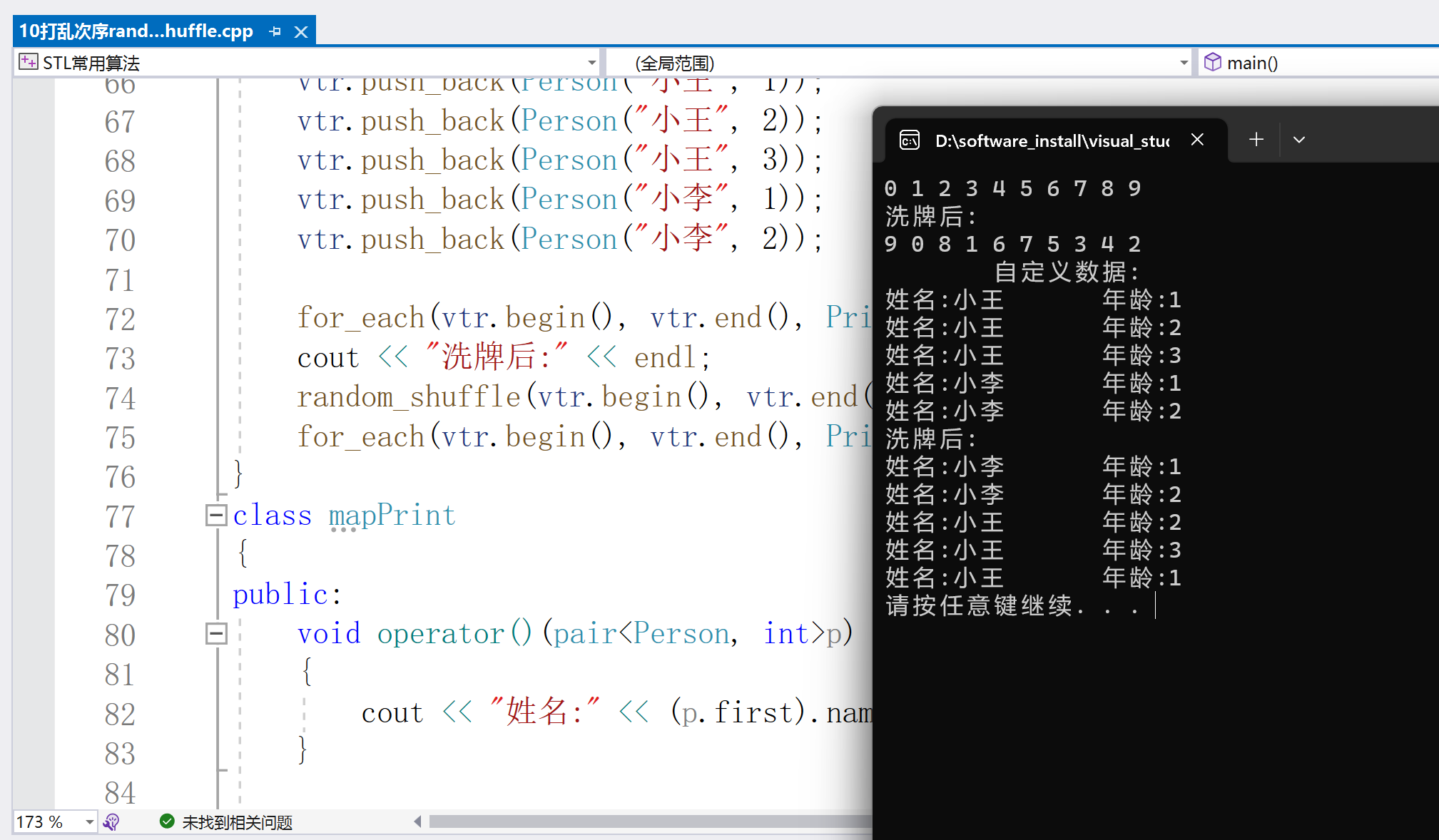
3.merge合并容器
容器合并:
merge()實現吧兩個容器合并在一起,存放到第三個容器中。
注意:merge()合并一定要保證容器元素有序,默認是從小到大的順序。
merge(_InIt1 _First1, _InIt1 _Last1, _InIt2 _First2, _InIt2 _Last2, _OutIt _Dest) -->默認從小到大
merge(_InIt1 _First1, _InIt1 _Last1, _InIt2 _First2, _InIt2 _Last2, _OutIt _Dest, _Pr _Pred) -->重載版本,支持自定義排序規則
_First1、_Last1 --第一個容器的起始和結束迭代器
_Last2、_Dest --第二個元素的起始和結束迭代器
_Dest --要存儲的新容器起始迭代器
_Pred --謂詞,設定排序規則
謂詞:
函數對象返回中為bool類;
函數對象形參只有一個 --> 一元謂詞
函數對象形參有兩個 --> 二元謂詞
示例:
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Print
