rtc節(jié)點
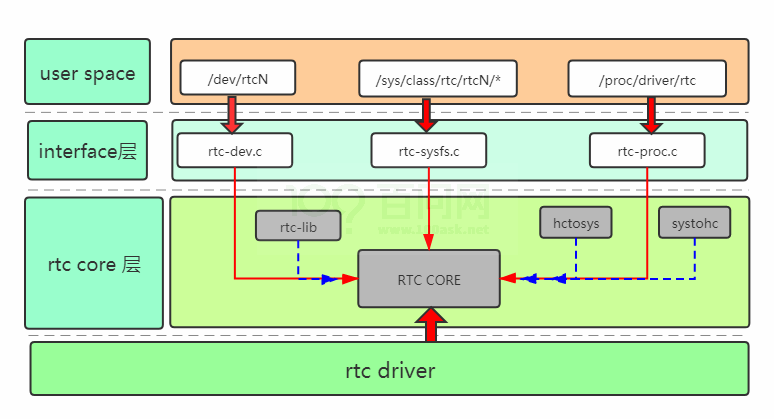
rtc-sysfs文件主要的操作就是在sys下創(chuàng)建rtc的屬性節(jié)點,可以方便用戶方便快捷的訪問,查找問題。下來大概看看sys下的rtc節(jié)點,有個直觀的認(rèn)識。
[root@test ~]# cat /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/
date hctosys power/ time?
dev max_user_freq since_epoch uevent?
device/ name subsystem/ wakealarm?
這是手機(jī)上rtc的節(jié)點屬性,可以看到手機(jī)上只有一個rtc0設(shè)備。也可以查看/dev/rtc0設(shè)備
[root@test ~]# ls -l /dev/rtc0?
crw-rw---- 1 root root 254, 0 Jan 1 1970 /dev/rtc0
可以看到rtc的主設(shè)備號是254, 次設(shè)備號是0。這些信息也可以在/proc/devices下看到。
[root@test ~]# cat /proc/devices?
Character devices:
1 mem
2 pty
...
254 rtc
也可以看到rtc的主設(shè)備號是254, 這都是通過上一節(jié)說的rtc-dev.c中注冊得到的。
rtc-sysfs.c分析
void __init rtc_sysfs_init(struct class *rtc_class)
{
rtc_class->dev_groups = rtc_groups;
}
設(shè)置rtc的設(shè)備組屬性,rtc_groups是一個attribute_group的結(jié)構(gòu)體。這個函數(shù)會在class.c中rtc_init中調(diào)用到,關(guān)于rtc_group會在后面說到。
static inline int rtc_does_wakealarm(struct rtc_device *rtc)
{
if (!device_can_wakeup(rtc->dev.parent)) //用來判斷是否具有wakeup的能力
return 0;?
return rtc->ops->set_alarm != NULL; //用來判斷是否具有alarm的能力
}
該函數(shù)是用來檢測rtc是否支持wakeup功能和alarm功能。 wakeup的能力就是能喚醒suspend-to-RAM/suspend-to-disk設(shè)備。wakeup的能力是通過如下代碼:
static inline bool device_can_wakeup(struct device *dev)
{
return dev->power.can_wakeup;
}
也就是判斷can_wakeup是否為true,至于rtc是否支持就需要看對應(yīng)的rtc驅(qū)動是否實現(xiàn)該功能。
比如驅(qū)動: rtc-ds1305.c中就調(diào)用如下的代碼設(shè)置wakeup的能力。
device_set_wakeup_capable(&spi->dev, 1);
也可以通過如下方式判斷是否支持wakeup功能:
root@test:/ # cat /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/device/power/wakeup
enabled
顯示enabled就代表此rtc支持 wakeup功能,也就是說有喚醒suspend/standby的系統(tǒng)或者設(shè)備。
而對于rtc是否支持alarm功能,就通過驅(qū)動的ops操作函數(shù)集合看set_alarm有沒有實現(xiàn)就ok。
如果rtc即支持wakeup功能也支持alarm功能,則:
void rtc_sysfs_add_device(struct rtc_device *rtc)
{
int err;
/* not all RTCs support both alarms and wakeup */
if (!rtc_does_wakealarm(rtc)) //檢測是否支持wakeup和alarm功能
return;
err = device_create_file(&rtc->dev, &dev_attr_wakealarm); //創(chuàng)建wakealarm屬性
if (err)
dev_err(rtc->dev.parent,
"failed to create alarm attribute, %d\n", err);
}
如果rtc都支持wakup和alarm功能,就創(chuàng)建wakealarm屬性節(jié)點。否則不創(chuàng)建。
接下來分析wakealarm屬性的show和store函數(shù)。
static DEVICE_ATTR(wakealarm, S_IRUGO | S_IWUSR, rtc_sysfs_show_wakealarm, rtc_sysfs_set_wakealarm);
這里出現(xiàn)了DEVICE_ATTR,有必要說一下這個宏定義。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#define DEVICE_ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store) \
struct device_attribute dev_attr_##_name = __ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store)
#define __ATTR(_name, _mode, _show, _store) { \
.attr = {.name = __stringify(_name), \
