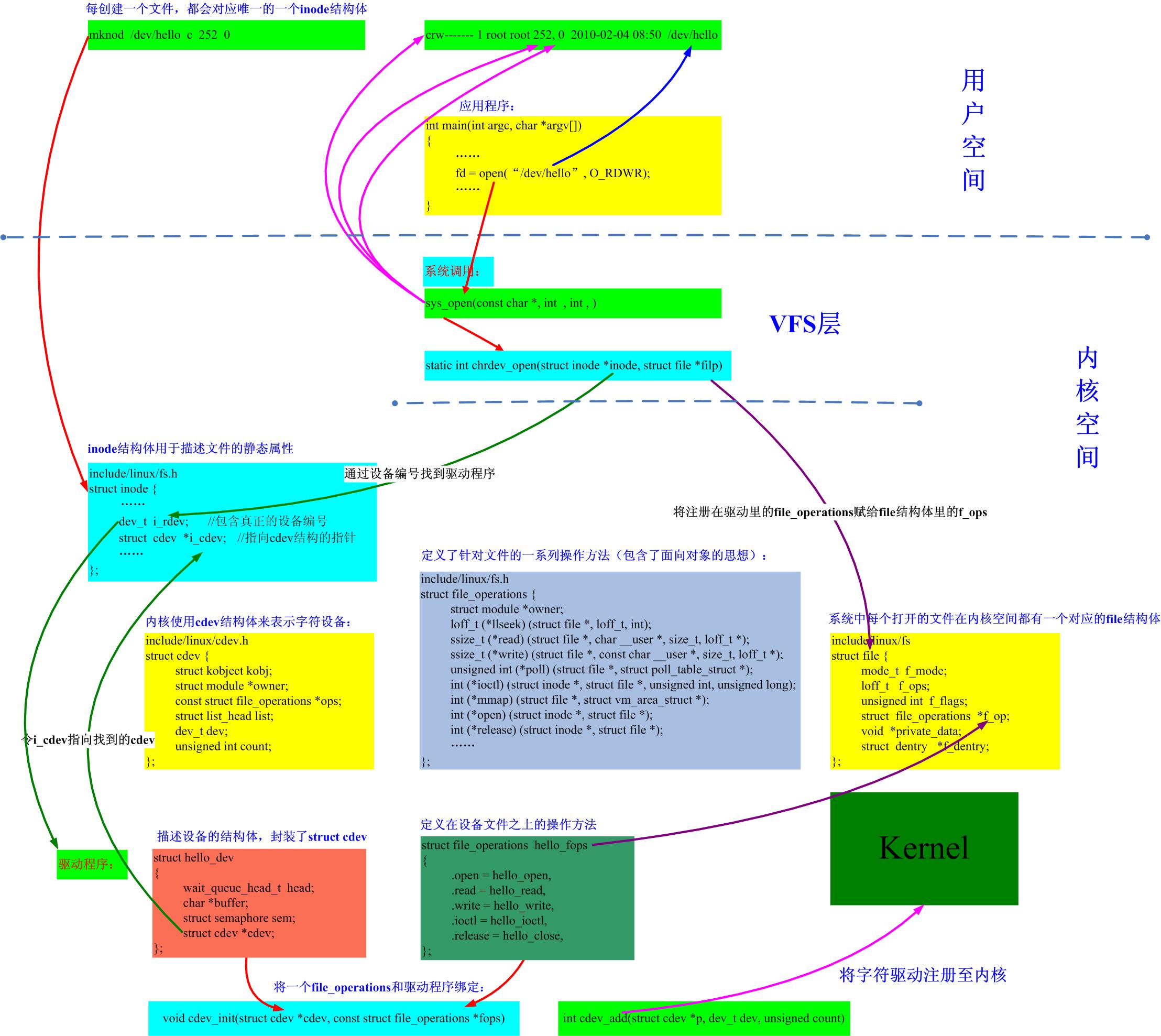
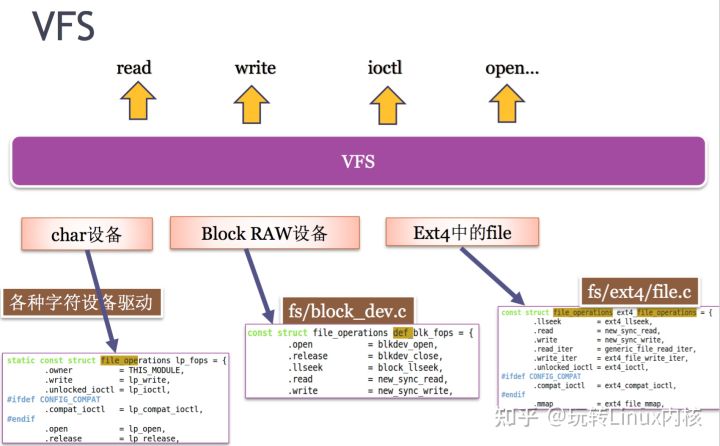
驅(qū)動(dòng)程序就是向下控制硬件,向上提供接口,這里的向上提供的接口最終對(duì)應(yīng)到應(yīng)用層有三種方式:設(shè)備文件,/proc,/sys,其中最常用的就是使用設(shè)備文件,而Linux設(shè)備中用的最多的就是字符設(shè)備,本文就以字符設(shè)備為例來(lái)分析創(chuàng)建并打開(kāi)一個(gè)字符設(shè)備的文件內(nèi)部機(jī)制。
struct inode
Linux中一切皆文件,當(dāng)我們?cè)贚inux中創(chuàng)建一個(gè)文件時(shí),就會(huì)在相應(yīng)的文件系統(tǒng)創(chuàng)建一個(gè)inode與之對(duì)應(yīng),文件實(shí)體和文件的inode是一一對(duì)應(yīng)的,創(chuàng)建好一個(gè)inode會(huì)存在存儲(chǔ)器中,第一次open就會(huì)將inode在內(nèi)存中有一個(gè)備份,同一個(gè)文件被多次打開(kāi)并不會(huì)產(chǎn)生多個(gè)inode,當(dāng)所有被打開(kāi)的文件都被close之后,inode在內(nèi)存中的實(shí)例才會(huì)被釋放。既然如此,當(dāng)我們使用mknod(或其他方法)創(chuàng)建一個(gè)設(shè)備文件時(shí),也會(huì)在文件系統(tǒng)中創(chuàng)建一個(gè)inode,這個(gè)inode和其他的inode一樣,用來(lái)存儲(chǔ)關(guān)于這個(gè)文件的靜態(tài)信息(不變的信息),包括這個(gè)設(shè)備文件對(duì)應(yīng)的設(shè)備號(hào),文件的路徑以及對(duì)應(yīng)的驅(qū)動(dòng)對(duì)象etc。inode作為VFS四大對(duì)象之一,在驅(qū)動(dòng)開(kāi)發(fā)中很少需要自己進(jìn)行填充,更多的是在open()方法中進(jìn)行查看并根據(jù)需要填充我們的file結(jié)構(gòu)。
對(duì)于不同的文件類型,inode被填充的成員內(nèi)容也會(huì)有所不同,以創(chuàng)建字符設(shè)備為例,我們知道,add_chrdev_region其實(shí)是把一個(gè)驅(qū)動(dòng)對(duì)象和一個(gè)(一組)設(shè)備號(hào)聯(lián)系到一起。而創(chuàng)建設(shè)備文件,其實(shí)是把設(shè)備文件和設(shè)備號(hào)聯(lián)系到一起。至此,這三者就被綁定在一起了。這樣,內(nèi)核就有能力創(chuàng)建一個(gè)struct inode實(shí)例了,下面是4.8.5內(nèi)核中的inode。這個(gè)inode是VFS的inode,是最具體文件系統(tǒng)的inode的進(jìn)一步封裝,也是驅(qū)動(dòng)開(kāi)發(fā)中關(guān)心的inode,針對(duì)具體的文件系統(tǒng),還有struct ext2_inode_info 等結(jié)構(gòu)。