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout v1;
vectorv2;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
v2.push_back(2);
v2.push_back(16);
v2.push_back(12);
v2.push_back(14);
sort(v2.begin(), v2.end(), less());
vectorv3;
v3.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());
cout ());
merge(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin(),greater());
for_each(v3.begin(), v3.end(), Print());
cout
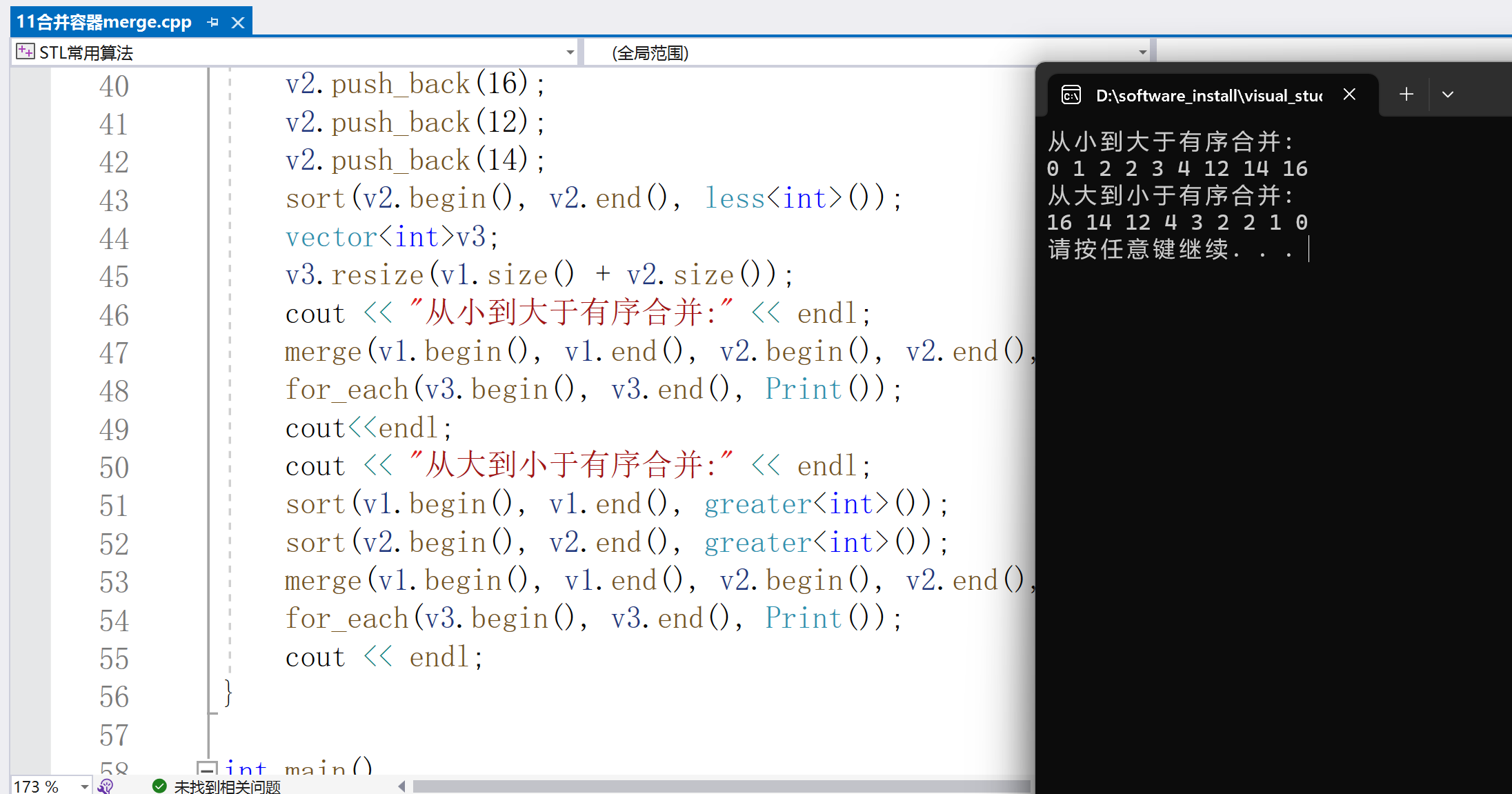
4.reverse元素反轉
函數功能: 元素反轉,將容器中的元素前后顛倒
reverse(const _BidIt _First, const _BidIt _Last)
形參:_First、_Last --起始和結束迭代器
