概述
本文將介紹如何使用 LIS2MDL 傳感器來(lái)讀取數(shù)據(jù)。主要步驟包括初始化傳感器接口、驗(yàn)證設(shè)備ID、配置傳感器的數(shù)據(jù)輸出率和濾波器,以及通過(guò)輪詢方式持續(xù)讀取磁力數(shù)據(jù)和溫度數(shù)據(jù)。讀取到的數(shù)據(jù)會(huì)被轉(zhuǎn)換為適當(dāng)?shù)膯挝徊⑼ㄟ^(guò)串行通信輸出。 這個(gè)傳感器常用于多種電子設(shè)備中,以提供精確的磁場(chǎng)強(qiáng)度數(shù)據(jù),從而用于指南針應(yīng)用、位置追蹤或者動(dòng)作檢測(cè)等功能。
最近在弄ST和瑞薩RA的課程,需要樣片的可以加群申請(qǐng):615061293 。
視頻教學(xué)
[https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV16K4y1B7MQ/]
樣品申請(qǐng)
[https://www.wjx.top/vm/OhcKxJk.aspx#]
源碼下載
[https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_24312945/88722848]
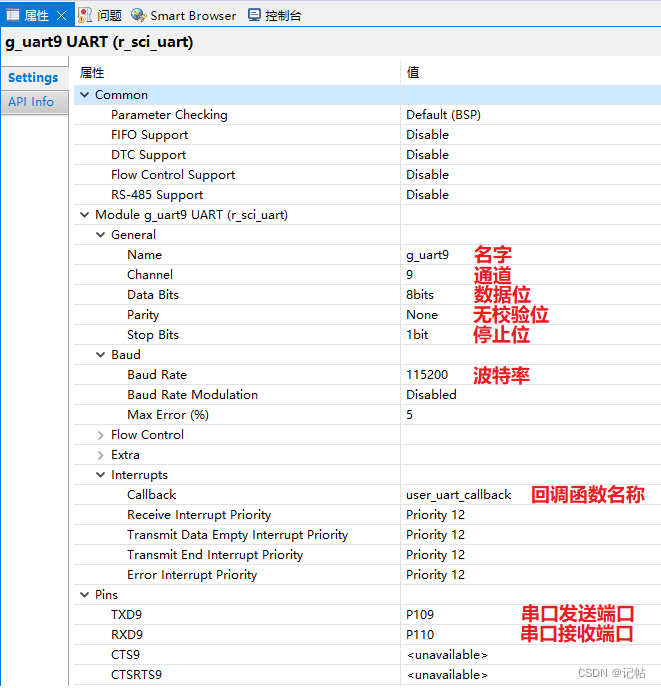
速率
該模塊支持的速度為普通模式(100k)、快速模式(400k)、快速模式+(1M)、高速模式(3.4M)。

新建工程
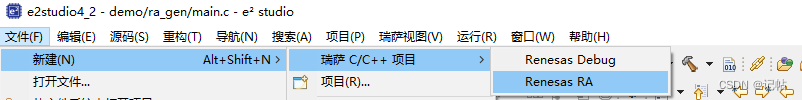
工程模板
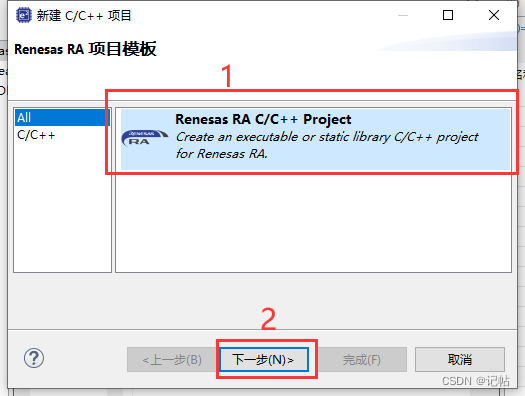
保存工程路徑
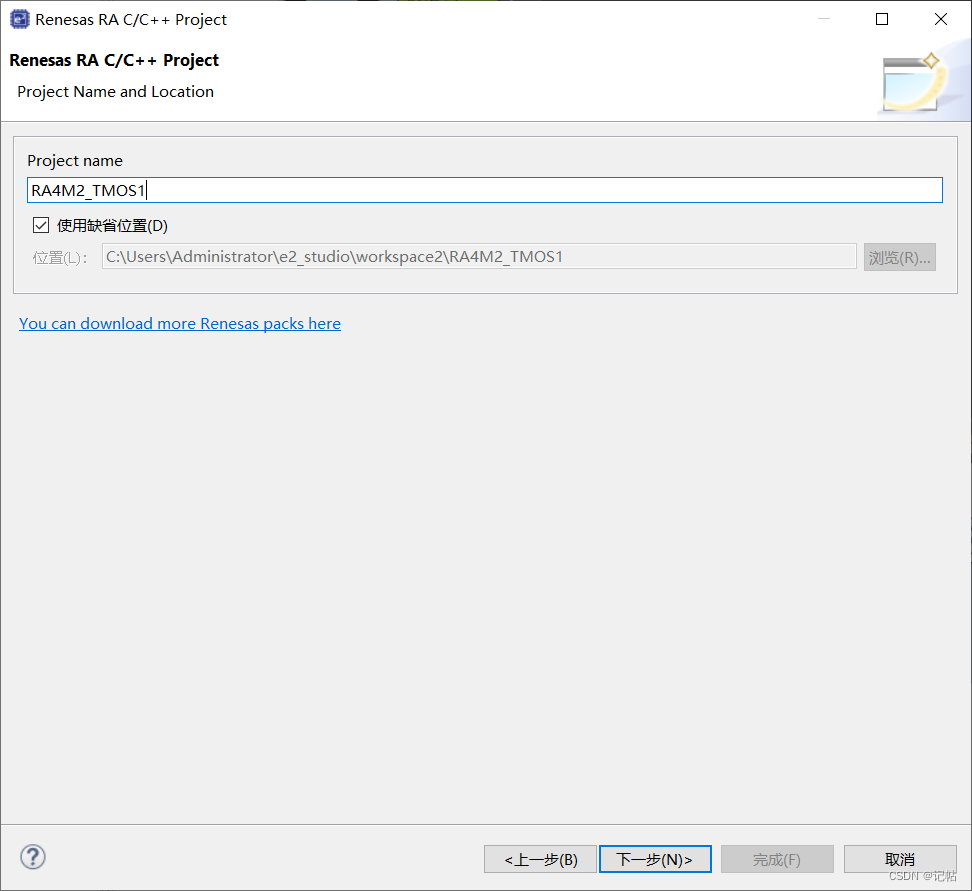
芯片配置
本文中使用R7FA4M2AD3CFL來(lái)進(jìn)行演示。 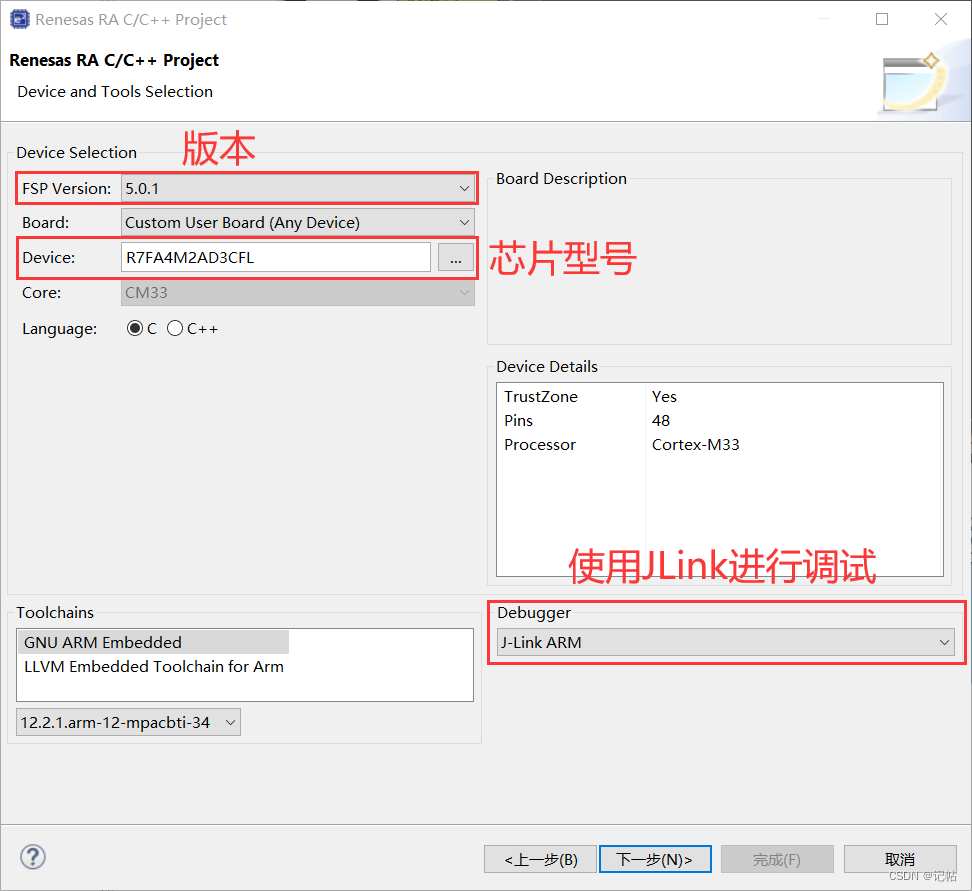
工程模板選擇
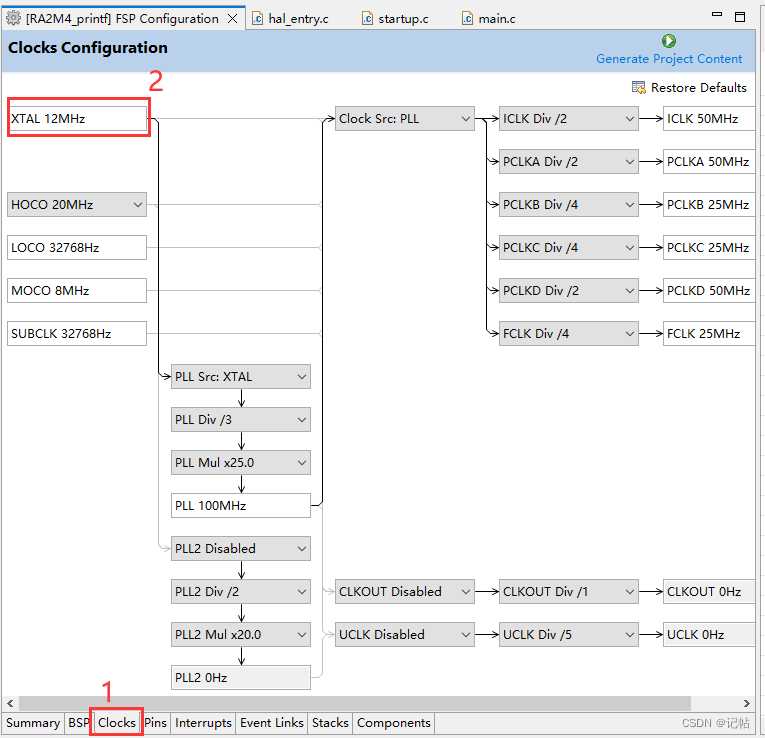
時(shí)鐘設(shè)置
開(kāi)發(fā)板上的外部高速晶振為12M.
