1. 數組和std::array
std::array是C++容器庫提供的一個固定大小數組的容器。其與內置的數組相比,是一種更安全、更容易使用的數組類型。std::array在頭文件中定義,其聲明如下:
template<
class T,
std::size_t N
> struct array; //C++11 起
std::array是一個聚合類型,其語義等同于保有一個C語言風格數組T[N]作為其唯一非靜態數據成員的結構體,但其不同于C數組的是它不會自動退化為T*。同時該結構體結合了C風格數組的性能、可訪問性和容器的優點(可獲取大小、支持賦值和隨機訪問等)。
2. array的用法
2.1 成員函數
2.1.1 隱式定義的成員函數
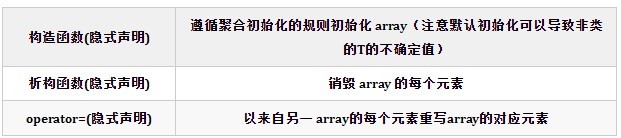
聚合初始化就是從初始化器列表來初始化聚合體,其也是列表初始化的一種方式。
std::array< int, 3 > a = {1,2,3};
std::array< int, 3 > b;
b = a; //將a中的每個元素重寫到b中,使用operator=時候需要確保a b兩個容器長度相等,否則編譯失敗
2.1.2 元素訪問
at
at用于訪問指定的元素, 同時進行越界檢查 ,該函數返回位于指定位置pos的元素的引用,如果pos不在容器的范圍內,則拋出std::out_of_range異常。其函數聲明如下:
reference at( size_type pos ); //C++17 前
constexpr reference at( size_type pos ); //C++17 起
const_reference at( size_type pos ) const; //C++14 前
constexpr const_reference at( size_type pos ) const; //C++14 起
其具體用法如下:
std::array< int,3 > data = { 1, 2, 3};
std::cout<
operator[]
operator[]與at功能相同,即用來訪問指定的元素,但其與at不同的是:operator[]不進行邊界的檢查。其函數聲明如下所示:
reference operator[]( size_type pos ); //C++17 前
constexpr reference operator[]( size_type pos ); //C++17 起
const_reference operator[]( size_type pos ) const; //C++14 前
constexpr const_reference operator[]( size_type pos ) const; //C++14 起
注 :通過operator[]符訪問不存在的元素是未定義行為。
front
front用于訪問容器的第一個元素,其返回值為容器首元素的引用,其函數原型如下:
reference front(); //C++17 前
constexpr reference front(); //C++17 起
const_reference front() const; //C++14 前
constexpr const_reference front() const; //C++14 起
注 :在空容器上對
front的調用是未定義的。
back
back主要功能是用來訪問容器最后一個元素,其返回值為容器最后一個元素的引用,其函數原型如下所示:
reference back(); //C++17 前
constexpr reference back(); //C++17 起
const_reference back() const; //C++14 前
constexpr const_reference back() const; //C++14 起
注 :在空容器上調用
back導致未定義行為。
data
data可以直接訪問容器底層數組,其返回值為指向作為元素存儲工作的底層數組的指針。其函數聲明如下:
T* data() noexcept; //C++11 起, C++17 前
constexpr T* data() noexcept; //C++17 起
const T* data() const noexcept; //C++11 起, C++17 前
constexpr const T* data() const noexcept; //C++17 起
其返回的指針使得范圍[ data(), data() + size() )始終是合法范圍。
2.2.3 迭代器
begin、end和cbegin、cend
begin和cbegin返回指向deque首元素的迭代器,end和cend返回指向deque末元素后一元素的迭代器。其函數聲明如下:
iterator begin() noexcept; //C++17 前
constexpr iterator begin() noexcept; //C++17 起
const_iterator begin() const noexcept; //C++17 前
constexpr const_iterator begin() const noexcept; //C++17 起
const_iterator cbegin() const noexcept; //C++17 前
constexpr const_iterator cbegin() const noexcept; //C++17 起
iterator end() noexcept; //C++17 前
constexpr iterator end() noexcept; //C++17 起
const_iterator end() const noexcept; //C++17 前
constexpr const_iterator end() const noexcept; //C++17 起
const_iterator cend() const noexcept; //C++17 前