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person() {}
Person(string name, int age) :name(name), age(age) {
}
Person(const Person& p)
{
this->age = p.age;
name = p.name;
}
bool operatorvtr;
vtr.push_back(Person("小王",18));
vtr.push_back(Person("小劉", 15));
vtr.push_back(Person("小林", 20));
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Print());
cout
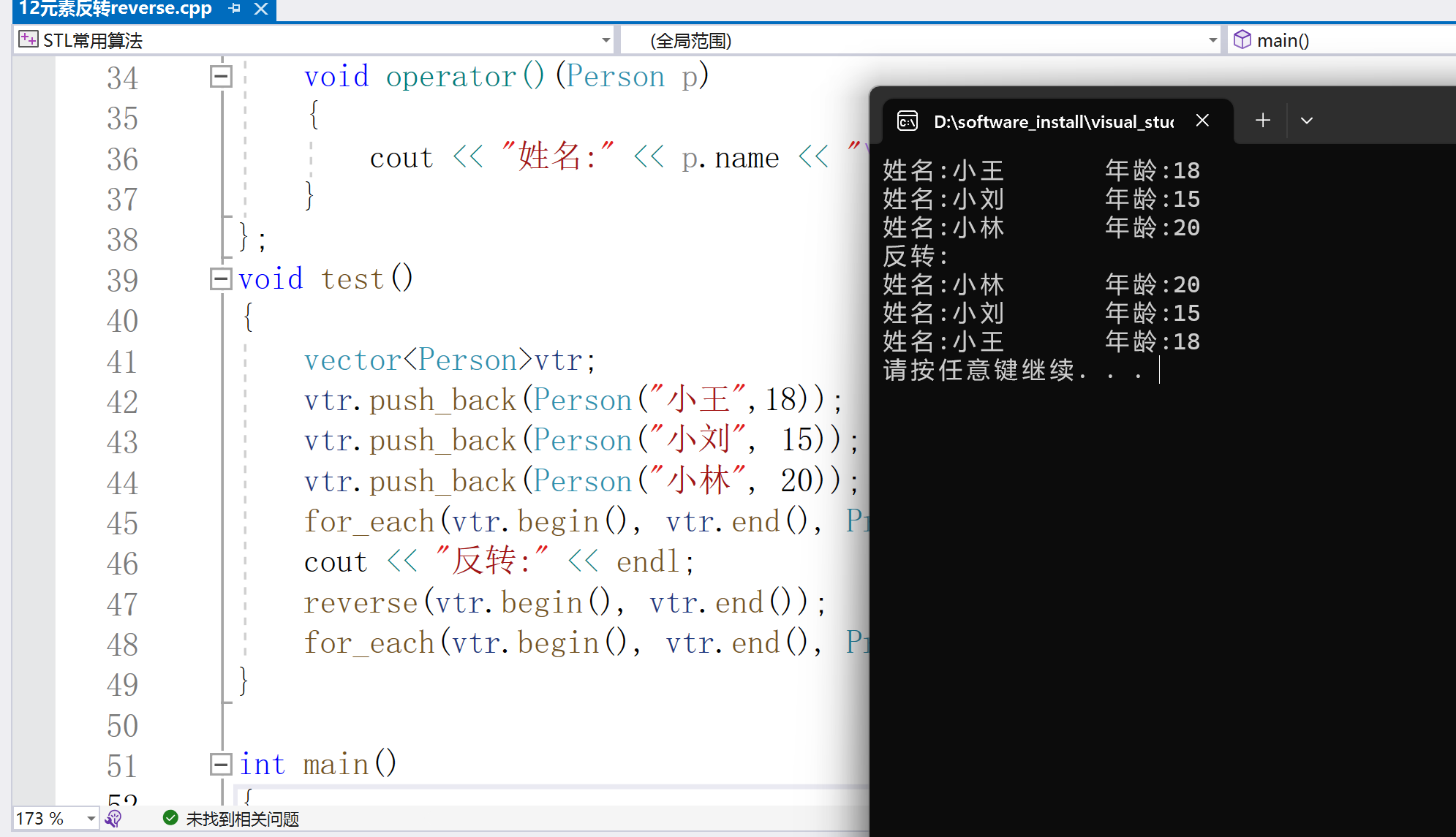
5.copy元素拷貝
_OutIt copy(_InIt _First, _InIt _Last, _OutIt _Dest)
形參:_First、_Last --原容器的起始和結束位置
_Dest --目標容器的起始位置
該函數功能類似于重載運算符=功能
#include
#include
#include
void test()
{
std::vectorvtr, vtr2;
