在學(xué)習(xí)Mysql的時(shí)候,我們都有這個(gè)常識(shí):對(duì)于DB的操作,其實(shí)本質(zhì)上是對(duì)于磁盤的操作,如果對(duì)于DB的訪問次數(shù)過多,其實(shí)就是涉及了大量的磁盤IO,這就會(huì)導(dǎo)致MYsql出現(xiàn)性能上的瓶頸。
項(xiàng)目背景
為了提高M(jìn)ysql數(shù)據(jù)庫的訪問瓶頸,常用的方法有如下兩個(gè):
- 在服務(wù)器端增加緩存服務(wù)器緩存常用的數(shù)據(jù)(例如redis)
- 增加連接池,來提高M(jìn)Ysql Server的訪問效率,在高并發(fā)的情況下,每一個(gè)用戶大量的TCP三次握手。Mysql Server的連接認(rèn)證,Mysql Server關(guān)閉連接回收資源和TCP四次揮手所耗費(fèi)的性能時(shí)間也是明顯的,增加連接池就是為了減少這一部分的性能損耗。
注:常見的MySQL、Oracle、SQLServer等數(shù)據(jù)庫都是基于C/S架構(gòu)設(shè)計(jì)的。
市面上主流的Mysql數(shù)據(jù)庫連接池,對(duì)于短時(shí)間內(nèi)的大量增刪改查操作的性能提升很明顯,但大多數(shù)都是Java實(shí)現(xiàn)的,該項(xiàng)目的開展就是為了提高M(jìn)ysql Server的訪問效率,實(shí)現(xiàn)基于C++代碼的數(shù)據(jù)庫連接池模塊。
針對(duì)于系統(tǒng)啟動(dòng)時(shí)就創(chuàng)建一定數(shù)量的連接,用戶一旦執(zhí)行CURD操作,直接拿出一條連接即可,不需要TCP的連接過程和資源回收過程,使用完該連接后歸還給連接池的連接隊(duì)列,供之后使用。
功能點(diǎn)介紹
連接池一般包含了數(shù)據(jù)庫連接所用的ip地址、port端口號(hào)、username用戶名、password密碼以及其他一些性能參數(shù):比如初始連接量、最大連接量、最大空閑時(shí)間、連接超時(shí)時(shí)間等,本項(xiàng)目重點(diǎn)實(shí)現(xiàn)上述通用功能:
1、初始連接量(initSize):
初始連接量表示連接池事先會(huì)和MySQL Server創(chuàng)建的initSize數(shù)量的Connection連接。在完成初始連接量之后,當(dāng)應(yīng)用發(fā)起MySQL訪問時(shí),不用創(chuàng)建新的MySQLServer連接,而是從連接池中直接獲取一個(gè)連接,當(dāng)使用完成后,再把連接歸還到連接池中。
2、最大連接量(maxSize)
當(dāng)并發(fā)訪問MySQL Server的請(qǐng)求增加,初始連接量不夠用了,此時(shí)會(huì)增加連接量,但是增加的連接量的上限就是maxSIze。因?yàn)槊恳粋€(gè)連接都會(huì)占用一個(gè)socket資源,一般連接池和服務(wù)器都是部署在一臺(tái)主機(jī)上,如果連接池的連接數(shù)量過多,那么服務(wù)器就不能響應(yīng)太多的客戶端請(qǐng)求了。
3、最大空閑時(shí)間(maxIdleTime)
當(dāng)高并發(fā)過去,因?yàn)楦卟l(fā)而新創(chuàng)建的連接在很長時(shí)間(maxIdleTime)內(nèi)沒有得到使用,那么這些新創(chuàng)建的連接處于空閑,并且占用著一定的資源,這個(gè)時(shí)候就需要將其釋放掉,最終只用保存iniSize個(gè)連接就行。
4、連接超時(shí)時(shí)間(connectionTimeOut)
當(dāng)MySQL的并發(fā)訪問請(qǐng)求量過大,連接池中的連接數(shù)量已經(jīng)達(dá)到了maxSize,并且此時(shí)連接池中沒有可以使用的連接,那么此時(shí)應(yīng)用阻塞connectionTimeOut的時(shí)間,如果此時(shí)間內(nèi)有使用完的連接歸還到連接池,那么他就可以使用,如果超過這個(gè)時(shí)間還是沒有連接,那么它獲取數(shù)據(jù)庫連接池失敗,無法訪問數(shù)據(jù)庫。
功能點(diǎn)實(shí)現(xiàn)的相關(guān)原理綜述
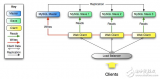
- 連接池只需要一個(gè)實(shí)例,所以ConnectionPool以單例`模式設(shè)計(jì);
- 從ConnectionPool中可以獲取和Mysql的連接Connection;
- 空閑連接Connection全部維護(hù)在一個(gè)線程安全的Connection隊(duì)列中,使用線程互斥鎖保證隊(duì)列的線程安;
- 如果Connection隊(duì)列為空,還需要再獲取連接,此時(shí)需要?jiǎng)討B(tài)創(chuàng)建連接,上限數(shù)量是maxSize;
- 隊(duì)列中空閑連接時(shí)間超過maxIdleTime的就會(huì)被釋放掉,只保留初始的initSize個(gè)連接就可以了,這個(gè)功能點(diǎn)肯定要放在獨(dú)立的線程中去做;