constexpr const_iterator cend() const noexcept; //C++17 起
如果array為空,則返回的迭代器將等于end或cend。end和cend指向deque末元素后一元素的迭代器,該元素的表現為占位符,試圖訪問它將導致未定義行為。
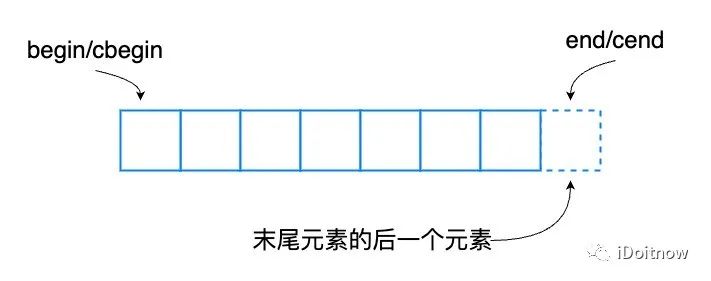
rbegin、rend和crbegin、crend
rbegin和crbegin返回指向array首元素的逆向迭代器。它對應非逆向array的末元素,若array為空,則返回的迭代器等于rend或crend。rend和crend返回指向逆向deque末元素后一元素的逆向迭代器,它對應非逆向array首元素的前一元素,此元素表現為占位符,試圖訪問它導致未定義行為。它們的聲明如下:
reverse_iterator rbegin() noexcept; //C++17 前
constexpr reverse_iterator rbegin() noexcept; //C++17 起
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const noexcept; //C++17 前
constexpr const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const noexcept; //C++17 起
const_reverse_iterator crbegin() const noexcept; //C++17 前
constexpr const_reverse_iterator crbegin() const noexcept; //C++17 起
reverse_iterator rend(); //C++11 前
reverse_iterator rend() noexcept; //C++11 起
const_reverse_iterator rend() const; //C++11 前
const_reverse_iterator rend() const noexcept; //C++11 起
const_reverse_iterator crend() const noexcept; //C++11 起

2.2.4 容量
empty
empty用來檢查容器是否為空,若為空則返回true,否則為false。其函數聲明如下:
constexpr bool empty() const noexcept; //C++11 起,C++20 前
[[nodiscard]] constexpr bool empty() const noexcept; //C++20 起
其底層實現就是檢查容器是否無元素,即判斷是否begin() == end()。
size
size函數返回容器中元素數量,即std::distance(begin(), end())。其函數聲明如下:
constexpr size_type size() const noexcept; //C++11 起
max_size
max_size函數返回根據系統或庫實現限制的容器可保有的元素最大數量,即對于最大容器的 std::distance(begin(), end())。其函數聲明為:
constexpr size_type max_size() const noexcept; //C++11 起
注 :因為每個
std::array都是固定大小容器,故max_size返回的值等于N(亦為size所返回的值)
2.2.5 修改器
fill
fill函數原型如下所示:
void fill( const T& value ); //C++11 起, C++20 前
constexpr void fill( const T& value ); //C++20 起
fill函數主要用于以指定值填充容器,即將定值 value 賦給容器中的所有元素。
具體用法示例如下:
std::array< int, 3 > arr = {1, 2, 3};
arr.fill(1); // arr = {1, 1, 1}
swap
swap函數的主要作用是交換兩個array容器的內容,其與deque的swap不同的是不導致迭代器和引用關聯到別的容器。其函數聲明如下:
void swap( array& other ) noexcept(); //C++11 起, C++20 前
constexpr void swap( array& other ) noexcept(); //C++20 起
其用法示例如下圖所示:
std::array< int, 3 > a1{1, 2, 3}, a2{4, 5, 6};
auto it1 = a1.begin(); //*it1 = 1
auto it2 = a2.begin(); //*it2 = 4
int &ref1 = a1[1]; // ref1 = 2
int &ref2 = a2[1]; // ref1 = 5
std::cout < < *it1 < < ' ' < < *it2 < < ' ' < < ref1 < < ' ' < < ref2 < < 'n';
// 打印結果為1 4 2 5
a1.swap(a2);
// 此時a1 = {4, 5, 6},a2 = {1, 2, 3}
std::cout < < *it1 < < ' ' < < *it2 < < ' ' < < ref1 < < ' ' < < ref2 < < 'n';
// 打印結果為4 1 5 2
/*注:
交換后迭代器與引用保持與原 array 關聯,
例如it1仍指向元素 a1[0] ,ref1仍指代 a1[1] */
2.2 非成員函數
operator==,!=,<,<=,>,>=,<=>(std::array)
C++提供operator==,!=,<,<=,>,>=,<=>(std::array)非成員函數用來比較兩個array的大小,相關函數及函數聲明如下:
//1. ==
//返回值:在 array 內容相等時返回 true,否則返回 false
template< class T, std::size_t N >
bool operator==( const std::array< T, N >& lhs,
const std::array< T, N >& rhs ); //C++20 前
template< class T, std::size_t N >
constexpr bool operator==( const std::array< T, N >& lhs,
const std::array< T, N >& rhs ); //C++20 起
//2. !=
//返回值:在 array 內容不相等時返回 true,否則返回 false
template< class T, std::size_t N >
bool operator!=( const std::array< T, N >& lhs,
const std::array< T, N >& rhs ); //C++20 前
//3. <
//返回值:在 lhs 的內容按字典序小于 rhs 的內容時返回 true,否則返回 false
template< class T, std::size_t N >
bool operator< ( const std::array< T, N >& lhs,
const std::array< T, N >& rhs ); //C++20 前
//4. <=
//返回值:在 lhs 的內容按字典序小于或等于 rhs 的內容時返回 true,否則返回 false
template< class T, std::size_t N >
bool operator<=( const std::array< T, N >& lhs,
const std::array< T, N >& rhs ); //C++20 前
//5. >
//返回值:在 lhs 的內容按字典序大于 rhs 的內容時返回 true,否則返回 false
template< class T, std::size_t N >
bool operator >( const std::array< T, N >& lhs,
const std::array< T, N >& rhs ); //C++20 前
//6. >=
//返回值:在 lhs 的內容按字典序大于或等于 rhs 的內容時返回 true,否則返回 false
template< class T, std::size_t N >
bool operator >=( const std::array< T, N >& lhs,
const std::array< T, N >& rhs ); //C++20 前
//7. <= >
//返回值:lhs 與 rhs 中的首對不等價元素的相對順序,如果有這種元素;否則是 lhs.size() <= > rhs.size()。
template< class T, std::size_t N >
constexpr operator<= >( const std::array< T, N >& lhs,
const std::array< T, N >& rhs ); //C++20 起
1,2中會檢查lhs和rhs的內容是相等,即他們是否擁有相同數量的元素且lhs中每個元素與rhs的相同位置元素比較相等。同時函數中
T必須符合 可相等比較(EqualityComparable) 的要求3-6中按照字典比較lhs和rhs的內容,其內部等價于調用
std::lexicographical_compare函數進行比較。同時函數中T必須符合[ 可小于比較(LessThanComparable) 的要求。7中也是按字典序比較lhs和rhs的內容。其內部等價于調用
std::lexicographical_compare_three_way進行比較。返回類型同合成三路比較的結果類型。其邏輯大致如下:lhs < rhs ? std::weak_ordering::less : rhs < lhs ? std::weak_ordering::greater : std::weak_ordering::equivalent //注:通常情況下less對應的是-1,greater對應1,equivalent對應0lhs與rhs中的首對不等價元素的相對順序,如果有這種元素;否則是
lhs.size() <=> rhs.size()。
其具體的應用示例如下所示:
std::array< int, 3 > alice{1, 2, 3};
std::array< int, 3 > bob{7, 8, 9};
std::array< int, 3 > eve{1, 2, 3};
std::cout < < std::boolalpha;
// 比較不相等的容器
std::cout < < "alice == bob returns " < < (alice == bob) < < 'n';
std::cout < < "alice != bob returns " < < (alice != bob) < < 'n';
std::cout < < "alice < bob returns " < < (alice < bob) < < 'n';
std::cout < < "alice <= bob returns " < < (alice <= bob) < < 'n';
std::cout < < "alice > bob returns " < < (alice > bob) < < 'n';
std::cout < < "alice >= bob returns " < < (alice >= bob) < < 'n';
std::cout < < 'n';
// 比較相等的容器
std::cout < < "alice == eve returns " < < (alice == eve) < < 'n';