vtr.push_back("C++");
vtr.push_back("copy算法");
vtr.push_back("學習");
vtr.push_back("案例");
std::cout ::iterator p = vtr2.begin(); p != vtr2.end(); p++)
{
std::cout
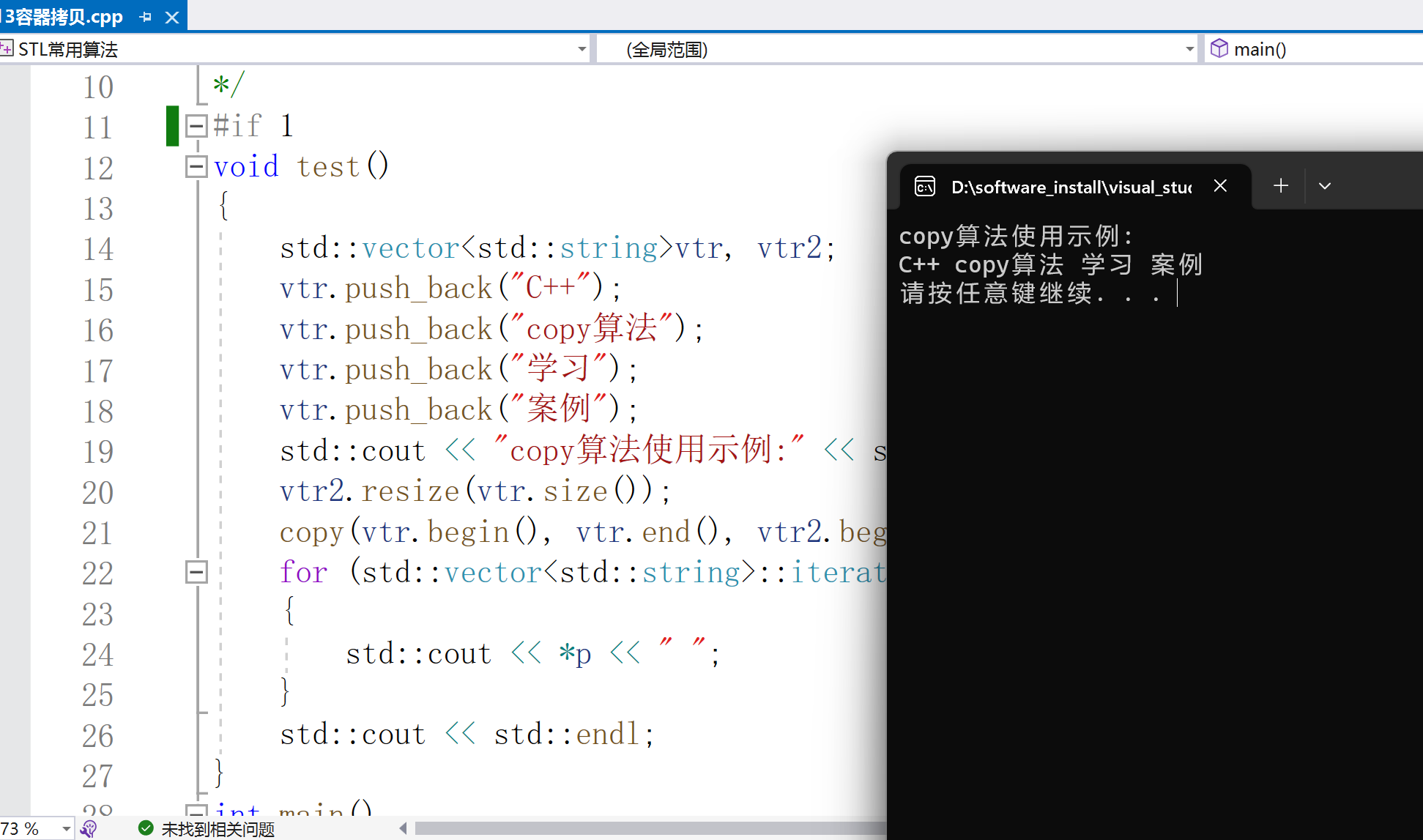
6.replace元素替換
元素替換
void replace(const _FwdIt _First, const _FwdIt _Last, const _Ty& _Oldval, const _Ty& _Newval)
形參:_First、_Last --要替換的數據區間
_Oldval --要替換的內容
_Newval --替換后的內容
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#include
using namespace std;
class Print
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout vtr;
vtr.push_back(10);
vtr.push_back(10);