//include/linux/fs.h 596 /* 597 * Keep mostly read-only and often accessed (especially for 598 * the RCU path lookup and 'stat' data) fields at the beginning 599 * of the 'struct inode' 600 */ 601 struct inode { 602 umode_t i_mode; 603 unsigned short i_opflags; 604 kuid_t i_uid; 605 kgid_t i_gid; 606 unsigned int i_flags; 607 608 #ifdef CONFIG_FS_POSIX_ACL 609 struct posix_acl *i_acl; 610 struct posix_acl *i_default_acl; 611 #endif 612 613 const struct inode_operations *i_op; 614 struct super_block *i_sb; 615 struct address_space *i_mapping; 616 617 #ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY 618 void *i_security; 619 #endif 620 621 /* Stat data, not accessed from path walking */ 622 unsigned long i_ino; 623 /* 624 * Filesystems may only read i_nlink directly. They shall use the 625 * following functions for modification: 626 * 627 * (set|clear|inc|drop)_nlink 628 * inode_(inc|dec)_link_count 629 */ 630 union { 631 const unsigned int i_nlink; 632 unsigned int __i_nlink; 633 }; 634 dev_t i_rdev; 635 loff_t i_size; 636 struct timespec i_atime; 637 struct timespec i_mtime; 638 struct timespec i_ctime; 639 spinlock_t i_lock; /* i_blocks, i_bytes, maybe i_size */ 640 unsigned short i_bytes; 641 unsigned int i_blkbits; 642 blkcnt_t i_blocks; 643 644 #ifdef __NEED_I_SIZE_ORDERED 645 seqcount_t i_size_seqcount; 646 #endif 647 648 /* Misc */ 649 unsigned long i_state; 650 struct rw_semaphore i_rwsem; 651 652 unsigned long dirtied_when; /* jiffies of first dirtying */ 653 unsigned long dirtied_time_when; 654 655 struct hlist_node i_hash; 656 struct list_head i_io_list; /* backing dev IO list */ 657 #ifdef CONFIG_CGROUP_WRITEBACK 658 struct bdi_writeback *i_wb; /* the associated cgroup wb */ 659 660 /* foreign inode detection, see wbc_detach_inode() */ 661 int i_wb_frn_winner; 662 u16 i_wb_frn_avg_time; 663 u16 i_wb_frn_history; 664 #endif 665 struct list_head