- 如果Connection隊(duì)列為空,而此時(shí)連接的數(shù)量已達(dá)上限maxSize,那么等待ConnectionTimeout時(shí)間還獲取不到空閑的連接,那么獲取連接失敗,此處從Connection隊(duì)列獲取空閑連接,可以使用帶超時(shí)時(shí)間的mutex互斥鎖來實(shí)現(xiàn)連接超時(shí)時(shí)間;
- 用戶獲取的連接用shared_ptr智能指針來管理,用lambda表達(dá)式定制連接釋放的功能(不真正釋放連接,而是把連接歸還到連接池中);
- 連接的生產(chǎn)和連接的消費(fèi)采用生產(chǎn)者-消費(fèi)者線程模型來設(shè)計(jì),使用了線程間的同步通信機(jī)制條件變量和互斥鎖。
圖示如下:

關(guān)鍵技術(shù)點(diǎn)
1、MySql數(shù)據(jù)庫編程
目的:在C++下輸入Sql語句對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)庫進(jìn)行操作的代碼封裝
說明:這里的MYSQL的數(shù)據(jù)庫編程直接采用oracle公司提供的C++客戶端開發(fā)包 , 讀者可以自己查閱資料或搜索官方文檔自行學(xué)習(xí)相關(guān)API的使用方法。
Connection.h:
{
public:
// 初始化數(shù)據(jù)庫連接
Connection();
// 釋放數(shù)據(jù)庫連接資源
~Connection();
// 連接數(shù)據(jù)庫
bool connect(string ip,
unsigned short port,
string user,
string password,
string dbname);
// 更新操作 insert、delete、update
bool update(string sql);
// 查詢操作 select
MYSQL_RES* query(string sql);
// 刷新一下連接的起始的空閑時(shí)間點(diǎn)
void refreshAliveTime() { _alivetime = clock(); }
// 返回存活的時(shí)間
clock_t getAliveeTime()const { return clock() - _alivetime; }
private:
MYSQL* _conn; // 表示和MySQL Server的一條連接
clock_t _alivetime; // 記錄進(jìn)入空閑狀態(tài)后的起始存活時(shí)間
};
Connection.cpp:
{
// 初始化數(shù)據(jù)庫連接
_conn = mysql_init(nullptr);
}
Connection::~Connection()
{
// 釋放數(shù)據(jù)庫連接資源
if (_conn != nullptr)
mysql_close(_conn);
}
bool Connection::connect(string ip, unsigned short port,
string username, string password, string dbname)
{
// 連接數(shù)據(jù)庫
MYSQL* p = mysql_real_connect(_conn, ip.c_str(), username.c_str(),
password.c_str(), dbname.c_str(), port, nullptr, 0);
return p != nullptr;
}
bool Connection::update(string sql)
{
// 更新操作 insert、delete、update
if (mysql_query(_conn, sql.c_str()))
{
LOG("更新失敗:" + sql);
return false;
}
return true;
}
MYSQL_RES* Connection::query(string sql)
{
// 查詢操作 select
if (mysql_query(_conn, sql.c_str()))
{
LOG("查詢失敗:" + sql);
return nullptr;
}
return mysql_use_result(_conn);
}
這里需要說明的是:在Windows上使用數(shù)據(jù)庫需要進(jìn)行相關(guān)配置,大致配置內(nèi)容如下:
- 右鍵項(xiàng)目- C/C++ - 常規(guī) -附加包含目錄 - 增加mysql.h的頭文件路徑;
- 右鍵項(xiàng)目 - 鏈接器 - 常規(guī) - 附加庫目錄 - 填寫libmysql.lib的路徑;
- 右鍵項(xiàng)目 - 鏈接器 - 輸入 - 附加依賴項(xiàng) - 填寫libmysql.lib的路徑;
- 把libmysql.dll的動(dòng)態(tài)鏈接庫(Linux下后綴名是.so庫)放在工程目錄下。
2、數(shù)據(jù)庫連接池單例代碼
連接池僅需要一個(gè)實(shí)例,同時(shí)服務(wù)器肯定是多線程的,必須保證線程安全,所以采用懶漢式線程安全的單例:
CommonConnectionPool.h: 部分代碼
{
public:
// 獲取連接池對(duì)象實(shí)例
static ConnectionPool* getConnectionPool();
// 給外部提供接口,從連接池中獲取一個(gè)可用的空閑連接
shared_ptr getConnection();
private:
// 單例#1 構(gòu)造函數(shù)私有化
ConnectionPool();
};
CommonConnectionPool.cpp: 部分代碼
ConnectionPool* ConnectionPool::getConnectionPool()
{
static ConnectionPool pool; //靜態(tài)對(duì)象初始化由編譯器自動(dòng)進(jìn)行l(wèi)ock和unlock
return &pool;
}
3、queue隊(duì)列容器
連接池的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)是queue隊(duì)列,最早生成的連接connection放在隊(duì)頭,此時(shí)記錄一個(gè)起始時(shí)間,這一點(diǎn)在后面最大空閑時(shí)間時(shí)會(huì)發(fā)揮作用:如果隊(duì)頭都沒有超過最大空閑時(shí)間,那么其他的一定沒有
CommonConnectionPool.cpp的連接池構(gòu)造函數(shù):
ConnectionPool::ConnectionPool()
{
// 加載配置項(xiàng)了
if (!loadConfigFile())
{
return;
}
// 創(chuàng)建初始數(shù)量的連接
for (int i = 0; i < _initSize; ++i)
{
Connection* p = new Connection();//創(chuàng)建一個(gè)新的連接
p->connect(_ip, _port, _username, _password, _dbname);
p->refreshAliveTime(); // 刷新一下開始空閑的起始時(shí)間
_connectionQue.push(p);
_connectionCnt++;
}
}
連接數(shù)量沒有到達(dá)上限,繼續(xù)創(chuàng)建新的連接
{
Connection* p = new Connection();
p->connect(_ip, _port, _username, _password, _dbname);
p->refreshAliveTime(); // 刷新一下開始空閑的起始時(shí)間
_connectionQue.push(p);
_connectionCnt++;
}
掃描整個(gè)隊(duì)列,釋放多余的連接(高并發(fā)過后,新建的連接超過最大超時(shí)時(shí)間時(shí))
while (_connectionCnt > _initSize)
{
Connection* p = _connectionQue.front();
if (p->getAliveTime() >= (_maxIdleTime * 1000))
{
_connectionQue.pop();
_connectionCnt--;
// 調(diào)用~Connection()釋放連接
delete p;
}
else
{
// 如果隊(duì)頭的連接沒有超過_maxIdleTime,其他連接肯定沒有
break;
}
}
4、多線程編程
為了將多線程編程的相關(guān)操作應(yīng)用到實(shí)際,也為了進(jìn)行壓力測(cè)試,用結(jié)果證明使用連接池之后對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)庫的訪問效率確實(shí)比不使用連接池的時(shí)候高很多,使用了多線程來進(jìn)行數(shù)據(jù)庫的訪問操作,并且觀察多線程下連接池對(duì)于性能的提升。
代碼如下:
{
thread t1([]() {
for (int i = 0; i < 250; ++i)
{
Connection conn;
char sql[1024] = { 0 };
sprintf(sql, "insert into user(name,age,sex) values('%s',%d,'%s')",
"zhang san", 20, "M");
conn.connect("127.0.0.1", 3306, "root", "991205", "chat");
conn.update(sql);
}
});
thread t2([]() {
for (int i = 0; i < 250; ++i)
{
Connection conn;
char sql[1024] = { 0 };
sprintf(sql, "insert into user(name,age,sex) values('%s',%d,'%s')",
"zhang san", 20, "M");
conn.connect("127.0.0.1", 3306, "root", "991205", "chat");