.mode = VERIFY_OCTAL_PERMISSIONS(_mode) }, \
.show = _show, \
.store = _store, \
}
以上就是DEVICE_ATTR的宏定義,則按照定義將wakealarm的屬性展開,如下:
struct device_attribute dev_attr_wakealarm {
.name = wakealarm,
.mode = S_IRUGO | S_IWUSR,
.show = rtc_sysfs_show_wakealarm,
.store = rtc_sysfs_set_wakealarm,
}
上面的屬性可以知道,wakealarm的屬性為可讀可寫的,當(dāng)cat wakealarm的時候最終調(diào)用show函數(shù),echo的時候最終調(diào)用strore函數(shù)。
root@test:/ # cat /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/wakealarm?
root@test:/ #?
當(dāng)讀wakealarm的時候,沒有任何值,說明目前沒有設(shè)備alarm。
也可以通過cat /proc/driver/rtc獲得更多的信息:
rtc_time : 07:07:46
rtc_date : 2012-01-01
alrm_time : 00:00:00
alrm_date : 1970-01-01
alarm_IRQ : no
alrm_pending : no
update IRQ enabled : no
periodic IRQ enabled : no
periodic IRQ frequency : 1
max user IRQ frequency : 64
24hr : yes
可以看到alarm_IRQ是no, 當(dāng)設(shè)置正確的alarm值后就會變?yōu)閥es的。接下來設(shè)置當(dāng)前的時間之后的100s
root@test:/ # echo +100 > /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/wakealarm?
root@test:/ # cat /proc/driver/rtc?
rtc_time : 07:09:32
rtc_date : 2012-01-01
alrm_time : 07:11:05
alrm_date : 2012-01-01
alarm_IRQ : yes
alrm_pending : no
update IRQ enabled : no
periodic IRQ enabled : no
periodic IRQ frequency : 1
max user IRQ frequency : 64
24hr : yes
可以看到alrm_time變?yōu)楫?dāng)前時間+100s了,同時alarm_IRQ也變?yōu)閥es。
同時再次cat wakealarm,即可獲得值。
root@test:/ # cat /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/wakealarm?
1325401865
此值是unix的時間戳,必須要轉(zhuǎn)換為UTC時間,可以通過如下的網(wǎng)址轉(zhuǎn)換,http://tool.chinaz.com/Tools/unixtime.aspx
可以看到轉(zhuǎn)換后的時間是2012/1/1 15:11:5,為什么感覺和alrm_time對不上呢? 那是因為北京在東八區(qū),相差8個小時,15-8=7則就是alrm_time。
當(dāng)cat wakealarm有值的時候,再次echo值進(jìn)如wakealarm的時候就會出現(xiàn)設(shè)備忙,所以再次設(shè)備時候必須清除以前的設(shè)置。
root@test:/ # cat /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/wakealarm?
1325401865
root@test:/ # echo +100 > /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/wakealarm
sh: echo: write error: Device or resource busy
那如何就可以清空wakealarm的值,可以通過echo 0 > wakealarm就可以清空
root@test:/ # cat /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/wakealarm
1325401865
root@test:/ # echo 0 > /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/wakealarm
root@test:/ # cat /sys/class/rtc/rtc0/wakealarm
root@test:/ #
在知道了上述的設(shè)置之后,再來看代碼,在看代碼之前先看一下必要的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)。
struct rtc_time {
int tm_sec; //秒
int tm_min; //分鐘
int tm_hour; //小時
int tm_mday; //一月中的第幾天
int tm_mon; //月份
int tm_year; //年份
int tm_wday; //周
int tm_yday; //一年中的第幾天
int tm_isdst; //夏令時標(biāo)識符
};
/*
* This data structure is inspired by the EFI (v0.92) wakeup
* alarm API.