vtr.push_back(30);
vtr.push_back(10);
vtr.push_back(35);
vtr.push_back(10);
cout
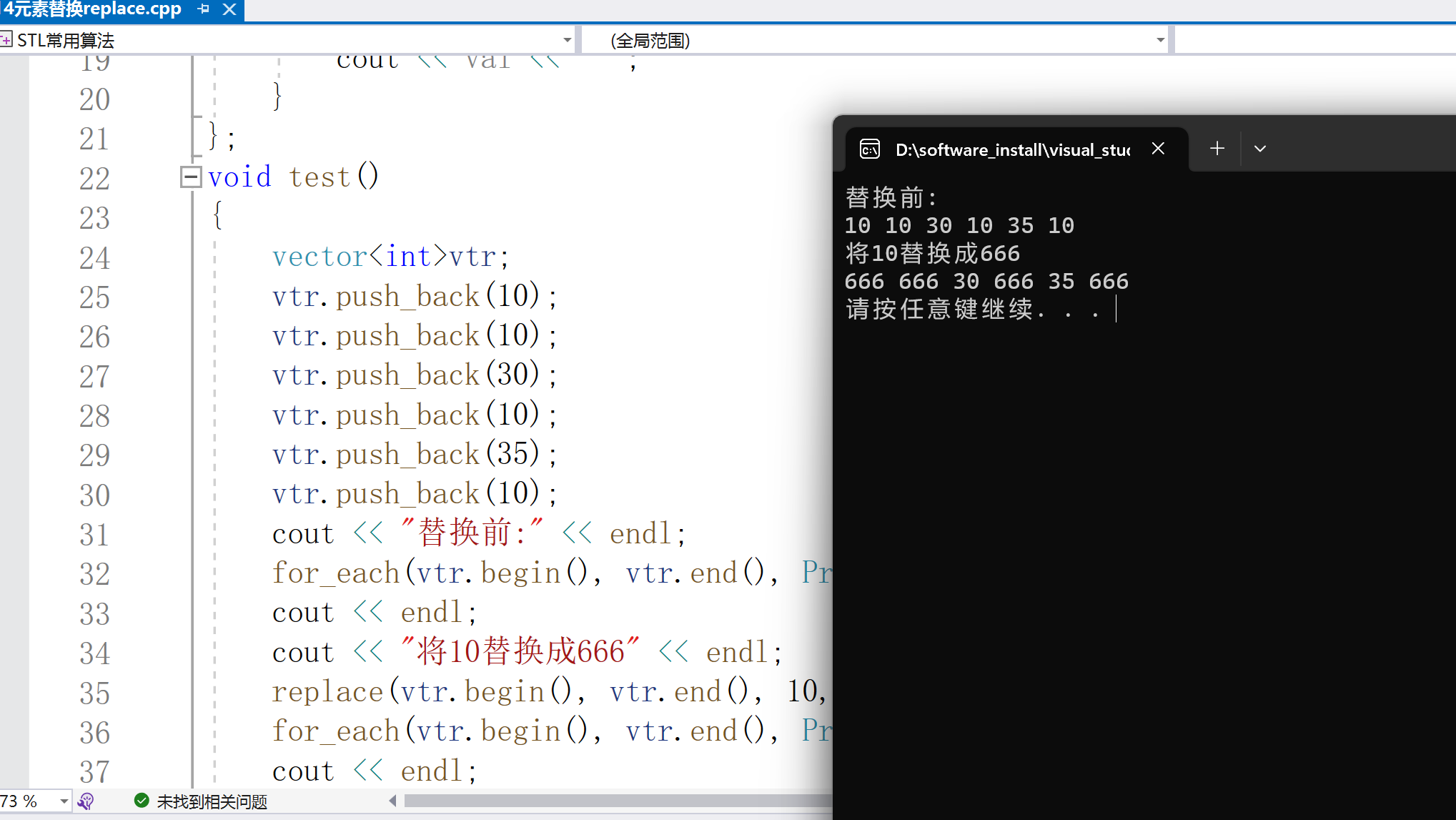
7.條件替換replace_if
條件替換
replace_if(const _FwdIt _First, const _FwdIt _Last, _Pr _Pred, const _Ty& _Val)
形參:_First、_Last --要替換的區間
_Pred --謂詞,替換條件
_Val --替換后的值
示例:
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Myreplace
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val >= 30;
}
};
void test()
{
vectorvtr;
vtr.push_back(10);
vtr.push_back(10);
vtr.push_back(30);
vtr.push_back(10);
vtr.push_back(50);
vtr.push_back(10);