i_lru; /* inode LRU list */ 666 struct list_head i_sb_list; 667 struct list_head i_wb_list; /* backing dev writeback list */ 668 union { 669 struct hlist_head i_dentry; 670 struct rcu_head i_rcu; 671 }; 672 u64 i_version; 673 atomic_t i_count; 674 atomic_t i_dio_count; 675 atomic_t i_writecount; 676 #ifdef CONFIG_IMA 677 atomic_t i_readcount; /* struct files open RO */ 678 #endif 679 const struct file_operations *i_fop; /* former ->i_op->default_file_ops */ 680 struct file_lock_context *i_flctx; 681 struct address_space i_data; 682 struct list_head i_devices; 683 union { 684 struct pipe_inode_info *i_pipe; 685 struct block_device *i_bdev; 686 struct cdev *i_cdev; 687 char *i_link; 688 unsigned i_dir_seq; 689 }; 690 691 __u32 i_generation; 692 693 #ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY 694 __u32 i_fsnotify_mask; /* all events this inode cares about */ 695 struct hlist_head i_fsnotify_marks; 696 #endif 697 698 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_FS_ENCRYPTION) 699 struct fscrypt_info *i_crypt_info; 700 #endif 701 702 void *i_private; /* fs or device private pointer */ 703 };
這里面與本文相關(guān)的成員主要有:
struct inode
--602-->i_mode表示訪問(wèn)權(quán)限控制
--604-->UID
--605-->GID
--606-->i_flags文件系統(tǒng)標(biāo)志
--630-->硬鏈接數(shù)計(jì)數(shù)
--635-->i_size以字節(jié)為單位的文件大小
--636-->最后access時(shí)間
--637-->最后modify時(shí)間
--638-->最后change時(shí)間
--669-->i_dentry; //目錄項(xiàng)鏈表
--673-->i_count引用計(jì)數(shù),當(dāng)引用計(jì)數(shù)變?yōu)?時(shí),會(huì)釋放inode實(shí)例
--675-->i_writecount寫(xiě)者計(jì)數(shù)
--679-->創(chuàng)建設(shè)備文件的時(shí)候i_fops填充的是def_chr_fops,blk_blk_fops,def_fifo_fops,bad_sock_fops之一,參見(jiàn)創(chuàng)建過(guò)程中調(diào)用的init_special_inode()