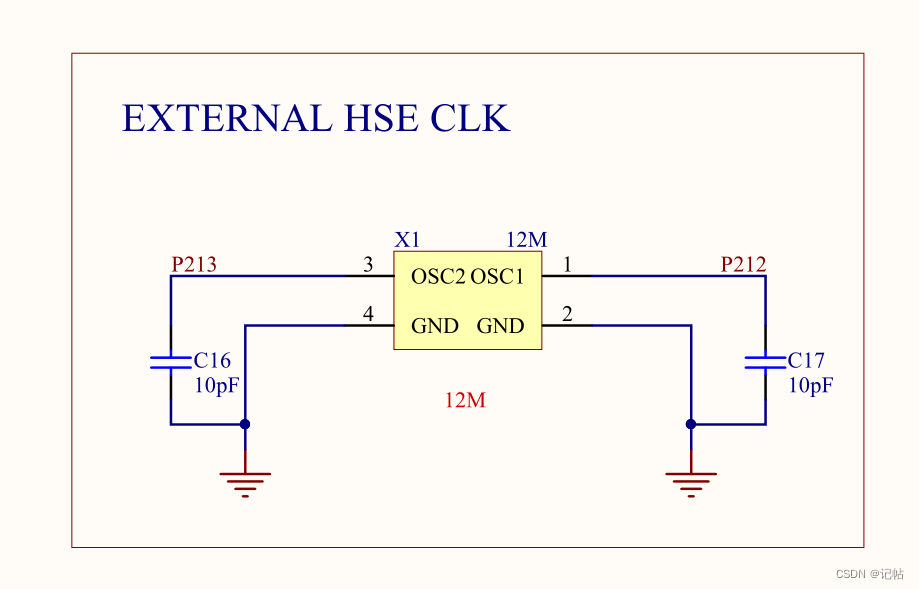 需要修改XTAL為12M。
需要修改XTAL為12M。
UART配置
 點(diǎn)擊Stacks->New Stack->Driver->Connectivity -> UART Driver on r_sci_uart。
點(diǎn)擊Stacks->New Stack->Driver->Connectivity -> UART Driver on r_sci_uart。 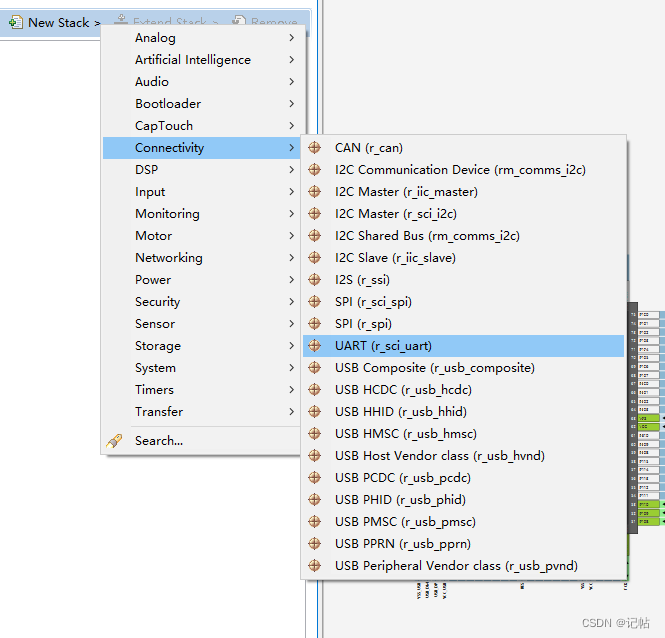
UART屬性配置
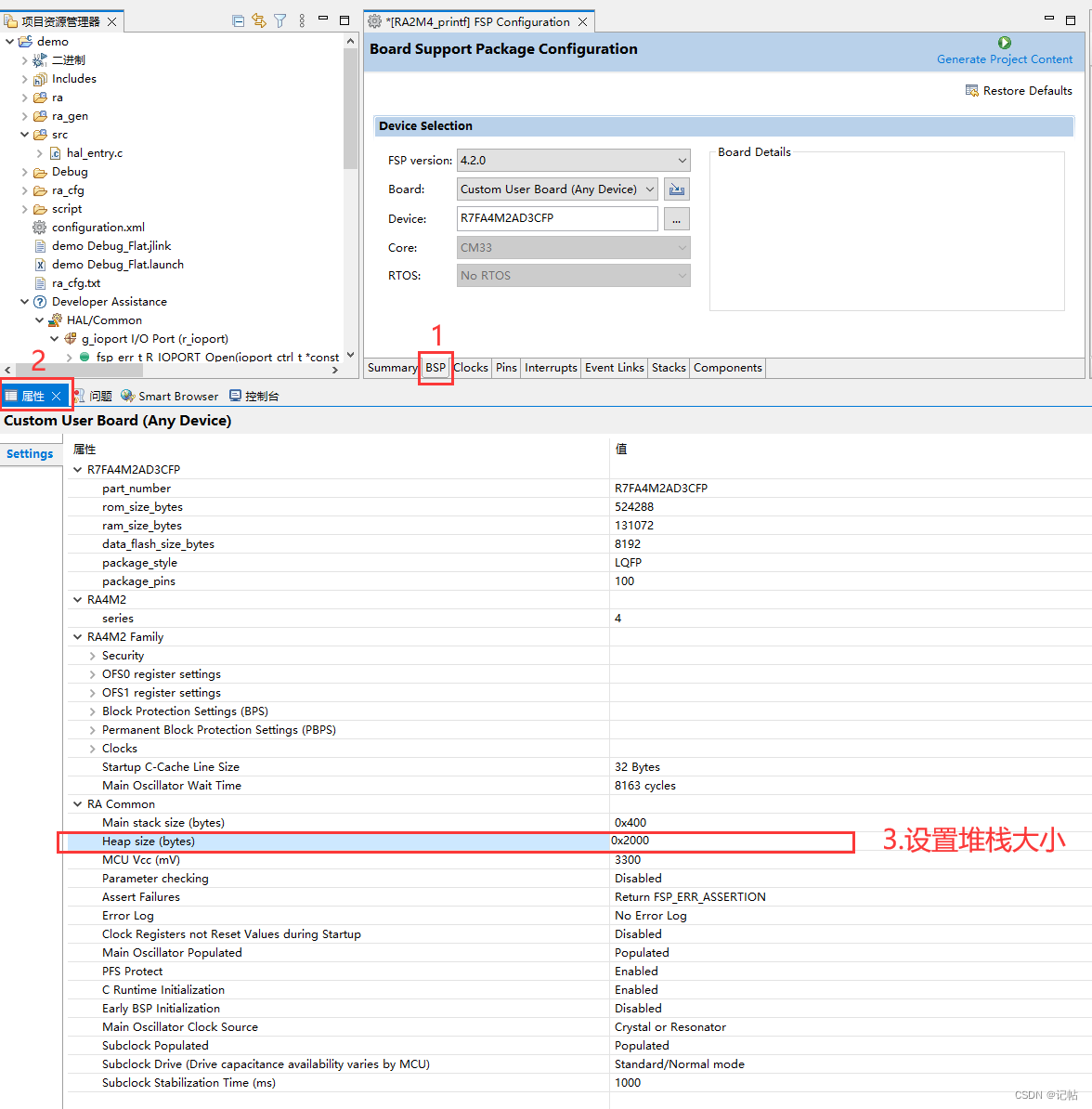
設(shè)置e2studio堆棧
printf函數(shù)通常需要設(shè)置堆棧大小。這是因?yàn)閜rintf函數(shù)在運(yùn)行時(shí)需要使用棧空間來(lái)存儲(chǔ)臨時(shí)變量和函數(shù)調(diào)用信息。如果堆棧大小不足,可能會(huì)導(dǎo)致程序崩潰或不可預(yù)期的行為。
printf函數(shù)使用了可變參數(shù)列表,它會(huì)在調(diào)用時(shí)使用棧來(lái)存儲(chǔ)參數(shù),在函數(shù)調(diào)用結(jié)束時(shí)再清除參數(shù),這需要足夠的棧空間。另外printf也會(huì)使用一些臨時(shí)變量,如果棧空間不足,會(huì)導(dǎo)致程序崩潰。
因此,為了避免這類(lèi)問(wèn)題,應(yīng)該根據(jù)程序的需求來(lái)合理設(shè)置堆棧大小。
e2studio的重定向printf設(shè)置
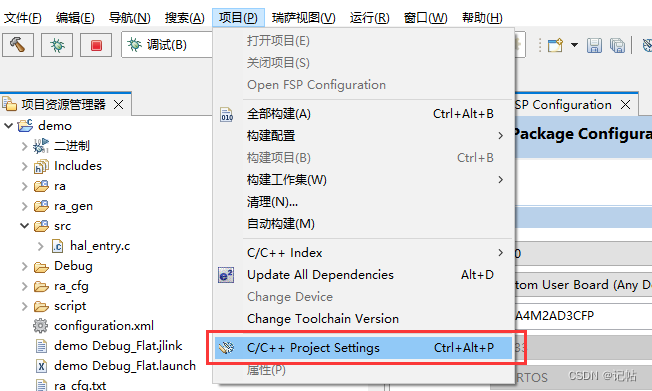
在嵌入式系統(tǒng)的開(kāi)發(fā)中,尤其是在使用GNU編譯器集合(GCC)時(shí),–specs 參數(shù)用于指定鏈接時(shí)使用的系統(tǒng)規(guī)格(specs)文件。這些規(guī)格文件控制了編譯器和鏈接器的行為,尤其是關(guān)于系統(tǒng)庫(kù)和啟動(dòng)代碼的鏈接。–specs=rdimon.specs 和 --specs=nosys.specs 是兩種常見(jiàn)的規(guī)格文件,它們用于不同的場(chǎng)景。
–specs=rdimon.specs
用途: 這個(gè)選項(xiàng)用于鏈接“Redlib”庫(kù),這是為裸機(jī)(bare-metal)和半主機(jī)(semihosting)環(huán)境設(shè)計(jì)的C庫(kù)的一個(gè)變體。半主機(jī)環(huán)境是一種特殊的運(yùn)行模式,允許嵌入式程序通過(guò)宿主機(jī)(如開(kāi)發(fā)PC)的調(diào)試器進(jìn)行輸入輸出操作。
應(yīng)用場(chǎng)景: 當(dāng)你需要在沒(méi)有完整操作系統(tǒng)的環(huán)境中運(yùn)行程序,但同時(shí)需要使用調(diào)試器來(lái)處理輸入輸出(例如打印到宿主機(jī)的終端),這個(gè)選項(xiàng)非常有用。
特點(diǎn): 它提供了一些基本的系統(tǒng)調(diào)用,通過(guò)調(diào)試接口與宿主機(jī)通信。
–specs=nosys.specs
用途: 這個(gè)選項(xiàng)鏈接了一個(gè)非常基本的系統(tǒng)庫(kù),這個(gè)庫(kù)不提供任何系統(tǒng)服務(wù)的實(shí)現(xiàn)。
應(yīng)用場(chǎng)景: 適用于完全的裸機(jī)程序,其中程序不執(zhí)行任何操作系統(tǒng)調(diào)用,比如不進(jìn)行文件操作或者系統(tǒng)級(jí)輸入輸出。
特點(diǎn): 這是一個(gè)更“裸”的環(huán)境,沒(méi)有任何操作系統(tǒng)支持。使用這個(gè)規(guī)格文件,程序不期望有操作系統(tǒng)層面的任何支持。
如果你的程序需要與宿主機(jī)進(jìn)行交互(如在開(kāi)發(fā)期間的調(diào)試),并且通過(guò)調(diào)試器進(jìn)行基本的輸入輸出操作,則使用 --specs=rdimon.specs。
如果你的程序是完全獨(dú)立的,不需要任何形式的操作系統(tǒng)服務(wù),包括不進(jìn)行任何系統(tǒng)級(jí)的輸入輸出,則使用 --specs=nosys.specs。
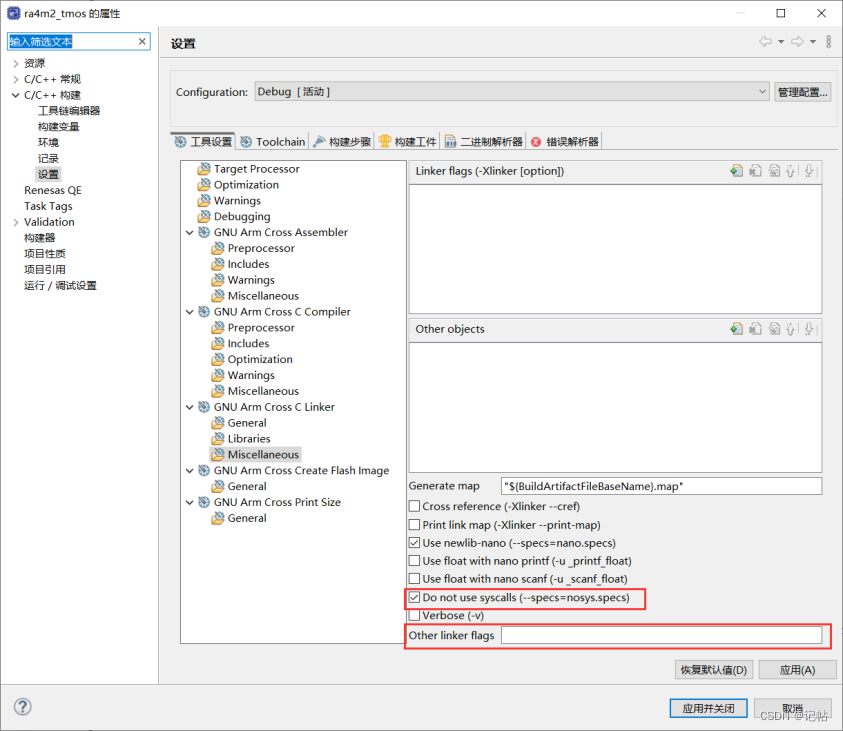
R_SCI_UART_Open()函數(shù)原型
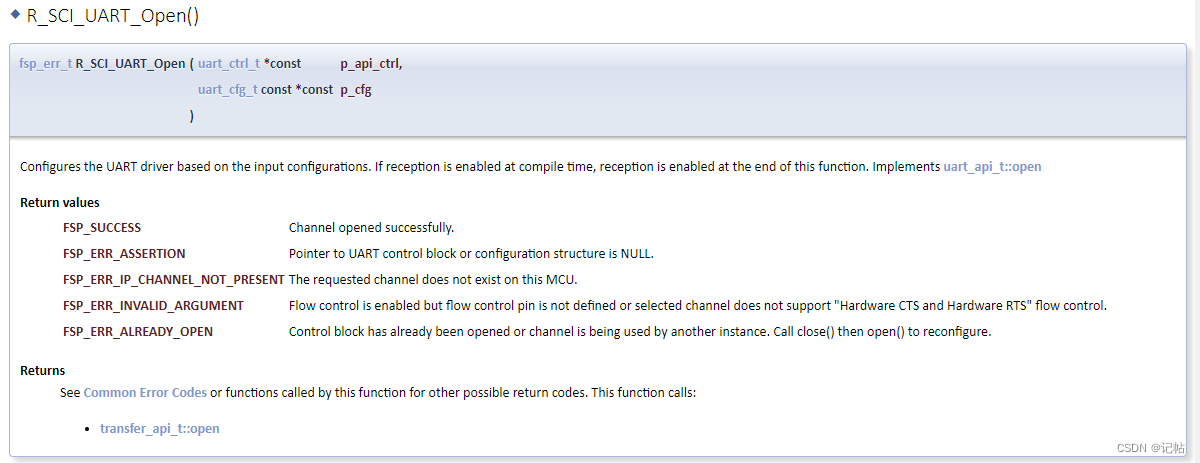
故可以用 R_SCI_UART_Open()函數(shù)進(jìn)行配置,開(kāi)啟和初始化UART。
/* Open the transfer instance with initial configuration. */
err = R_SCI_UART_Open(&g_uart9_ctrl, &g_uart9_cfg);