*/
struct rtc_wkalrm {
unsigned char enabled; /* 0 = alarm disabled, 1 = alarm enabled */
unsigned char pending; /* 0 = alarm not pending, 1 = alarm pending */
struct rtc_time time; /* time the alarm is set to */
};
先分析store函數(shù),當(dāng)之后往里面寫值的之后,才可以read出來。
static ssize_t
rtc_sysfs_set_wakealarm(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t n)
{
ssize_t retval;
unsigned long now, alarm;
unsigned long push = 0;
struct rtc_wkalrm alm;
struct rtc_device *rtc = to_rtc_device(dev);
char *buf_ptr;
int adjust = 0;
/* Only request alarms that trigger in the future. Disable them
* by writing another time, e.g. 0 meaning Jan 1 1970 UTC. //設(shè)置時間必須是在將來
*/
retval = rtc_read_time(rtc, &alm.time); //讀取當(dāng)前時間
if (retval < 0)
return retval;
rtc_tm_to_time(&alm.time, &now); //將當(dāng)前的時間轉(zhuǎn)化為從1970來經(jīng)歷的秒數(shù)
buf_ptr = (char *)buf;
if (*buf_ptr == '+') { //如果按照我們上面的設(shè)置,echo +100 > wakealarm, 則buf就是+100, 然后解析buf
buf_ptr++;
if (*buf_ptr == '=') {
buf_ptr++;
push = 1;
} else
adjust = 1; //執(zhí)行到這里
}
alarm = simple_strtoul(buf_ptr, NULL, 0); //將“100”轉(zhuǎn)化為數(shù)字
if (adjust) {
alarm += now; //alarm就是當(dāng)前時間+100
}
if (alarm > now || push) {
/* Avoid accidentally clobbering active alarms; we can't
* entirely prevent that here, without even the minimal
* locking from the /dev/rtcN api.
*/
retval = rtc_read_alarm(rtc, &alm); //讀取alarm時間
if (retval < 0)
return retval;
if (alm.enabled) { //第一次是沒有使能的,如果第二次設(shè)置的話
if (push) {
rtc_tm_to_time(&alm.time, &push);
alarm += push;
} else
return -EBUSY; //就會出現(xiàn)設(shè)備忙,在上面已經(jīng)演示過了
} else if (push)
return -EINVAL;
alm.enabled = 1; //先使能
} else {
alm.enabled = 0;
/* Provide a valid future alarm time. Linux isn't EFI,
* this time won't be ignored when disabling the alarm.
*/
alarm = now + 300;
}
rtc_time_to_tm(alarm, &alm.time); //又將秒數(shù)設(shè)置為農(nóng)歷時間格式
retval = rtc_set_alarm(rtc, &alm); //設(shè)置alarm時間
return (retval < 0) ? retval : n;
}
下面分析read操作,最終調(diào)用show函數(shù)。
static ssize_t rtc_sysfs_show_wakealarm(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
ssize_t retval;
unsigned long alarm;
struct rtc_wkalrm alm;
/* Don't show disabled alarms. For uniformity, RTC alarms are
* conceptually one-shot, even though some common RTCs (on PCs)
* don't actually work that way.
*
* NOTE: RTC implementations where the alarm doesn't match an
* exact YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM[:SS] date *must* disable their RTC
* alarms after they trigger, to ensure one-shot semantics.