--683-->特殊文件類型的union,pipe,cdev,blk.link etc,i_cdev表示這個(gè)inode屬于一個(gè)字符設(shè)備文件,本文中創(chuàng)建設(shè)備文件的時(shí)候會(huì)把與之相關(guān)的設(shè)備號(hào)的驅(qū)動(dòng)對(duì)象cdev拿來(lái)填充
--702-->inode的私有數(shù)據(jù)
上面的幾個(gè)成員只有struct def_chr_fops?值得一追,后面有大用:
//fs/char_dev.c429 const struct file_operations def_chr_fops = { 430 .open = chrdev_open,431 .llseek = noop_llseek,432 };
struct file
Linux內(nèi)核會(huì)為每一個(gè)進(jìn)程維護(hù)一個(gè)文件描述符表,這個(gè)表其實(shí)就是struct file[]的索引。open()的過(guò)程其實(shí)就是根據(jù)傳入的路徑填充好一個(gè)file結(jié)構(gòu)并將其賦值到數(shù)組中并返回其索引。下面是file的主要內(nèi)容
//include/linux/fs.h 877 struct file { 878 union { 879 struct llist_node fu_llist; 880 struct rcu_head fu_rcuhead; 881 } f_u; 882 struct path f_path; 883 struct inode *f_inode; /* cached value */ 884 const struct file_operations *f_op; 885 886 /* 887 * Protects f_ep_links, f_flags. 888 * Must not be taken from IRQ context. 889 */ 890 spinlock_t f_lock; 891 atomic_long_t f_count; 892 unsigned int f_flags; 893 fmode_t f_mode; 894 struct mutex f_pos_lock; 895 loff_t f_pos; 896 struct fown_struct f_owner; 897 const struct cred *f_cred; 898 struct file_ra_state f_ra;f 904 /* needed for tty driver, and maybe others */ 905 void *private_data; 912 struct address_space *f_mapping; 913 } __attribute__((aligned(4))); /* lest something weird decides that 2 is OK */
struct file
--882-->f_path里存儲(chǔ)的是open傳入的路徑,VFS就是根據(jù)這個(gè)路徑逐層找到相應(yīng)的inode
--883-->f_inode里存儲(chǔ)的是找到的inode
--884-->f_op里存儲(chǔ)的就是驅(qū)動(dòng)提供的file_operations對(duì)象,這個(gè)對(duì)象在open的時(shí)候被填充,具體地,應(yīng)用層的open通過(guò)層層搜索會(huì)調(diào)用inode.i_fops->open,即chrdev_open()