assert(FSP_SUCCESS == err);
回調(diào)函數(shù)user_uart_callback ()
當(dāng)數(shù)據(jù)發(fā)送的時(shí)候,可以查看UART_EVENT_TX_COMPLETE來(lái)判斷是否發(fā)送完畢。
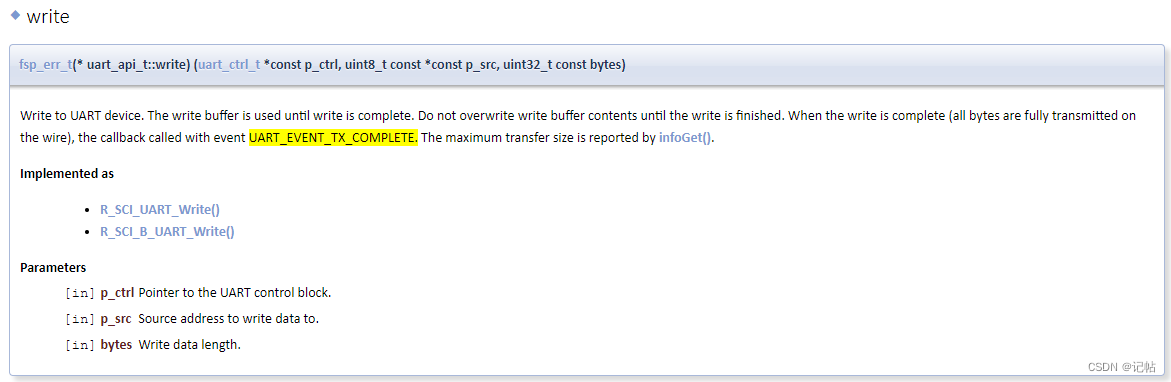
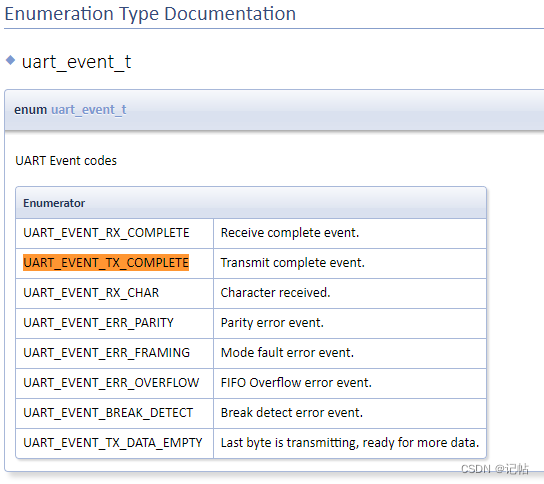
可以檢查檢查 "p_args" 結(jié)構(gòu)體中的 "event" 字段的值是否等于 "UART_EVENT_TX_COMPLETE"。如果條件為真,那么 if 語(yǔ)句后面的代碼塊將會(huì)執(zhí)行。
fsp_err_t err = FSP_SUCCESS;
volatile bool uart_send_complete_flag = false;
void user_uart_callback (uart_callback_args_t * p_args)
{
if(p_args- >event == UART_EVENT_TX_COMPLETE)
{
uart_send_complete_flag = true;
}
}
printf輸出重定向到串口
打印最常用的方法是printf,所以要解決的問(wèn)題是將printf的輸出重定向到串口,然后通過(guò)串口將數(shù)據(jù)發(fā)送出去。 注意一定要加上頭文件#include
#ifdef __GNUC__ //串口重定向
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int __io_putchar(int ch)
#else
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int fputc(int ch, FILE *f)
#endif
PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE
{
err = R_SCI_UART_Write(&g_uart9_ctrl, (uint8_t *)&ch, 1);
if(FSP_SUCCESS != err) __BKPT();
while(uart_send_complete_flag == false){}
uart_send_complete_flag = false;
return ch;
}
int _write(int fd,char *pBuffer,int size)
{
for(int i=0;i< size;i++)
{
__io_putchar(*pBuffer++);
}
return size;
}
通信模式
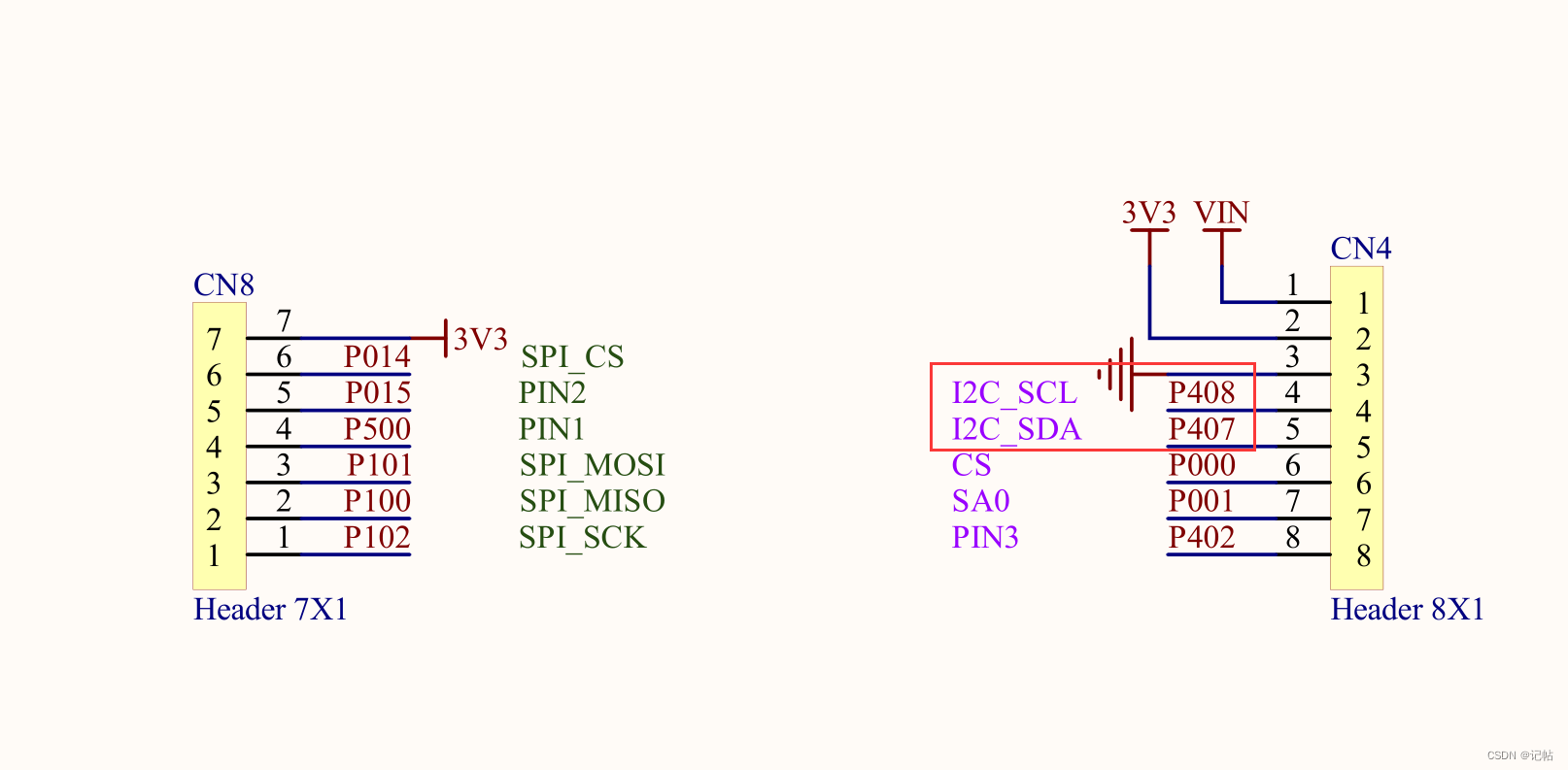
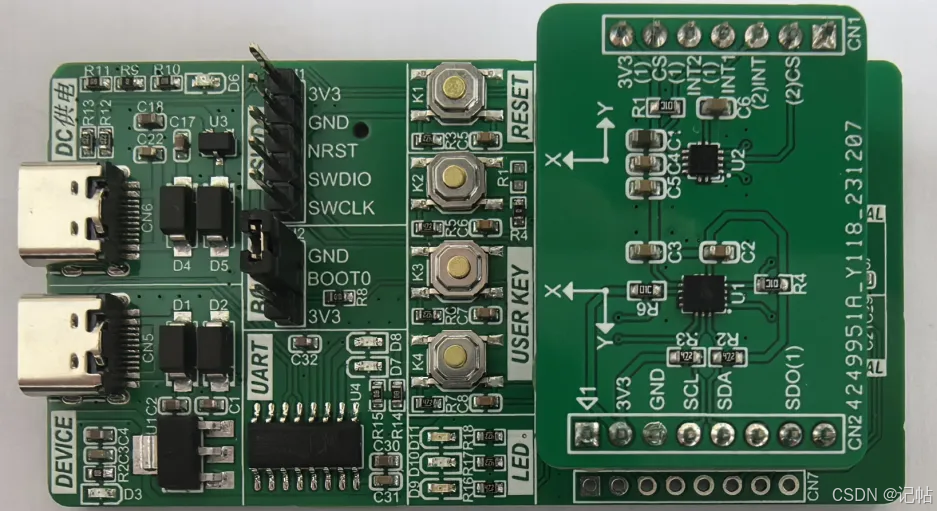
對(duì)于LIS2MDL,可以使用SPI或者IIC進(jìn)行通訊。 最小系統(tǒng)圖如下所示。
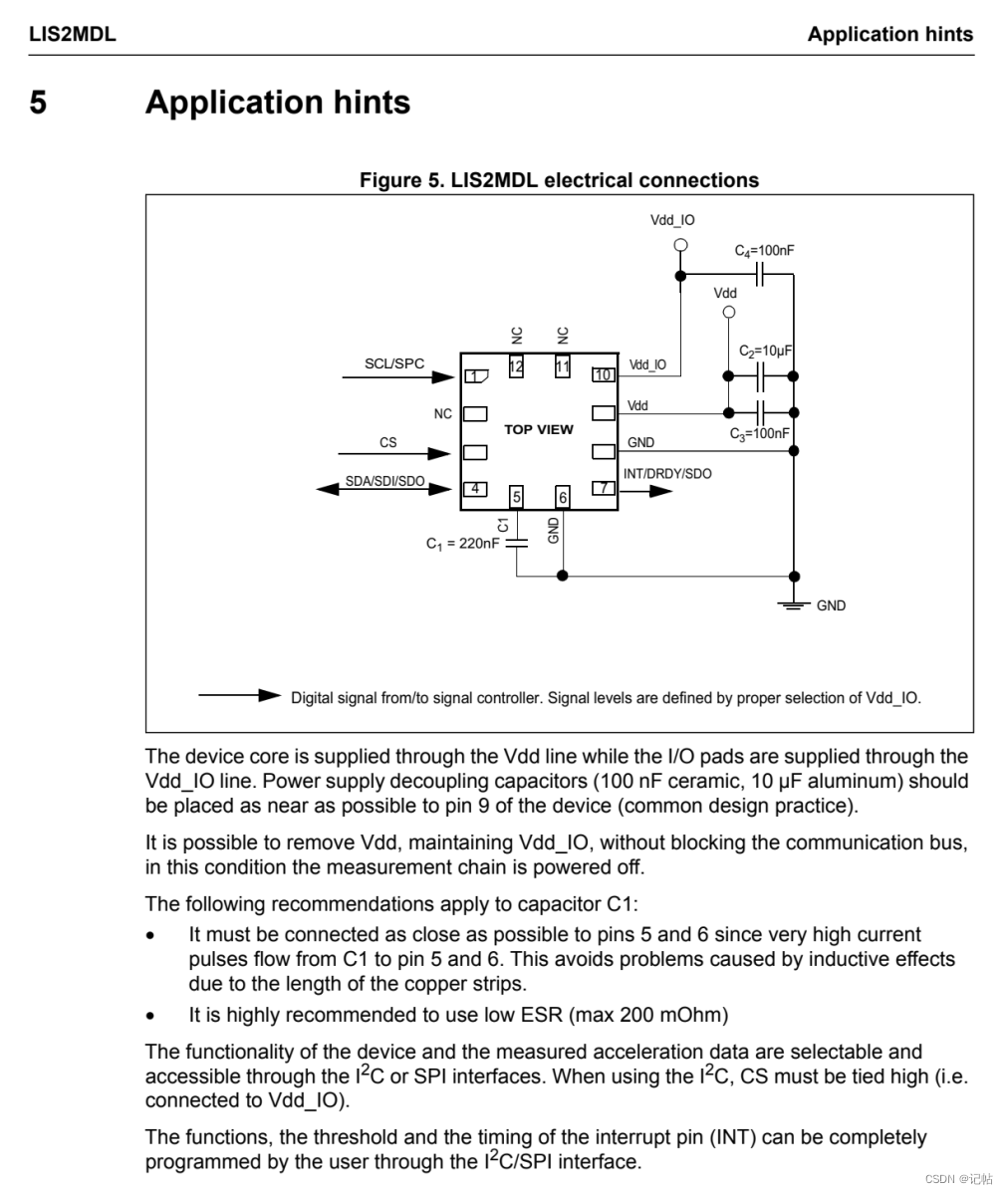
在CS管腳為1的時(shí)候,為IIC模式
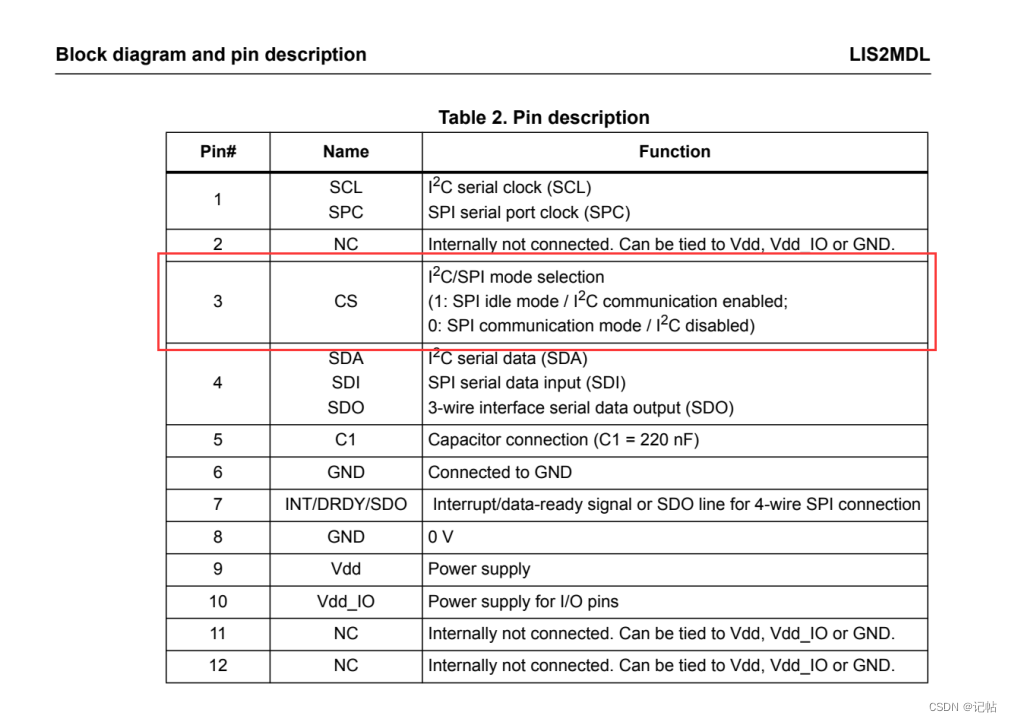
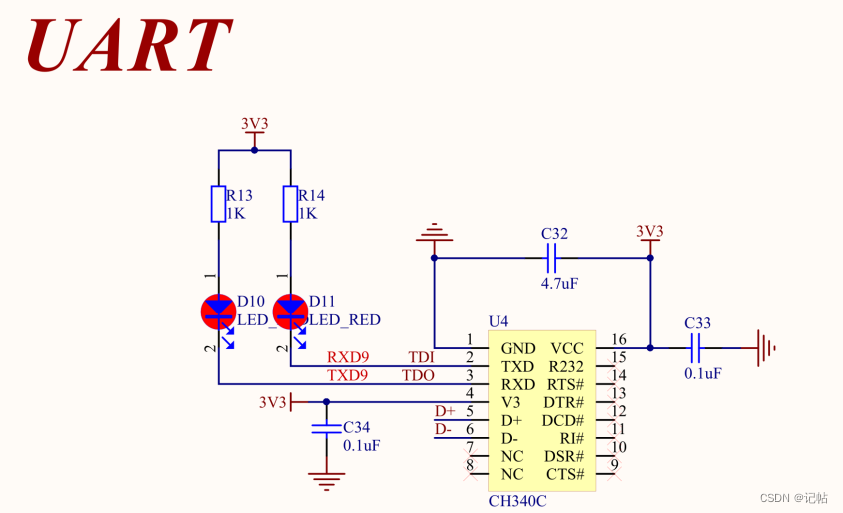
本文使用的板子原理圖如下所示。
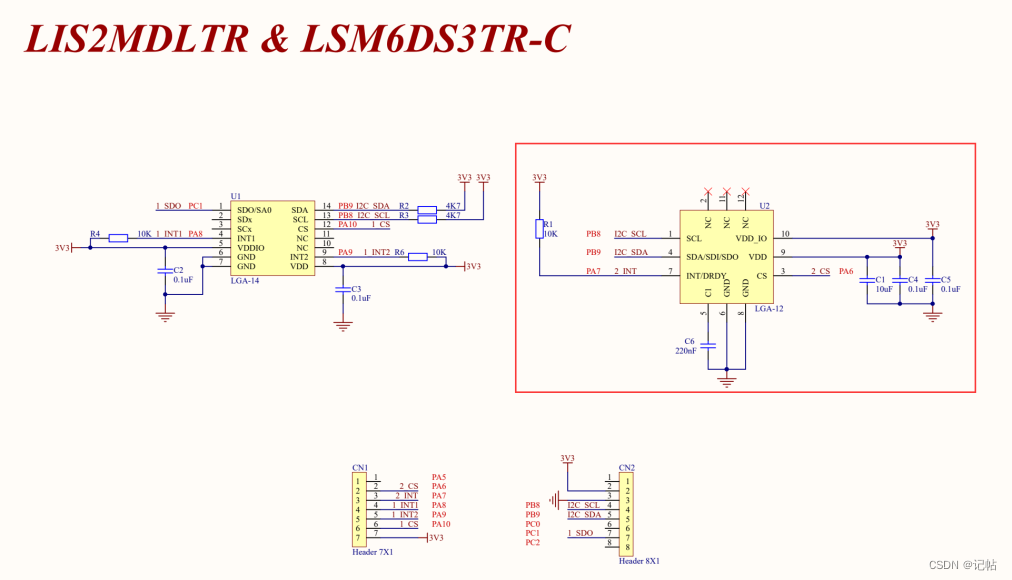
CS對(duì)應(yīng)到RA4M2板子上的端口為P014。

配置為輸出管腳。

R_IOPORT_PinWrite(&g_ioport_ctrl, BSP_IO_PORT_00_PIN_14, BSP_IO_LEVEL_HIGH);
IIC屬性配置
查看手冊(cè),可以得知LIS2MDL的IIC地址為“0011110” ,即0x1E

IIC配置
配置RA4M2的I2C接口,使其作為I2C master進(jìn)行通信。 查看開(kāi)發(fā)板原理圖,對(duì)應(yīng)的IIC為P407和P408。
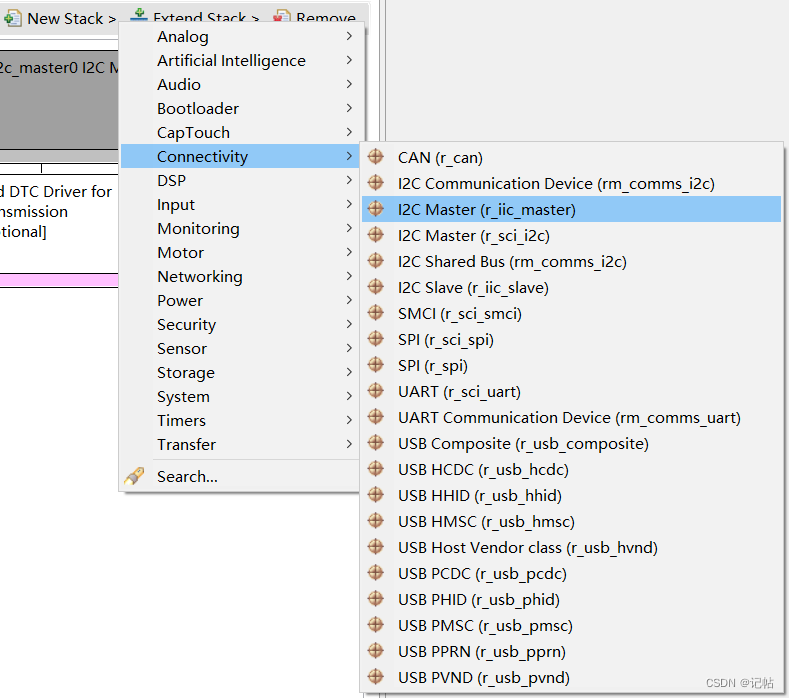
點(diǎn)擊Stacks->New Stack->Connectivity -> I2C Master(r_iic_master)。
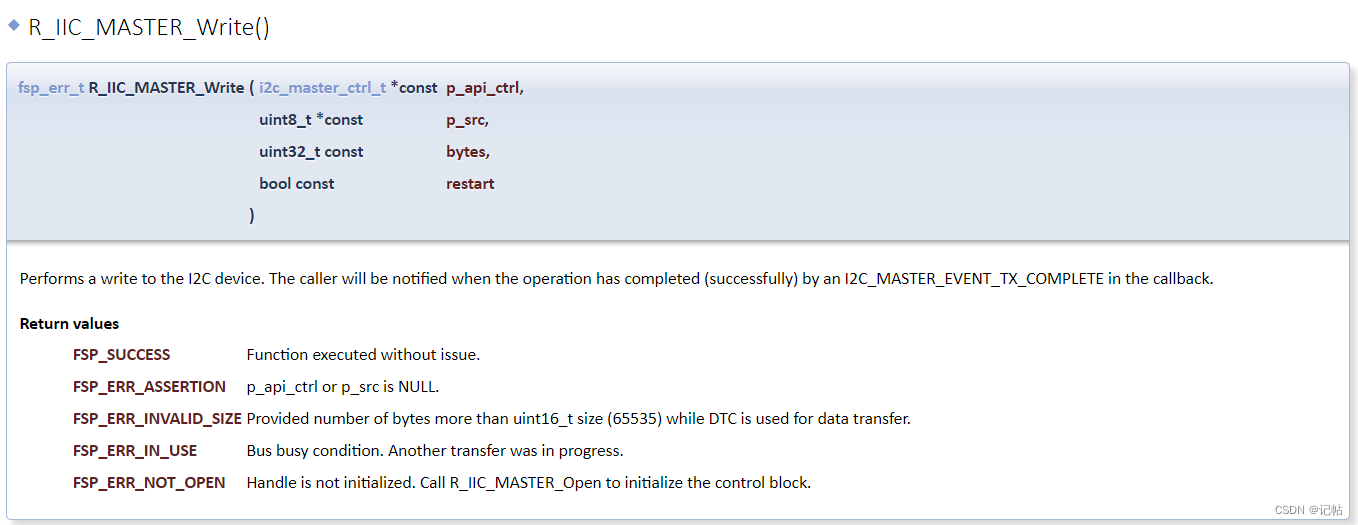
設(shè)置IIC的配置,需要注意從機(jī)的地址。

R_IIC_MASTER_Open()函數(shù)原型
R_IIC_MASTER_Open()函數(shù)為執(zhí)行IIC初始化,開(kāi)啟配置如下所示。
/* Initialize the I2C module */
err = R_IIC_MASTER_Open(&g_i2c_master0_ctrl, &g_i2c_master0_cfg);
/* Handle any errors. This function should be defined by the user. */