conn.update(sql);
}
});
thread t3([]() {
for (int i = 0; i < 250; ++i)
{
Connection conn;
char sql[1024] = { 0 };
sprintf(sql, "insert into user(name,age,sex) values('%s',%d,'%s')",
"zhang san", 20, "M");
conn.connect("127.0.0.1", 3306, "root", "991205", "chat");
conn.update(sql);
}
});
thread t4([]() {
for (int i = 0; i < 250; ++i)
{
Connection conn;
char sql[1024] = { 0 };
sprintf(sql, "insert into user(name,age,sex) values('%s',%d,'%s')",
"zhang san", 20, "male");
conn.connect("127.0.0.1", 3306, "root", "991205", "chat");
conn.update(sql);
}
});
t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join();
t4.join();
return 0;
}
五、線程互斥、線程同步通信(生產(chǎn)者-消費(fèi)者模型)、unique_lock
連接池中連接隊(duì)列的連接的生產(chǎn)和消費(fèi)需要保證其線程安全,于是我們需要引入互斥鎖mutex,線程同步通信確保執(zhí)行順序,以及唯一鎖。
代碼如下:
{
private:
// 設(shè)置條件變量,用于連接生產(chǎn)線程和連接消費(fèi)線程的通信
condition_variable cv;
// 維護(hù)連接隊(duì)列的線程安全互斥鎖
mutex _queueMutex;
};
for (;;)
{
unique_lock lock(_queueMutex);
while (!_connectionQue.empty())
{
// 隊(duì)列不為空,此處生產(chǎn)線程進(jìn)入等待狀態(tài)
cv.wait(lock);
}
// 連接數(shù)量沒有達(dá)到上限,繼續(xù)創(chuàng)建新的連接
if (_connectionCnt < _maxSize)
{
Connection* p = new Connection();
p->connect(_ip, _port, _username, _password, _dbname);
// 刷新一下開始空閑的起始時(shí)間
p->refreshAliveTime();
_connectionQue.push(p);
_connectionCnt++;
}
// 通知消費(fèi)者線程,可以消費(fèi)連接了
cv.notify_all();
}
thread produce(std::bind(&ConnectionPool::produceConnectionTask, this));
produce.detach();
// 啟動(dòng)一個(gè)新的定時(shí)線程,掃描超過maxIdleTime時(shí)間的空閑連接,進(jìn)行對(duì)于的連接回收
thread scanner(std::bind(&ConnectionPool::scannerConnectionTask, this));
scanner.detach();
六、CAS原子操作
對(duì)于連接池內(nèi)的連接數(shù)量,生產(chǎn)者和消費(fèi)者線程都會(huì)去改變其值,那么這個(gè)變量的修改就必須保證其原子性,于是使用C++11中提供的原子類:atomic_int
// 生產(chǎn)新連接時(shí):
_connectionCnt++;
// 當(dāng)新連接超過最大超時(shí)時(shí)間后被銷毀時(shí)
_connectionCnt--;
七、shared_ptr及l(fā)ambda表達(dá)式
對(duì)于使用完成的連接,不能直接銷毀該連接,而是需要將該連接歸還給連接池的隊(duì)列,供之后的其他消費(fèi)者使用,于是我們使用智能指針,自定義其析構(gòu)函數(shù),完成放回的操作:
[&](Connection* pcon) {
// 這里是在服務(wù)器應(yīng)用線程中調(diào)用的,所以一定要考慮隊(duì)列的線程安全操作
unique_lock lock(_queueMutex);
pcon->refreshAliveTime();
_connectionQue.push(pcon);
});
八、壓力測(cè)試
測(cè)試添加連接池后效率是否提升:
未使用連接池
1.單線程
{
clock_t begin = clock();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; ++i)
{
Connection conn;
char sql[1024] = { 0 };