--891-->f_count的作用是記錄對(duì)文件對(duì)象的引用計(jì)數(shù),也即當(dāng)前有多少個(gè)使用CLONE_FILES標(biāo)志克隆的進(jìn)程在使用該文件。典型的應(yīng)用是在POSIX線程中。就像在內(nèi)核中普通的引用計(jì)數(shù)模塊一樣,最后一個(gè)進(jìn)程調(diào)用put_files_struct()來(lái)釋放文件描述符。
--892-->f_flags當(dāng)打開(kāi)文件時(shí)指定的標(biāo)志,對(duì)應(yīng)系統(tǒng)調(diào)用open的int flags,比如驅(qū)動(dòng)程序?yàn)榱酥С址亲枞筒僮餍枰獧z查這個(gè)標(biāo)志是否有O_NONBLOCK。
--893-->f_mode;對(duì)文件的讀寫(xiě)模式,對(duì)應(yīng)系統(tǒng)調(diào)用open的mod_t mode參數(shù),比如O_RDWR。如果驅(qū)動(dòng)程序需要這個(gè)值,可以直接讀取這個(gè)字段。
--905-->private_data表示file結(jié)構(gòu)的私有數(shù)據(jù)
我在Linux設(shè)備管理(二)_從cdev_add說(shuō)起一文中已經(jīng)分析過(guò)chrdev_open(),這里僅作概述。
//fs/chr_dev.c348 /*349 * Called every time a character special file is opened350 */351 static int chrdev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)352 { /* 搜索cdev */ ...390 replace_fops(filp, fops);391 if (filp->f_op->open) {392 ret = filp->f_op->open(inode, filp);393 if (ret)394 goto out_cdev_put;395 } ...402 }
可以看出,這個(gè)函數(shù)有三個(gè)任務(wù)(劃重點(diǎn)!!!):
chrdev_open()
--352-389-->利用container_of等根據(jù)inode中的成員找到相應(yīng)的cdev
--390-->用cdev.fops替換filp->f_op,即填充了一個(gè)空的struct file的f_op成員。
--392-->回調(diào)替換之后的filp->f_op->open,由于替換,這個(gè)其實(shí)就是cdev.fops
至此,我們知道了我們寫(xiě)的驅(qū)動(dòng)中的open()在何時(shí)會(huì)被回調(diào),這樣我們就可以實(shí)現(xiàn)很多有意思的功能,比如,
我們可以在open中通過(guò)inode->cdev來(lái)識(shí)別具體的設(shè)備,并將其私有數(shù)據(jù)隱藏到file結(jié)構(gòu)的private_data中,進(jìn)而識(shí)別同一個(gè)驅(qū)動(dòng)操作一類設(shè)備;
我們也可以在回調(diào)cdev.fops->open()階段重新填充file結(jié)構(gòu)的fop,進(jìn)而實(shí)現(xiàn)同一個(gè)驅(qū)動(dòng)操作不同的設(shè)備,這種思想就是內(nèi)核驅(qū)動(dòng)中常用的分層!
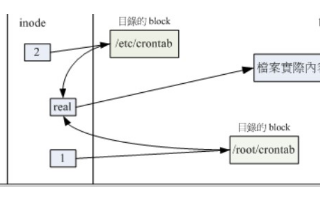
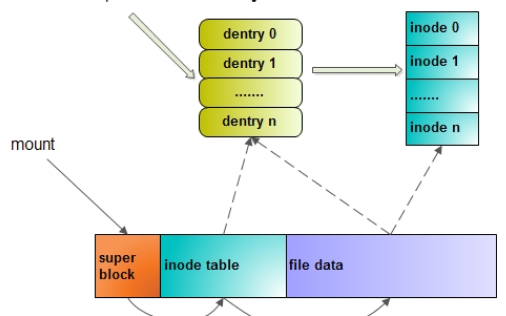
最后總結(jié)一下這些結(jié)構(gòu)之間的關(guān)系:
?
 電子發(fā)燒友App
電子發(fā)燒友App






















評(píng)論