assert(FSP_SUCCESS == err);
R_IIC_MASTER_Write()函數(shù)原型
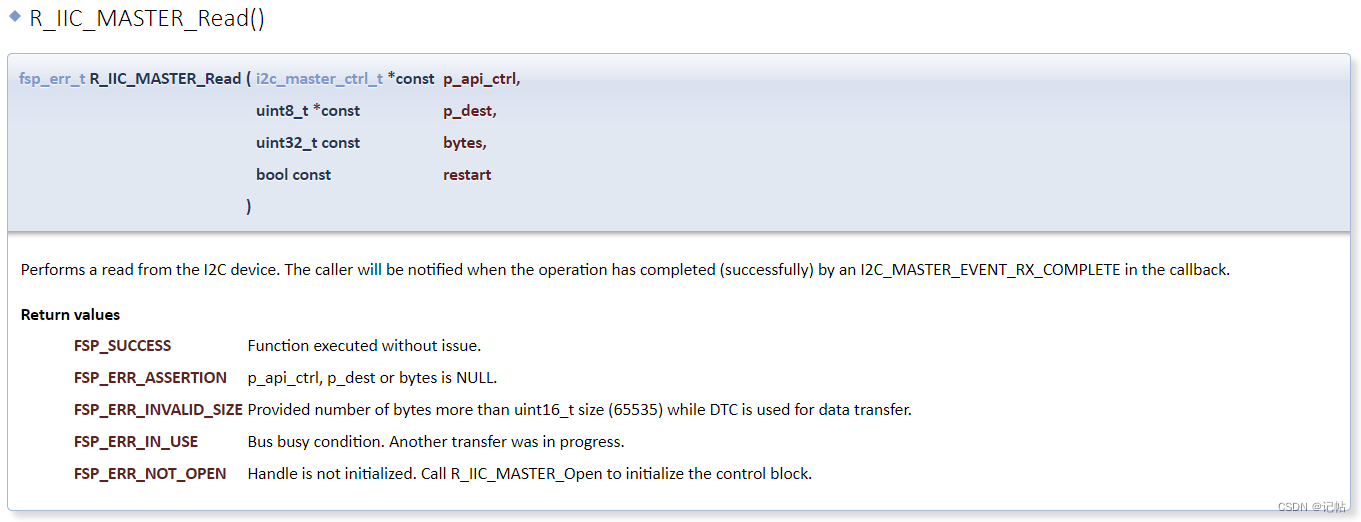
R_IIC_MASTER_Write()函數(shù)是向IIC設(shè)備中寫(xiě)入數(shù)據(jù),寫(xiě)入格式如下所示。
err = R_IIC_MASTER_Write(&g_i2c_master0_ctrl, ®, 1, true);
assert(FSP_SUCCESS == err);
R_IIC_MASTER_Read()函數(shù)原型
R_SCI_I2C_Read()函數(shù)是向IIC設(shè)備中讀取數(shù)據(jù),讀取格式如下所示。
/* Read data from I2C slave */
err = R_IIC_MASTER_Read(&g_i2c_master0_ctrl, bufp, len, false);
assert(FSP_SUCCESS == err);
sci_i2c_master_callback()回調(diào)函數(shù)
對(duì)于數(shù)據(jù)是否發(fā)送完畢,可以查看是否獲取到I2C_MASTER_EVENT_TX_COMPLETE字段。
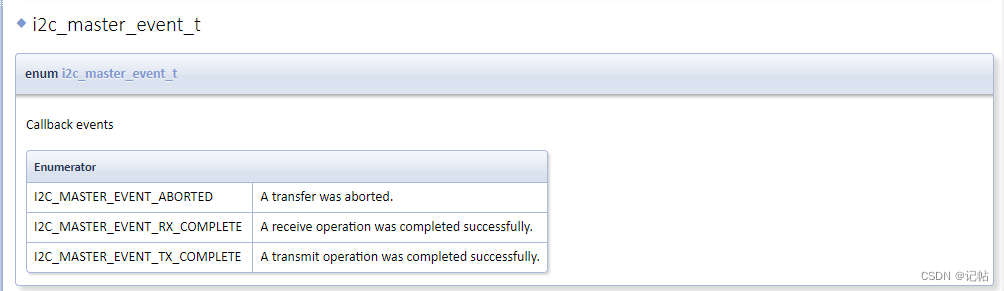
/* Callback function */
i2c_master_event_t i2c_event = I2C_MASTER_EVENT_ABORTED;
uint32_t timeout_ms = 100000;
void sci_i2c_master_callback(i2c_master_callback_args_t *p_args)
{
i2c_event = I2C_MASTER_EVENT_ABORTED;
if (NULL != p_args)
{
/* capture callback event for validating the i2c transfer event*/
i2c_event = p_args- >event;
}
}
參考程序
[https://github.com/STMicroelectronics/lis2mdl-pid]
初始換管腳
使能CS為高電平,配置為IIC模式。
R_IOPORT_PinWrite(&g_ioport_ctrl, BSP_IO_PORT_00_PIN_14, BSP_IO_LEVEL_HIGH);
/* Initialize the I2C module */
err = R_IIC_MASTER_Open(&g_i2c_master0_ctrl, &g_i2c_master0_cfg);
/* Handle any errors. This function should be defined by the user. */
assert(FSP_SUCCESS == err);
/* Initialize mems driver interface */
stmdev_ctx_t dev_ctx;
dev_ctx.write_reg = platform_write;
dev_ctx.read_reg = platform_read;
dev_ctx.handle = &SENSOR_BUS;
/* Wait sensor boot time */
platform_delay(BOOT_TIME);
獲取ID
可以向WHO_AM_I (4Fh)獲取固定值,判斷是否為0x40
 is2mdl_device_id_get為獲取函數(shù)。
is2mdl_device_id_get為獲取函數(shù)。
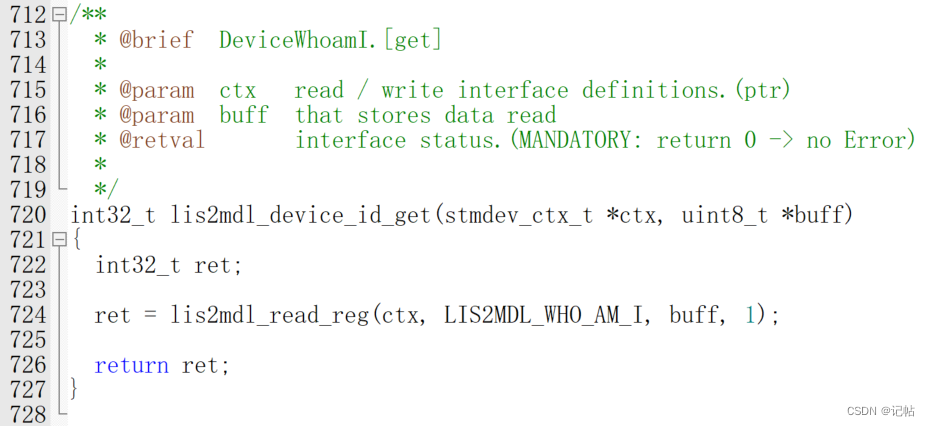
對(duì)應(yīng)的獲取ID驅(qū)動(dòng)程序,如下所示。
/* Wait sensor boot time */
platform_delay(BOOT_TIME);
/* Check device ID */
lis2mdl_device_id_get(&dev_ctx, &whoamI);
printf("LIS2MDL_ID=0x%x,whoamI=0x%xn",LIS2MDL_ID,whoamI);
if (whoamI != LIS2MDL_ID)
while (1) {
/* manage here device not found */
}
復(fù)位操作
可以向CFG_REG_A (60h)的SOFT_RST寄存器寫(xiě)入1進(jìn)行復(fù)位。

lis2mdl_reset_set為重置函數(shù)。
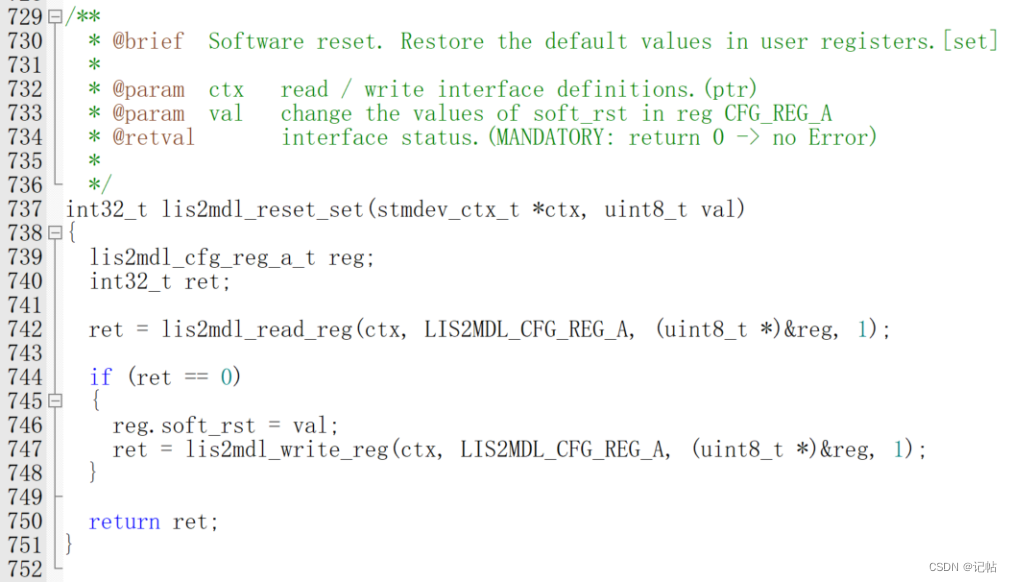
對(duì)應(yīng)的驅(qū)動(dòng)程序,如下所示。
/* Restore default configuration */
lis2mdl_reset_set(&dev_ctx, PROPERTY_ENABLE);
do {
lis2mdl_reset_get(&dev_ctx, &rst);
} while (rst);