sprintf(sql, "insert into user(name,age,sex) values('%s',%d,'%s')",
"zhang san", 20, "M");
conn.connect("127.0.0.1", 3306, "root", "123456", "chat");
conn.update(sql);
}
clock_t end = clock();
cout << (end - begin) << "ms" << endl;
return 0;
}
運(yùn)行時(shí)間如下:

添加圖片注釋,不超過 140 字(可選)
2.多線程
{
Connection conn;
conn.connect("127.0.0.1", 3306, "root", "991205", "chat");
clock_t begin = clock();
thread t1([]() {
for (int i = 0; i < 250; ++i)
{
Connection conn;
char sql[1024] = { 0 };
sprintf(sql, "insert into user(name,age,sex) values('%s',%d,'%s')",
"zhang san", 20, "M");
conn.connect("127.0.0.1", 3306, "root", "123456", "chat");
conn.update(sql);
}
});
thread t2([]() {
for (int i = 0; i < 250; ++i)
{
Connection conn;
char sql[1024] = { 0 };
sprintf(sql, "insert into user(name,age,sex) values('%s',%d,'%s')",
"zhang san", 20, "M");
conn.connect("127.0.0.1", 3306, "root", "123456", "chat");
conn.update(sql);
}
});
thread t3([]() {
for (int i = 0; i < 250; ++i)
{
Connection conn;
char sql[1024] = { 0 };
sprintf(sql, "insert into user(name,age,sex) values('%s',%d,'%s')",
"zhang san", 20, "M");
conn.connect("127.0.0.1", 3306, "root", "123456", "chat");
conn.update(sql);
}
});
thread t4([]() {
for (int i = 0; i < 250; ++i)
{
Connection conn;
char sql[1024] = { 0 };
sprintf(sql, "insert into user(name,age,sex) values('%s',%d,'%s')",
"zhang san", 20, "M");
conn.connect("127.0.0.1", 3306, "root", "123456", "chat");
conn.update(sql);
}
});
t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join();
t4.join();
clock_t end = clock();
cout << (end - begin) << "ms" << endl;
return 0;
}
運(yùn)行時(shí)間如下:

使用連接池
1.單線程
{
clock_t begin = clock();
ConnectionPool* cp = ConnectionPool::getConnectionPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; ++i)
{
shared_ptr sp = cp->getConnection();
char sql[1024] = { 0 };
sprintf(sql, "insert into user(name,age,sex) values('%s',%d,'%s')",
"zhang san", 20, "M");
sp->update(sql);
}
clock_t end = clock();
cout << (end - begin) << "ms" << endl;
return 0;
}
運(yùn)行時(shí)間如下:

2.多線程
{
clock_t begin = clock();
thread t1([]() {
ConnectionPool* cp = ConnectionPool::getConnectionPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 250; ++i)
{
char sql[1024] = { 0 };
sprintf(sql, "insert into user(name,age,sex) values('%s',%d,'%s')",
"zhang san", 20, "M");
shared_ptr sp = cp->getConnection();