std::cout < < "alice != eve returns " < < (alice != eve) < < 'n';
std::cout < < "alice < eve returns " < < (alice < eve) < < 'n';
std::cout < < "alice <= eve returns " < < (alice <= eve) < < 'n';
std::cout < < "alice > eve returns " < < (alice > eve) < < 'n';
std::cout < < "alice >= eve returns " < < (alice >= eve) < < 'n';
輸出結果為
alice == bob returns false
alice != bob returns true
alice < bob returns true
alice <= bob returns true
alice > bob returns false
alice >= bob returns false
alice == eve returns true
alice != eve returns false
alice < eve returns false
alice <= eve returns true
alice > eve returns false
alice >= eve returns true
std::get(std::array)
std::get(std::array)可以用來訪問array的一個元素,其函數聲明如下:
template< std::size_t I, class T, std::size_t N >
T& get( std::array< T,N >& a ) noexcept; //C++11 起, C++14 前
template< std::size_t I, class T, std::size_t N >
constexpr T& get( std::array< T,N >& a ) noexcept; //C++14 起
template< std::size_t I, class T, std::size_t N >
T&& get( std::array< T,N >&& a ) noexcept; //C++11 起, C++14 前
template< std::size_t I, class T, std::size_t N >
constexpr T&& get( std::array< T,N >&& a ) noexcept; //C++14 起
template< std::size_t I, class T, std::size_t N >
const T& get( const std::array< T,N >& a ) noexcept; //C++11 起, C++14 前
template< std::size_t I, class T, std::size_t N >
constexpr const T& get( const std::array< T,N >& a ) noexcept; //C++14 起
template< std::size_t I, class T, std::size_t N >
const T&& get( const std::array< T,N >&& a ) noexcept; //C++11 起, C++14 前
template< std::size_t I, class T, std::size_t N >
constexpr const T&& get( const std::array< T,N >&& a ) noexcept; //C++14 起
其主要作用是從a中提取第I個元素.I必須是范圍 [0, N) 中的整數值。與at()或 operator[]相反,這在編譯時強制。該函數的返回值為a中第I元素的引用。
其具體的用法如下:
std::array< int, 3 > arr;
// 設置值:
std::get< 0 >(arr) = 1;
std::get< 1 >(arr) = 2;
std::get< 2 >(arr) = 3;
// 獲取值:
std::cout < < "(" < < std::get< 0 >(arr) < < ", " < < std::get< 1 >(arr)
< < ", " < < std::get< 2 >(arr) < < ")n";
//輸出結果為 (1, 2, 3)
std::swap(std::array)
std::swap(std::array)函數是為std::array特化std::swap 算法。其函數聲明如下:
template< class T, std::size_t N >
void swap( std::array< T, N >& lhs,
std::array< T, N >& rhs ); //C++11 起, C++17 前
template< class T, std::size_t N >
void swap( std::array< T, N >& lhs,
std::array< T, N >& rhs ) noexcept(); //C++17 起, C++20 前
template< class T, std::size_t N >
constexpr void swap( std::array< T, N >& lhs,
std::array< T, N >& rhs ) noexcept(); //C++20 起
交換 lhs 與 rhs 的內容。調用lhs.swap(rhs)。其具體用法如下:
std::array< int, 3 > a1{1, 2, 3}, a2{4, 5, 6};
auto it1 = a1.begin(); //*it1 = 1
auto it2 = a2.begin(); //*it2 = 4