BDU設(shè)置
在很多傳感器中,數(shù)據(jù)通常被存儲(chǔ)在輸出寄存器中,這些寄存器分為兩部分:MSB和LSB。這兩部分共同表示一個(gè)完整的數(shù)據(jù)值。例如,在一個(gè)加速度計(jì)中,MSB和LSB可能共同表示一個(gè)加速度的測(cè)量值。
連續(xù)更新模式(BDU = ‘0’):在默認(rèn)模式下,輸出寄存器的值會(huì)持續(xù)不斷地被更新。這意味著在你讀取MSB和LSB的時(shí)候,寄存器中的數(shù)據(jù)可能會(huì)因?yàn)樾碌臏y(cè)量數(shù)據(jù)而更新。這可能導(dǎo)致一個(gè)問(wèn)題:當(dāng)你讀取MSB時(shí),如果寄存器更新了,接下來(lái)讀取的LSB可能就是新的測(cè)量值的一部分,而不是與MSB相對(duì)應(yīng)的值。這樣,你得到的就是一個(gè)“拼湊”的數(shù)據(jù),它可能無(wú)法準(zhǔn)確代表任何實(shí)際的測(cè)量時(shí)刻。
塊數(shù)據(jù)更新(BDU)模式(BDU = ‘1’):當(dāng)激活BDU功能時(shí),輸出寄存器中的內(nèi)容不會(huì)在讀取MSB和LSB之間更新。這就意味著一旦開(kāi)始讀取數(shù)據(jù)(無(wú)論是先讀MSB還是LSB),寄存器中的那一組數(shù)據(jù)就被“鎖定”,直到兩部分都被讀取完畢。這樣可以確保你讀取的MSB和LSB是同一測(cè)量時(shí)刻的數(shù)據(jù),避免了讀取到代表不同采樣時(shí)刻的數(shù)據(jù)。
簡(jiǎn)而言之,BDU位的作用是確保在讀取數(shù)據(jù)時(shí),輸出寄存器的內(nèi)容保持穩(wěn)定,從而避免讀取到拼湊或錯(cuò)誤的數(shù)據(jù)。這對(duì)于需要高精度和穩(wěn)定性的應(yīng)用尤為重要。
可以向CTRL3 (12h)的BDU寄存器寫(xiě)入1進(jìn)行開(kāi)啟。
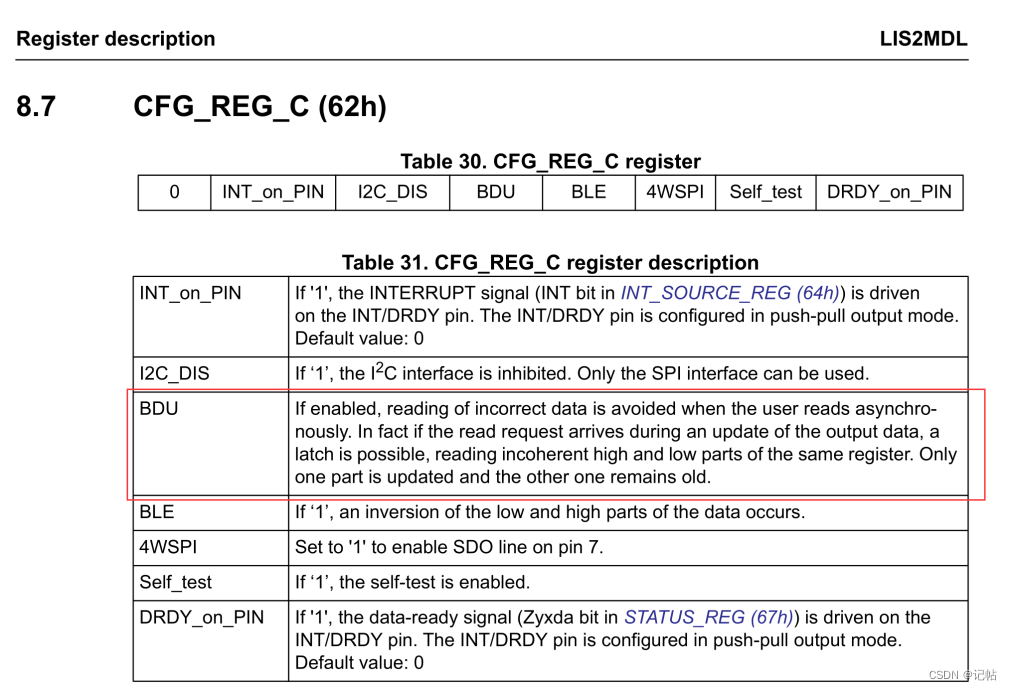
對(duì)應(yīng)的驅(qū)動(dòng)程序,如下所示。
/* Enable Block Data Update */
lis2mdl_block_data_update_set(&dev_ctx, PROPERTY_ENABLE);
設(shè)置速率
速率可以通過(guò)CFG_REG_A (60h)的ODR設(shè)置速率。
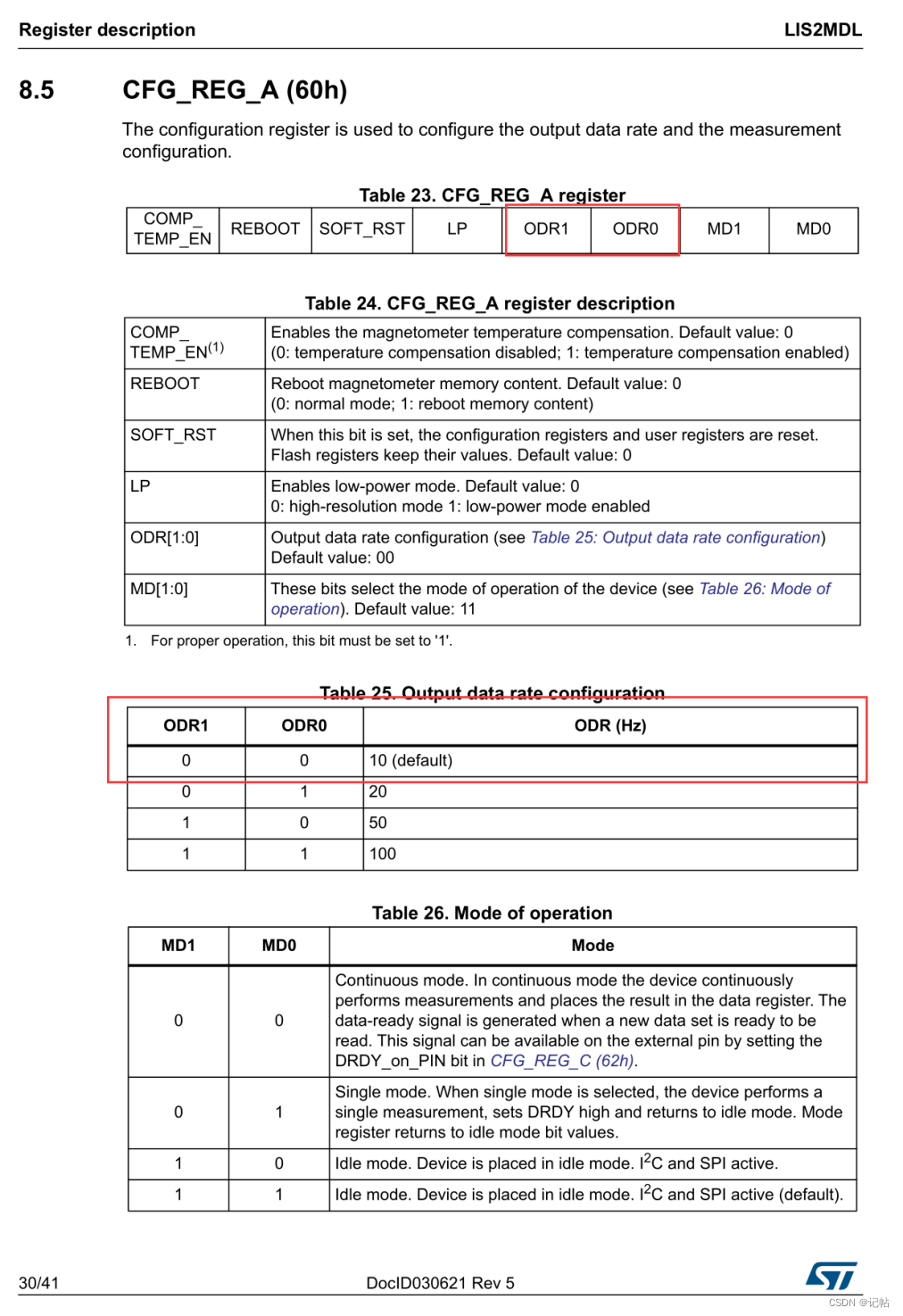
設(shè)置速率可以使用如下函數(shù)。
/* Set Output Data Rate */
lis2mdl_data_rate_set(&dev_ctx, LIS2MDL_ODR_10Hz);
啟用偏移消除
LIS2MDL 磁力計(jì)的配置寄存器(CFG_REG_B)的OFF_CANC - 這個(gè)位用于啟用或禁用偏移消除。
這意味著每次磁力計(jì)準(zhǔn)備輸出新的測(cè)量數(shù)據(jù)時(shí),它都會(huì)自動(dòng)進(jìn)行偏移校準(zhǔn),以確保數(shù)據(jù)的準(zhǔn)確性。這通常用于校準(zhǔn)傳感器,以消除由于傳感器偏移或環(huán)境因素引起的任何誤差。
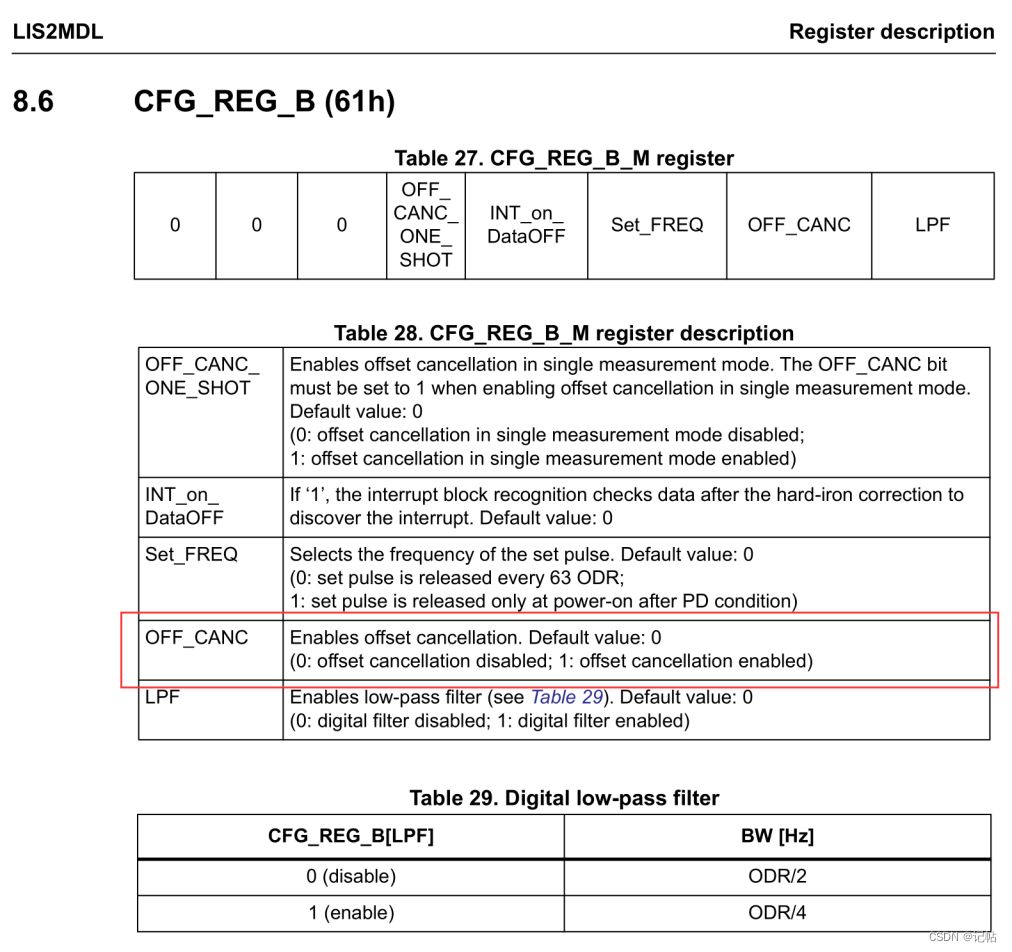
/* Set / Reset sensor mode */
lis2mdl_set_rst_mode_set(&dev_ctx, LIS2MDL_SENS_OFF_CANC_EVERY_ODR);
開(kāi)啟溫度補(bǔ)償
開(kāi)啟溫度補(bǔ)償可以通過(guò)CFG_REG_A (60h)的COMP_TEMP_EN進(jìn)行配置。
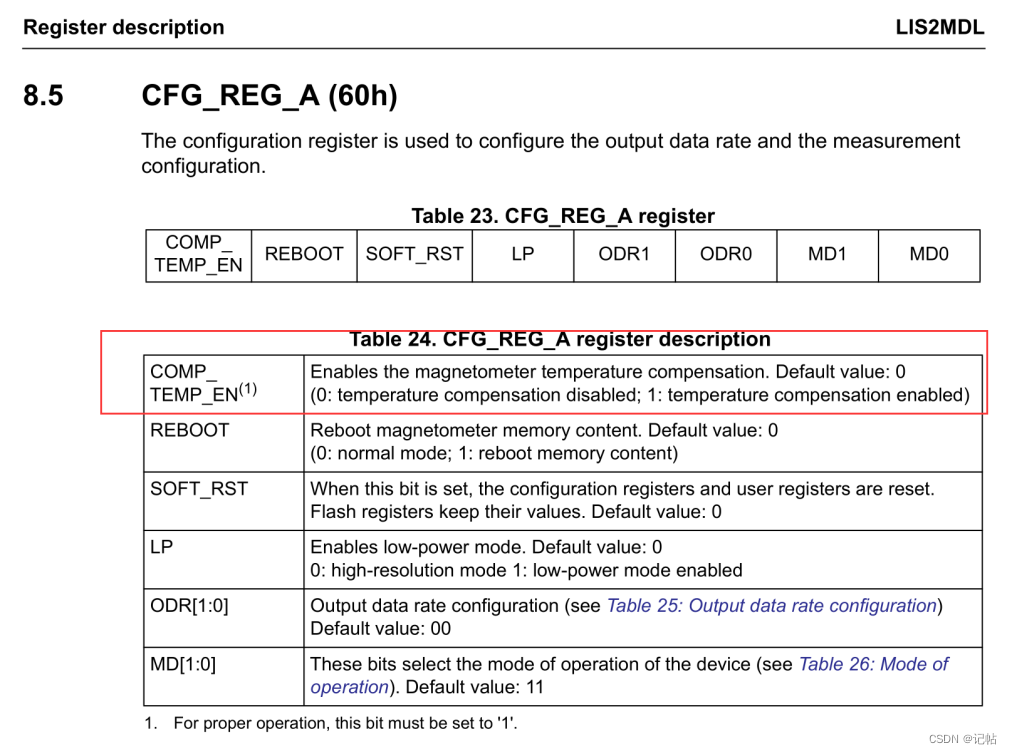
/* Enable temperature compensation */
lis2mdl_offset_temp_comp_set(&dev_ctx, PROPERTY_ENABLE);
設(shè)置為連續(xù)模式
LIS2MDL 磁力計(jì) CFG_REG_A (60h) 配置寄存器的MD1 和 MD0 - 這兩個(gè)位用于選擇設(shè)備的工作模式。
00 - 連續(xù)模式,設(shè)備連續(xù)進(jìn)行測(cè)量并將結(jié)果放在數(shù)據(jù)寄存器中。
01 - 單次模式,設(shè)備進(jìn)行單次測(cè)量,然后返回到空閑模式。
10 和 11 - 空閑模式,設(shè)備被置于空閑模式,但I(xiàn)2C和SPI接口仍然激活
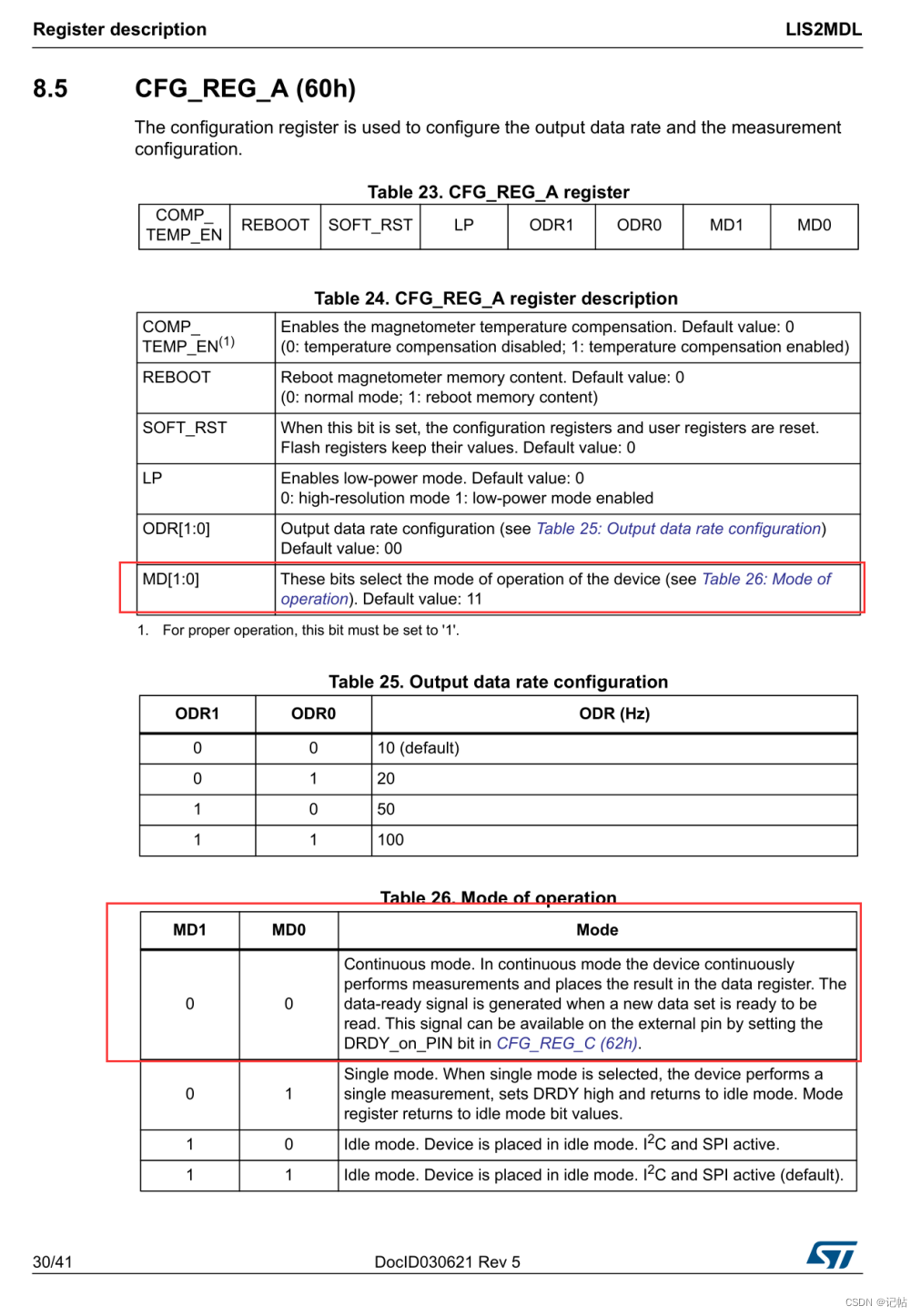
/* Set device in continuous mode */
lis2mdl_operating_mode_set(&dev_ctx, LIS2MDL_CONTINUOUS_MODE);
輪詢讀取數(shù)據(jù)