sp->update(sql);
}
});
thread t2([]() {
ConnectionPool* cp = ConnectionPool::getConnectionPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 250; ++i)
{
char sql[1024] = { 0 };
sprintf(sql, "insert into user(name,age,sex) values('%s',%d,'%s')",
"zhang san", 20, "M");
shared_ptr sp = cp->getConnection();
sp->update(sql);
}
});
thread t3([]() {
ConnectionPool* cp = ConnectionPool::getConnectionPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 250; ++i)
{
char sql[1024] = { 0 };
sprintf(sql, "insert into user(name,age,sex) values('%s',%d,'%s')",
"zhang san", 20, "M");
shared_ptr sp = cp->getConnection();
sp->update(sql);
}
});
thread t4([]() {
ConnectionPool* cp = ConnectionPool::getConnectionPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 250; ++i)
{
char sql[1024] = { 0 };
sprintf(sql, "insert into user(name,age,sex) values('%s',%d,'%s')",
"zhang san", 20, "M");
shared_ptr sp = cp->getConnection();
sp->update(sql);
}
});
t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join();
t4.join();
clock_t end = clock();
cout << (end - begin) << "ms" << endl;
return 0;
}

比較
在使用了連接池之后,性能確實(shí)提升了不少
- 數(shù)據(jù)量1000,單線程從1417ms變成697ms
- 數(shù)據(jù)量1000,多線程從420ms變成了307ms
-
磁盤
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1文章
367瀏覽量
25180 -
TCP
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
8文章
1351瀏覽量
78995 -
數(shù)據(jù)庫
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
7文章
3767瀏覽量
64279 -
ip地址
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
295瀏覽量
17010 -
MySQL
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1文章
802瀏覽量
26452
發(fā)布評(píng)論請(qǐng)先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
labview遠(yuǎn)程訪問服務(wù)器的mysql數(shù)據(jù)庫
labview有調(diào)用mysql數(shù)據(jù)庫問題????
ESP8266如何連接mysql數(shù)據(jù)庫
mysql數(shù)據(jù)庫同步原理
數(shù)據(jù)庫教程之PHP訪問MySQL數(shù)據(jù)庫的理論知識(shí)詳細(xì)說明
Serverless 解惑—函數(shù)計(jì)算如何訪問 MySQL 數(shù)據(jù)庫
MySQL數(shù)據(jù)庫如何安裝和使用說明
MySQL監(jiān)控-Datadog數(shù)據(jù)庫監(jiān)控調(diào)研
華為云數(shù)據(jù)庫-RDS for MySQL數(shù)據(jù)庫
有哪些不同的MySQL數(shù)據(jù)庫引擎?
MySQL數(shù)據(jù)庫管理與應(yīng)用
mysql是一個(gè)什么類型的數(shù)據(jù)庫
MySQL數(shù)據(jù)庫基礎(chǔ)知識(shí)
mysql數(shù)據(jù)庫基礎(chǔ)命令
數(shù)據(jù)庫數(shù)據(jù)恢復(fù)—未開啟binlog的Mysql數(shù)據(jù)庫數(shù)據(jù)恢復(fù)案例




 如何提高M(jìn)ysql數(shù)據(jù)庫的訪問瓶頸
如何提高M(jìn)ysql數(shù)據(jù)庫的訪問瓶頸










評(píng)論