int &ref1 = a1[1]; // ref1 = 2
int &ref2 = a2[1]; // ref1 = 5
std::cout < < *it1 < < ' ' < < *it2 < < ' ' < < ref1 < < ' ' < < ref2 < < 'n';
// 打印結果為1 4 2 5
std::swap(a1, a2);
// 此時a1 = {4, 5, 6},a2 = {1, 2, 3}
std::cout < < *it1 < < ' ' < < *it2 < < ' ' < < ref1 < < ' ' < < ref2 < < 'n';
// 打印結果為4 1 5 2
std::to_array
std::to_array函數聲明如下:
template< class T, std::size_t N >
constexpr std::array< std::remove_cv_t< T >, N > to_array(T (&a)[N]); //C++20 起
template< class T, std::size_t N >
constexpr std::array< std::remove_cv_t< T >, N > to_array(T (&&a)[N]); //C++20 起
std::to_array函數可以從一維內建數組 a 創建 std::array 對象,從 a 的對應元素復制初始化 std::array 的元素。不支持復制或移動多維內建數組。其具體用法如下:
#include < array >
#include < iostream >
int main()
{
// 復制字符串字面量
auto a1 = std::to_array("foo");
static_assert(a1.size() == 4);
// 推導元素類型和長度
auto a2 = std::to_array({0, 2, 1, 3});
// 推導長度而元素類型指定
// 發生隱式轉換
auto a3 = std::to_array< long >({0, 1, 3});
auto a4 = std::to_array< std::pair< int, float >>(
{{3, .0f}, {4, .1f}, {4, .1e23f}});
// 創建不可復制的 std::array
auto a5 = std::to_array({std::make_unique< int >(3)});
// 錯誤:不支持復制多維數組
// char s[2][6] = { "nice", "thing" };
// auto a6 = std::to_array(s);
}
std::tuple_size
std::tuple_size(std::array)函數的聲明如下:
template< class T, std::size_t N >
struct tuple_size std::array< T, N > > :
std::integral_constant< std::size_t, N > //C++11 起
{ };
其提供作為編譯時常量表達式訪問std::array中元素數量的方法。用法示例如下:
#include < iostream >
#include < array >
template< class T >
void test(T t)
{
int a[std::tuple_size< T >::value]; // 能用于編譯時
std::cout < < std::tuple_size< T >::value < < 'n';
}
int main()
{
std::array< float, 3 > arr;
test(arr); //輸出 3
}
std::tuple_element
std::tuple_element函數主要用來獲得 array 元素的類型,其聲明如下:
template< std::size_t I, class T, std::size_t N >
struct tuple_element I, std::array< T, N > >; //C++11 起
其使用類 tuple 接口,提供 array 元素類型的編譯時帶下標訪問。具體使用方法如下:
// 定義 array 并獲取位于位置 0 的元素類型
std::array< int, 10 > data {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
using T = std::tuple_element< 0, decltype(data) >::type; // int
3. 總結
數組std::array的優劣:
優點
- 無開銷隨機訪問。
- 快速遍歷;適合線性搜索。
劣勢
- 如果元素類型具有較高的復制/分配成本,則可能會變慢(重新排序元素需要復制/移動它們)。
- 在使用array容器的時候,其size必須是常量表達式(即編譯時已知)。
- 不支持大小更改操作(調整大小、插入、擦除等)。
-
存儲器
+關注
關注
38文章
7455瀏覽量
163623 -
交換機
+關注
關注
21文章
2624瀏覽量
99286 -
C語言
+關注
關注
180文章
7601瀏覽量
136251 -
C++語言
+關注
關注
0文章
147瀏覽量
6972 -
迭代器
+關注
關注
0文章
43瀏覽量
4302
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
C++教程之數組
C++語言入門教程之C++語言程序設計數組的詳細資料概述免費下載
C++程序設計教程之數組的詳細資料說明

在C++中如何用虛函數實現多態
C++入門之數組的概念
動態數組和C++ std::vector詳解
C++數組名和數組拷貝詳解




 ?數組和C++ std::array詳解
?數組和C++ std::array詳解











評論