對(duì)于數(shù)據(jù)是否準(zhǔn)備好,可以查看STATUS_REG (67h)的Zyxda位,判斷是否有新數(shù)據(jù)到達(dá)。
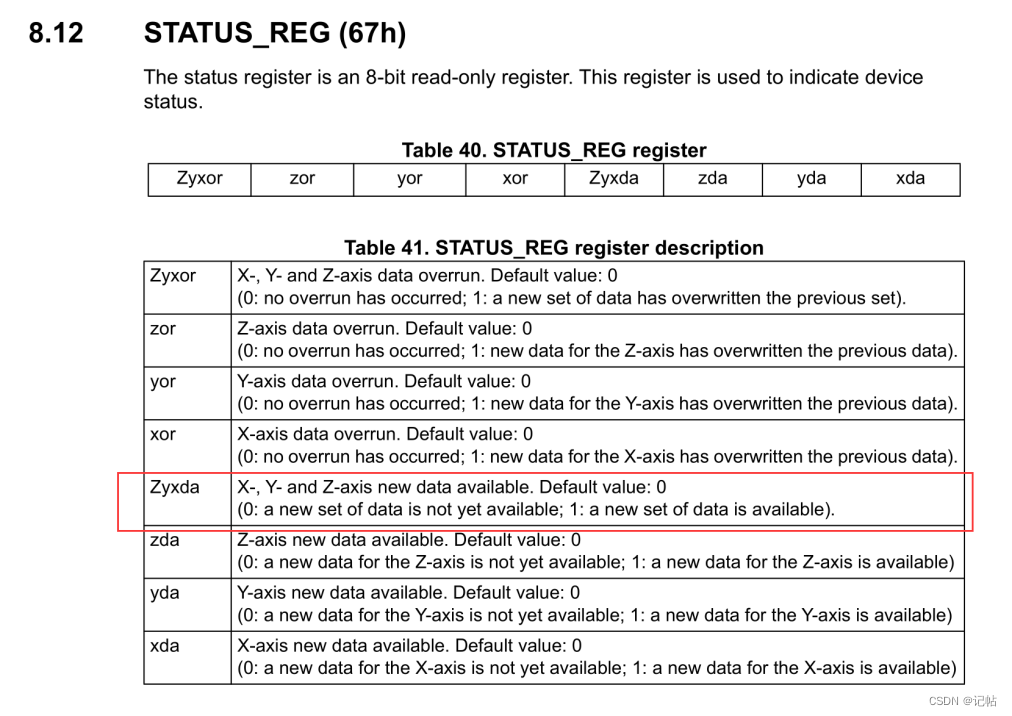
uint8_t reg;
/* Read output only if new value is available */
lis2mdl_mag_data_ready_get(&dev_ctx, ®);
數(shù)據(jù)OUTX_L_REG(68h)-OUTZ_H_REG(6Dh)獲取。
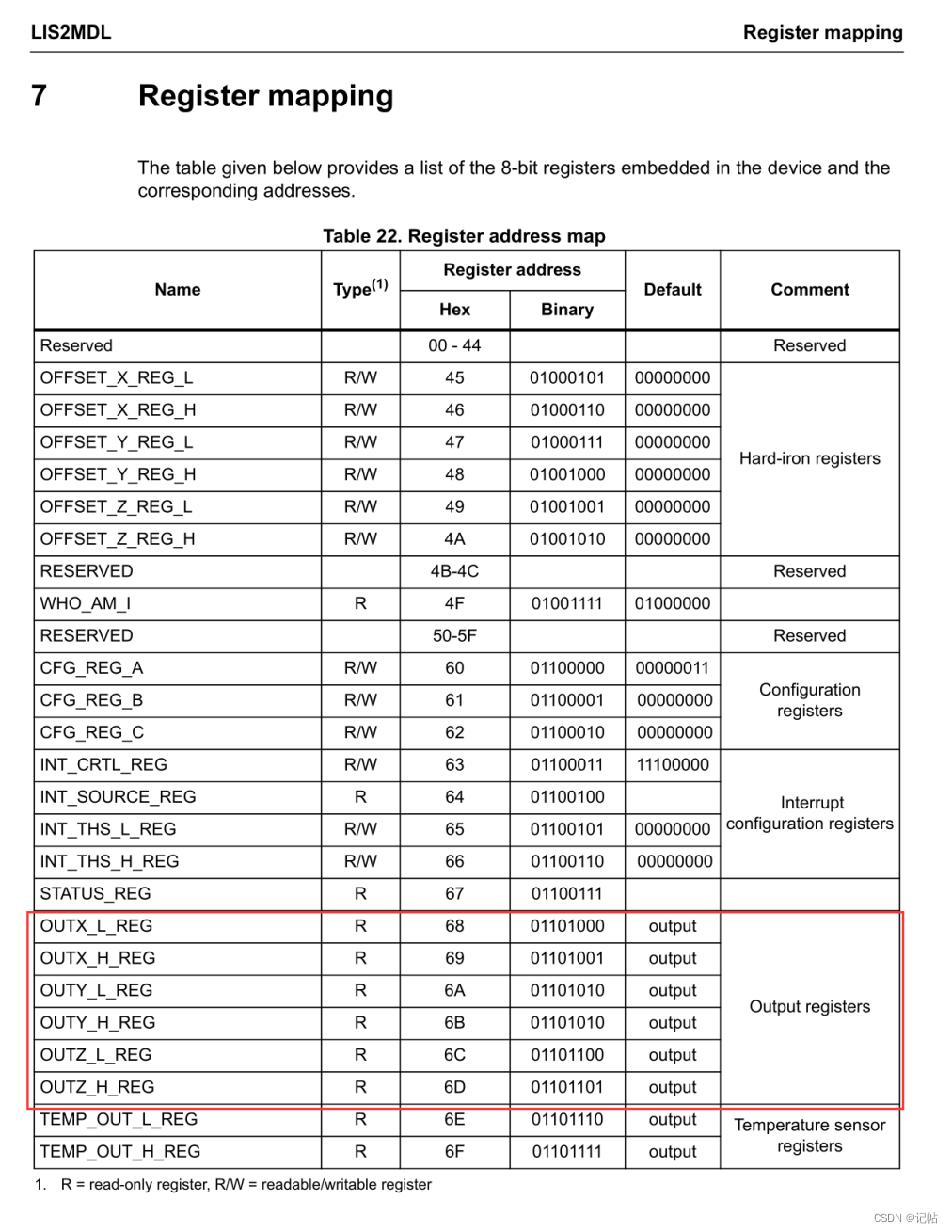
/* Read magnetic field data */
memset(data_raw_magnetic, 0x00, 3 * sizeof(int16_t));
lis2mdl_magnetic_raw_get(&dev_ctx, data_raw_magnetic);
magnetic_mG[0] = lis2mdl_from_lsb_to_mgauss(data_raw_magnetic[0]);
magnetic_mG[1] = lis2mdl_from_lsb_to_mgauss(data_raw_magnetic[1]);
magnetic_mG[2] = lis2mdl_from_lsb_to_mgauss(data_raw_magnetic[2]);
主程序
#include "hal_data.h"
#include < stdio.h >
#include "lis2mdl_reg.h"
fsp_err_t err = FSP_SUCCESS;
volatile bool uart_send_complete_flag = false;
void user_uart_callback (uart_callback_args_t * p_args)
{
if(p_args- >event == UART_EVENT_TX_COMPLETE)
{
uart_send_complete_flag = true;
}
}
/* Callback function */
i2c_master_event_t i2c_event = I2C_MASTER_EVENT_ABORTED;
uint32_t timeout_ms = 100000;
void sci_i2c_master_callback(i2c_master_callback_args_t *p_args)
{
i2c_event = I2C_MASTER_EVENT_ABORTED;
if (NULL != p_args)
{
/* capture callback event for validating the i2c transfer event*/
i2c_event = p_args- >event;
}
}
#ifdef __GNUC__ //串口重定向
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int __io_putchar(int ch)
#else
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int fputc(int ch, FILE *f)
#endif
PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE
{
err = R_SCI_UART_Write(&g_uart9_ctrl, (uint8_t *)&ch, 1);
if(FSP_SUCCESS != err) __BKPT();
while(uart_send_complete_flag == false){}
uart_send_complete_flag = false;
return ch;
}
int _write(int fd,char *pBuffer,int size)
{
for(int i=0;i< size;i++)
{
__io_putchar(*pBuffer++);
}
return size;
}
FSP_CPP_HEADER
void R_BSP_WarmStart(bsp_warm_start_event_t event);
FSP_CPP_FOOTER
#define SENSOR_BUS g_i2c_master0_ctrl
/* Private macro -------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define BOOT_TIME 20 //ms
/* Private variables ---------------------------------------------------------*/
static int16_t data_raw_magnetic[3];
static int16_t data_raw_temperature;
static float magnetic_mG[3];
static float temperature_degC;
static uint8_t whoamI, rst;