cout =30的值替換為666" ::iterator ptr = vtr.begin();ptr != vtr.end();ptr++)
{
cout
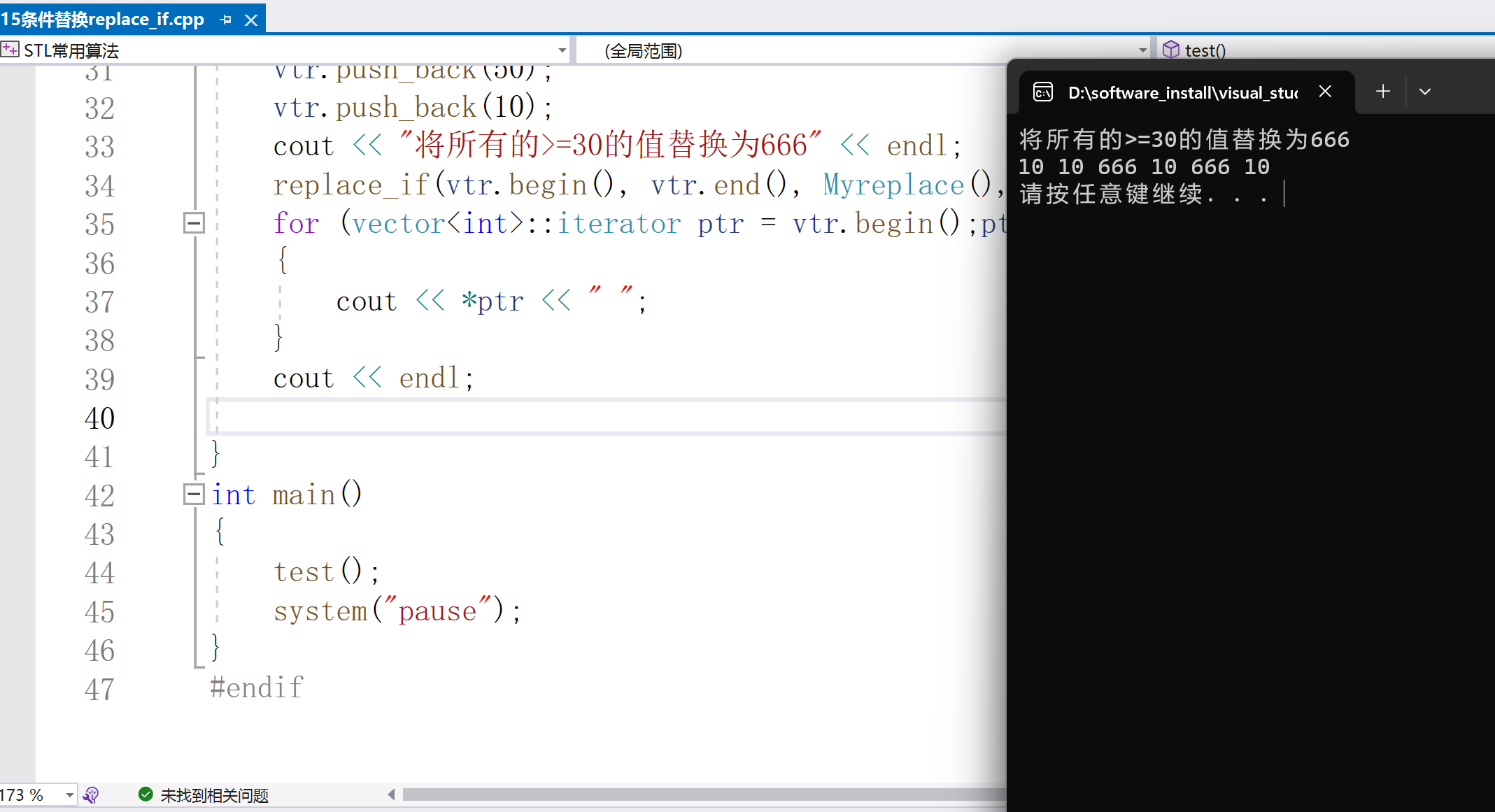
8.容器互換swap
容器元素互換:
swap(container v1,container v2);
將v1和v2的容器元素進行互換,類似于成員函數swap();
#include
using namespace std;
#include
#include
class Print
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout vtr1 = { 10,20,30,50 };
vectorvtr2 = { 10,29,88 };
cout
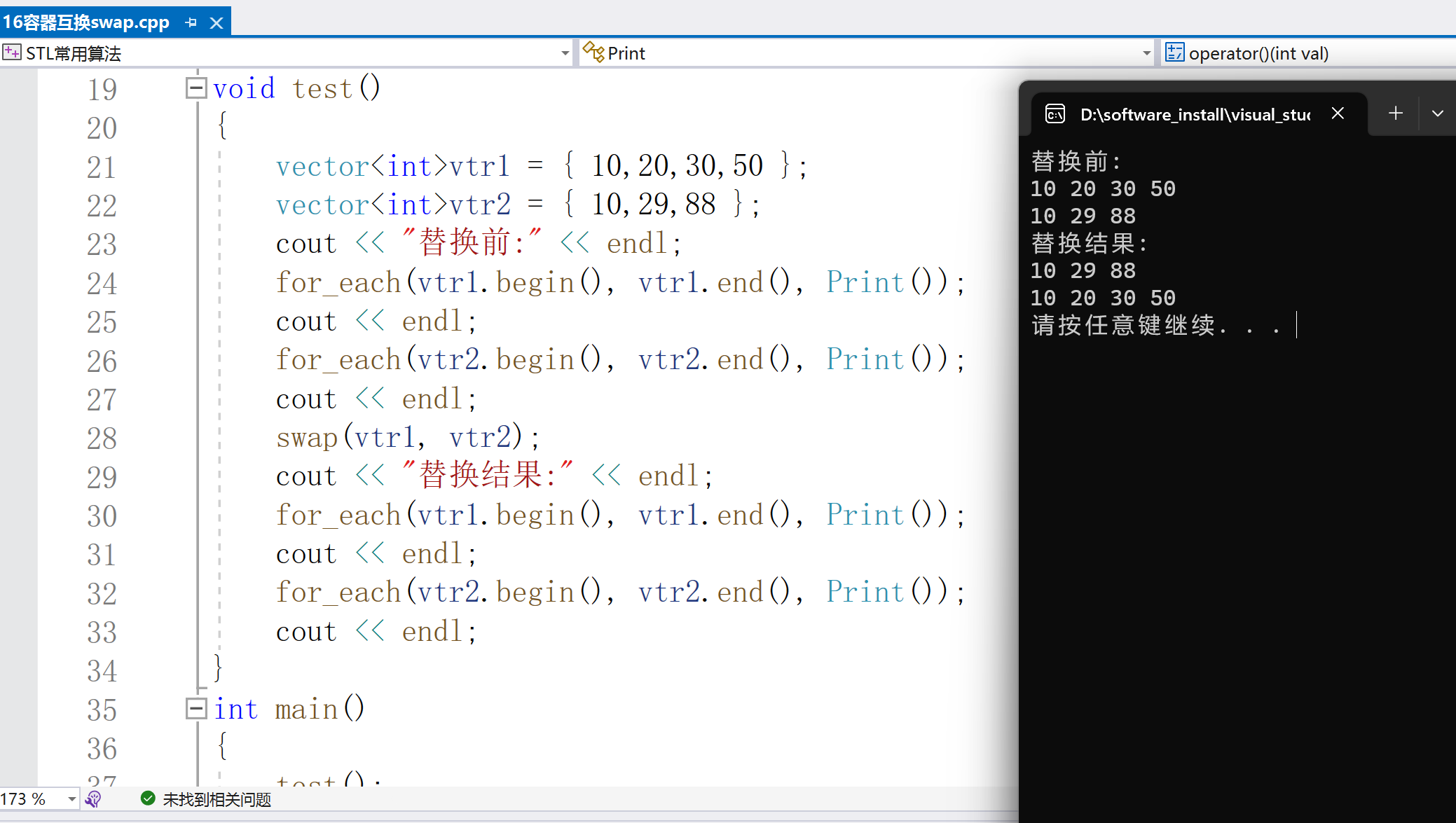
聲明:本文內容及配圖由入駐作者撰寫或者入駐合作網站授權轉載。文章觀點僅代表作者本人,不代表電子發燒友網立場。文章及其配圖僅供工程師學習之用,如有內容侵權或者其他違規問題,請聯系本站處理。
舉報投訴
-
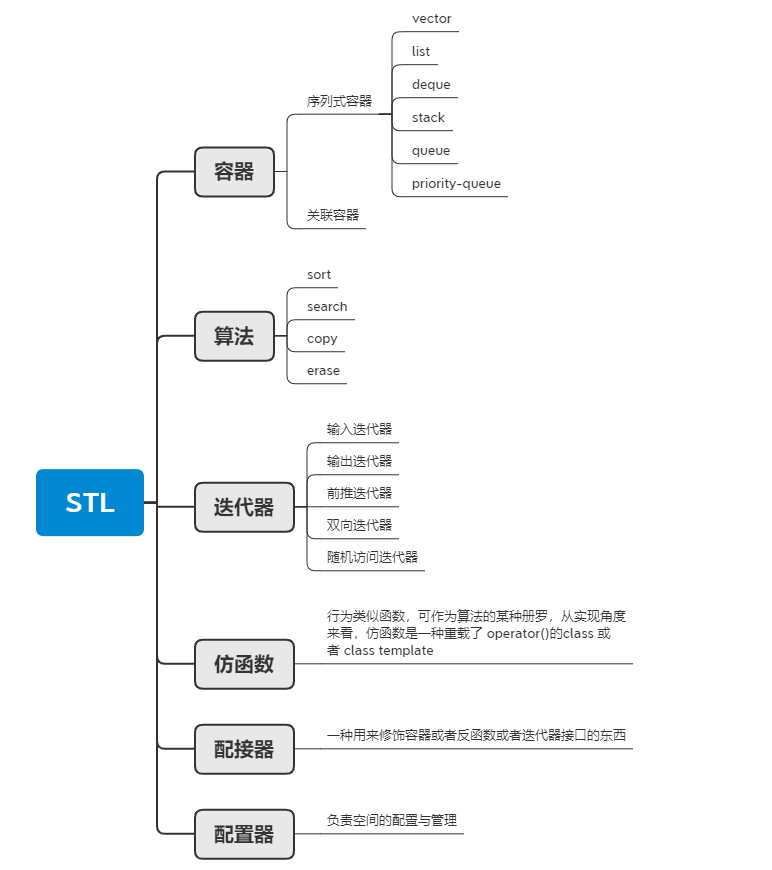
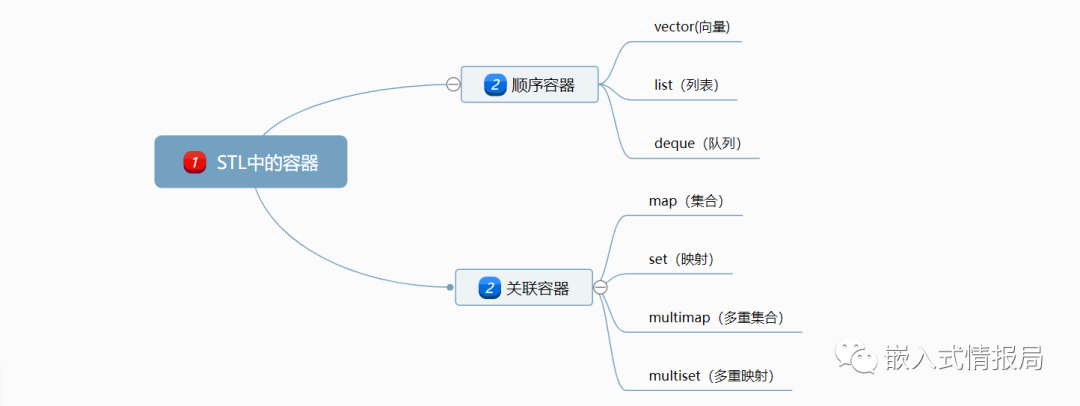