*/
retval = rtc_read_alarm(to_rtc_device(dev), &alm); //讀取alarm的值
if (retval == 0 && alm.enabled) { //如果enable了,然后顯示
rtc_tm_to_time(&alm.time, &alarm);
retval = sprintf(buf, "%lu\n", alarm);
}
return retval;
分析完wakealarm節(jié)點之后,還有一系列節(jié)點是rtc共有的,如下:
static struct attribute *rtc_attrs[] = {
&dev_attr_name.attr,
&dev_attr_date.attr,
&dev_attr_time.attr,
&dev_attr_since_epoch.attr,
&dev_attr_max_user_freq.attr,
&dev_attr_hctosys.attr,
NULL,
};
ATTRIBUTE_GROUPS(rtc);
在這里需要將ATTRIBUTE_GROOUP(rtc)展開,展開之后就是:
static const struct attribute_group rtc_group = {
.attrs = rtc_attrs,
}
static const struct attribute_group *rtc_groups[]={
&rtc_group,
null
}
而rtc_groups就是在rtc_sysfs_init賦值給dev_groups的。 在device_add_attrs函數(shù)中會添加這些屬性,如下:
static int device_add_attrs(struct device *dev)
{
struct class *class = dev->class;
const struct device_type *type = dev->type;
int error;
if (class) {
error = device_add_groups(dev, class->dev_groups);
if (error)
return error;
}
明白上述的創(chuàng)建原理之后,再依次看每個節(jié)點的意思。
static ssize_t name_show(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
return sprintf(buf, "%s\n", to_rtc_device(dev)->name);
}
static DEVICE_ATTR_RO(name);
只讀屬性,顯示rtc設(shè)備的名稱,在驅(qū)動中會有該rtc對應(yīng)的名稱。
static ssize_t date_show(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
ssize_t retval;
struct rtc_time tm;
retval = rtc_read_time(to_rtc_device(dev), &tm);
if (retval == 0) {
retval = sprintf(buf, "%04d-%02d-%02d\n",
tm.tm_year + 1900, tm.tm_mon + 1, tm.tm_mday);
}
return retval;
}
static DEVICE_ATTR_RO(date);
static ssize_t time_show(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
ssize_t retval;
struct rtc_time tm;
retval = rtc_read_time(to_rtc_device(dev), &tm);
if (retval == 0) {
retval = sprintf(buf, "%02d:%02d:%02d\n",
tm.tm_hour, tm.tm_min, tm.tm_sec);
}
return retval;
}
static DEVICE_ATTR_RO(time);
上述的兩個只讀屬性,一個是當(dāng)前的時間,一個是當(dāng)前的日期,不做過多解釋。
static ssize_t since_epoch_show(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
ssize_t retval;
struct rtc_time tm;
retval = rtc_read_time(to_rtc_device(dev), &tm);
if (retval == 0) {
unsigned long time;
rtc_tm_to_time(&tm, &time);
retval = sprintf(buf, "%lu\n", time);
}
return retval;
}
static DEVICE_ATTR_RO(since_epoch);
只讀屬性,該屬性的值表示當(dāng)前的時間轉(zhuǎn)換為自1970年來的秒數(shù)。
static ssize_t max_user_freq_show(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
return sprintf(buf, "%d\n", to_rtc_device(dev)->max_user_freq);
}
static ssize_t max_user_freq_store(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,
const char *buf, size_t n)
{
struct rtc_device *rtc = to_rtc_device(dev);
unsigned long val = simple_strtoul(buf, NULL, 0);
if (val >= 4096 || val == 0)
return -EINVAL;
rtc->max_user_freq = (int)val;
return n;
}
static DEVICE_ATTR_RW(max_user_freq);
可讀可寫屬性,show函數(shù)是讀取最大的freq, store是設(shè)置最大的頻率,不能超過4096.
/**
* rtc_sysfs_show_hctosys - indicate if the given RTC set the system time
*
* Returns 1 if the system clock was set by this RTC at the last
* boot or resume event.
*/
static ssize_t hctosys_show(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_RTC_HCTOSYS_DEVICE
if (rtc_hctosys_ret == 0 &&
strcmp(dev_name(&to_rtc_device(dev)->dev),
CONFIG_RTC_HCTOSYS_DEVICE) == 0)
return sprintf(buf, "1\n");
else
#endif
return sprintf(buf, "0\n");
}
static DEVICE_ATTR_RO(hctosys);
只讀屬性,如果返回1代表系統(tǒng)的clock最近一次使用rtc設(shè)置。返回0代表沒有。
?
 電子發(fā)燒友App
電子發(fā)燒友App























評論