static uint8_t tx_buffer[1000];
/* Extern variables ----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Private functions ---------------------------------------------------------*/
/*
* WARNING:
* Functions declare in this section are defined at the end of this file
* and are strictly related to the hardware platform used.
*
*/
static int32_t platform_write(void *handle, uint8_t reg, const uint8_t *bufp,
uint16_t len);
static int32_t platform_read(void *handle, uint8_t reg, uint8_t *bufp,
uint16_t len);
static void tx_com(uint8_t *tx_buffer, uint16_t len);
static void platform_delay(uint32_t ms);
static void platform_init(void);
/*******************************************************************************************************************//**
* main() is generated by the RA Configuration editor and is used to generate threads if an RTOS is used. This function
* is called by main() when no RTOS is used.
**********************************************************************************************************************/
void hal_entry(void)
{
/* TODO: add your own code here */
/* Open the transfer instance with initial configuration. */
err = R_SCI_UART_Open(&g_uart9_ctrl, &g_uart9_cfg);
assert(FSP_SUCCESS == err);
printf("hello world!n");
R_IOPORT_PinWrite(&g_ioport_ctrl, BSP_IO_PORT_00_PIN_14, BSP_IO_LEVEL_HIGH);
/* Initialize the I2C module */
err = R_IIC_MASTER_Open(&g_i2c_master0_ctrl, &g_i2c_master0_cfg);
/* Handle any errors. This function should be defined by the user. */
assert(FSP_SUCCESS == err);
/* Initialize mems driver interface */
stmdev_ctx_t dev_ctx;
dev_ctx.write_reg = platform_write;
dev_ctx.read_reg = platform_read;
dev_ctx.handle = &SENSOR_BUS;
/* Wait sensor boot time */
platform_delay(BOOT_TIME);
/* Check device ID */
lis2mdl_device_id_get(&dev_ctx, &whoamI);
printf("LIS2MDL_ID=0x%x,whoamI=0x%xn",LIS2MDL_ID,whoamI);
if (whoamI != LIS2MDL_ID)
while (1) {
/* manage here device not found */
}
/* Restore default configuration */
lis2mdl_reset_set(&dev_ctx, PROPERTY_ENABLE);
do {
lis2mdl_reset_get(&dev_ctx, &rst);
} while (rst);
/* Enable Block Data Update */
lis2mdl_block_data_update_set(&dev_ctx, PROPERTY_ENABLE);
/* Set Output Data Rate */
lis2mdl_data_rate_set(&dev_ctx, LIS2MDL_ODR_10Hz);
/* Set / Reset sensor mode */