算法
+關注
關注
23文章
4599瀏覽量
92638 -
C++
+關注
關注
22文章
2104瀏覽量
73487 -
STL
+關注
關注
0文章
85瀏覽量
18299
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
c語言入門知識之STL篇
這周終于可以給大家把STL方面的面試題總結出來了,突然發現它里面的細節非常多,只有你想不到的,沒有它沒有的。對于C++程序員來說,STL庫里面的知識也是非常重要的,只要想在技術這條路線上有長遠的發展,那么就一定要掌握它。不管是學
密碼編碼學(加密方法的C與C++實現) pdf第二版
密碼編碼學(加密方法的C與C++實現)分分三個部分。第一部分描述密碼學中的常用算法和數論算法,以及這些算法的
發表于 09-25 09:49
?0次下載
C++ STL的概念及舉例
本篇文章是作者本人使用STL 后的一些看法, 對於想要靠此文章學習STL, 是不可能的. 建議叁后面介紹的一些書入門.
STL的概念
在STL 中, 大至上分三個主要的
發表于 08-30 11:39
?1402次閱讀
STL算法在GIS中的應用
使用STL 算法實現GIS 算法可以保證它的簡潔和高效該文結合C++代碼實例抽象出了地理算子的概念應用在GIS 算法當中通過定制適配器來消除
發表于 06-28 16:55
?33次下載
C++編程思想第二卷_刁成嘉譯
本書介紹C++實用的編程技術和最佳的實踐方法,深入探究了異常處理方法和異常安全設計;介紹C++的字符串、輸入輸出流、STL算法、容器和模板的現代用法,包括模板元編程;解釋多重
發表于 10-21 17:01
?0次下載
C++課程資料詳細資料合集包括了:面向對象程序設計與C++,算法,函數等
本文檔的主要內容詳細介紹的是C++課程資料資料合集包括了:面向對象程序設計與C++,算法,函數,概述, C++語言基礎,構造數據類型,數據類型,C+
發表于 07-09 08:00
?18次下載
C++ STL基本概念是什么
STL,英文全稱 standard template library,中文可譯為標準模板庫或者泛型庫,其包含有大量的模板類和模板函數,是 C++ 提供的一個基礎模板的集合,用于完成諸如輸入/輸出、數學計算等功能。

C++入門之通用算法
C++ 是一種強大的編程語言,它提供了許多通用算法,可以用于各種容器類型。這些算法是通過迭代器來操作容器中的元素,因此它們是通用的,可以用于不同類型的容器。在本篇博客中,我們將詳細介紹 C++




 C++之STL算法(二)
C++之STL算法(二)











評論