lis2mdl_set_rst_mode_set(&dev_ctx, LIS2MDL_SENS_OFF_CANC_EVERY_ODR);
/* Enable temperature compensation */
lis2mdl_offset_temp_comp_set(&dev_ctx, PROPERTY_ENABLE);
/* Set device in continuous mode */
lis2mdl_operating_mode_set(&dev_ctx, LIS2MDL_CONTINUOUS_MODE);
while (1)
{
uint8_t reg;
/* Read output only if new value is available */
lis2mdl_mag_data_ready_get(&dev_ctx, ®);
if (reg) {
/* Read magnetic field data */
memset(data_raw_magnetic, 0x00, 3 * sizeof(int16_t));
lis2mdl_magnetic_raw_get(&dev_ctx, data_raw_magnetic);
magnetic_mG[0] = lis2mdl_from_lsb_to_mgauss(data_raw_magnetic[0]);
magnetic_mG[1] = lis2mdl_from_lsb_to_mgauss(data_raw_magnetic[1]);
magnetic_mG[2] = lis2mdl_from_lsb_to_mgauss(data_raw_magnetic[2]);
printf("Magnetic field [mG]:%4.2ft%4.2ft%4.2frn",magnetic_mG[0], magnetic_mG[1], magnetic_mG[2]);
/* Read temperature data */
memset(&data_raw_temperature, 0x00, sizeof(int16_t));
lis2mdl_temperature_raw_get(&dev_ctx, &data_raw_temperature);
temperature_degC = lis2mdl_from_lsb_to_celsius(data_raw_temperature);
printf("Temperature [degC]:%6.2frn",temperature_degC);
}
R_BSP_SoftwareDelay(10, BSP_DELAY_UNITS_MILLISECONDS);
}
#if BSP_TZ_SECURE_BUILD
/* Enter non-secure code */
R_BSP_NonSecureEnter();
#endif
}
演示

審核編輯 黃宇
-
傳感器
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
2541文章
49967瀏覽量
747583 -
磁力計(jì)
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1文章
71瀏覽量
20748
發(fā)布評(píng)論請(qǐng)先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
e2studio開(kāi)發(fā)磁力計(jì)LIS2MDL(1)----輪詢獲取磁力計(jì)數(shù)據(jù)

磁力計(jì)LIS2MDL開(kāi)發(fā)(1)----輪詢獲取磁力計(jì)數(shù)據(jù)

磁力計(jì)LIS2MDL開(kāi)發(fā)(2)----電子羅盤(pán)
陀螺儀LSM6DSOW開(kāi)發(fā)(6)----獲取磁力計(jì)數(shù)據(jù)
磁力計(jì)LIS2MDL開(kāi)發(fā)(4)----MotionMC 執(zhí)行磁力計(jì)校準(zhǔn)

LSM9DS1磁力計(jì)的自檢是否與LIS3MDL相同
如何在LIS3MDL磁力計(jì)傳感器中禁用DRDY和INT輸出
LIS3MDL三軸磁力計(jì)能滿足磁通密度為0.23高斯的應(yīng)用程序嗎
用于生成每個(gè)輸出樣本的樣本數(shù)量而言LIS3mdl磁力計(jì)的操作模式有何不同?
LIS2MDL軸標(biāo)簽是否指示正軸方向?
STLIS2MDL磁力計(jì)傳感器相關(guān)的使用信息和應(yīng)用提示
LIS2MDL磁力計(jì)傳感器相關(guān)資料
LIS2MDL 3D數(shù)字磁力計(jì)應(yīng)用筆記

e2studio開(kāi)發(fā)磁力計(jì)LIS2MDL(2)----電子羅盤(pán)





 e2studio開(kāi)發(fā)磁力計(jì)LIS2MDL(1)----輪詢獲取磁力計(jì)數(shù)據(jù)
e2studio開(kāi)發(fā)磁力計(jì)LIS2MDL(1)----輪詢獲取磁力計(jì)數(shù)據(jù)










評(píng)論