在對zynq進(jìn)行Linux驅(qū)動(dòng)開發(fā)時(shí),除了需要針對zynq內(nèi)ARM自帶的控制器適配驅(qū)動(dòng)外,還需要對zynq PL部分的IP核進(jìn)行驅(qū)動(dòng)開發(fā)。對于ARM來說,zynq PL部分的IP核就是一段地址空間,這段地址空間包含了該IP的一系列寄存器,ARM操作該IP核的寄存器也就是操作這段地址空間,而PL部分IP的驅(qū)動(dòng)也就是對IP寄存器的操作。
1、 硬件設(shè)計(jì)
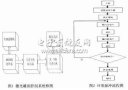
在vivado內(nèi)進(jìn)行設(shè)計(jì)時(shí),RapidIO IP核通過AXI總線與ARM相連,地址空間區(qū)域如圖:

從0x40000000-0x7FFFFFFF均為RapidIO IP的地址空間,注意這里的地址是物理地址,在zynq的裸程序中,可以通過xil_out32()或xil_in32()等函數(shù)直接操縱該地址的值,也即對RapidIO IP核寄存器的讀寫操作。
補(bǔ)充一點(diǎn),考慮到RapidIO IP使用的一致性以及預(yù)防配置出錯(cuò),硬件設(shè)計(jì)時(shí)已經(jīng)將RapidIO IP寄存器進(jìn)行了正確配置,這一部分是在硬件FPGA編程時(shí)實(shí)現(xiàn)的,軟件部分并不需要從頭開始配置RapidIO IP核。因此,對RapidIO IP驅(qū)動(dòng)的開發(fā)也只需要實(shí)現(xiàn)對寄存器的讀、寫這兩個(gè)函數(shù)即可。
2、 devicetree設(shè)計(jì)
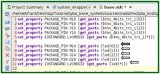
由于RapidIO IP核位于PL部分,需要在devicetree中增加相應(yīng)內(nèi)容,如下:
amba_pl {
#address-cells= <0x1>;
#size-cells= <0x1>;
compatible= "simple-bus";
ranges;
srio_axi_config@40000000{
compatible= "xlnx,xps-rio-1.00.a";
reg= <0x40000000 0x40000000>;
};
};
Amba_pl對應(yīng)PL部分的amba,devicetree中原有的amba對應(yīng)PS部分,兩個(gè)位于同一層。
3、 驅(qū)動(dòng)設(shè)計(jì)
RapidIO IP核驅(qū)動(dòng)實(shí)現(xiàn)對物理地址0x40000000到0x7fffffff的讀、寫操作,可以參考xilinxPL部分CAN IP核的驅(qū)動(dòng)代碼。實(shí)現(xiàn)過程需要注意地址的虛實(shí)轉(zhuǎn)換,0x40000000開始的這一段地址是物理地址,需要將這段地址進(jìn)行映射,確保CPU訪問的地址經(jīng)過MMU轉(zhuǎn)換后確實(shí)對應(yīng)這一地址。
/*
* rio-xiic.c
* Copyright (c) 2002-2007 Xilinx Inc.
* Copyright (c) 2009-2010 Intel Corporation
*
*/
/* Supports:
* Xilinx RapidIO
*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define DRIVER_NAME "xiic-rio"
#define SRIO_ZYNQ_BASEADDR 0x40000000
#define SRIO_ZYNQ_NODE_BASEADDR 0x10100
#define SRIO_ZYNQ_MAX_HOPCOUNT 13
struct xiic_rio {
struct mutex lock;
u8 *data;
};
/* We need global varriable for maped address */
static void __iomem* _rio_base = NULL;
static inline void rio_setreg32(unsigned int addrBase,unsigned int addrOffset,unsigned int value)
{
iowrite32(value, addrBase + addrOffset);
}
static inline int rio_getreg32(unsigned int addrBase,unsigned int addrOffset)
{
unsigned int reg_addr;
reg_addr=addrBase+addrOffset;
return ioread32(reg_addr);
}
static ssize_t hlMaintWrite(unsigned int dstId,unsigned short hopcount, unsigned int offset, unsigned int writedata)
{
unsigned int reg_addr;
if( hopcount > SRIO_ZYNQ_MAX_HOPCOUNT )
{
printk("!!!error, hopcount = %d, > %d
",hopcount,SRIO_ZYNQ_MAX_HOPCOUNT);
return -1;
}
rio_setreg32((unsigned int)_rio_base,SRIO_ZYNQ_NODE_BASEADDR,dstId);
reg_addr = (((hopcount+1)<<24)|offset);
rio_setreg32((unsigned int)_rio_base,reg_addr,writedata);
return 0;
}
static ssize_t hlMaintRead(unsigned int dstId,unsigned short hopcount, unsigned int offset, void *mrdataAdr)
{
unsigned int reg_addr;
if( hopcount > SRIO_ZYNQ_MAX_HOPCOUNT )
{
printk("!!!error, hopcount = %d, > %d
",hopcount,SRIO_ZYNQ_MAX_HOPCOUNT);
return -1;
}
rio_setreg32((unsigned int)_rio_base,SRIO_ZYNQ_NODE_BASEADDR,dstId);
reg_addr = (((hopcount+1)<<24)|offset);
mrdataAdr = rio_getreg32((unsigned int)_rio_base,reg_addr);
printk("M_SRIO_MAINT_REG_READ: hopcount = %d, offset = 0x%x, value = 0x%x
",hopcount,offset,mrdataAdr);
return 0;
}
static SIMPLE_DEV_PM_OPS(xiic_rio_pm_ops, hlMaintRead,hlMaintWrite);
static int xiic_rio_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct xiic_rio *rio;
struct resource *res;
unsigned int mtRdata=0;
rio = kzalloc(sizeof(struct xiic_rio), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!rio)
return -ENOMEM;
/* Get Mapped address */
_rio_base = ioremap_nocache(SRIO_ZYNQ_BASEADDR, 0xe000000);
if (!_rio_base)
return -ENOMEM;
res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0);
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, rio);
hlMaintRead(0xFF,0, 0, mtRdata);
return 0;
}
static int xiic_rio_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct xiic_rio *rio = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);
kfree(rio);
return 0;
}
static const struct of_device_id xiic_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "xlnx,xps-rio-1.00.a", },
{},
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, xiic_of_match);
static struct platform_driver xiic_rio_driver = {
.probe = xiic_rio_probe,
.remove = xiic_rio_remove,
.driver = {
.name = DRIVER_NAME,
.of_match_table = of_match_ptr(xiic_of_match),
.pm = &xiic_rio_pm_ops,
},
};
module_platform_driver(xiic_rio_driver);
MODULE_AUTHOR("info@mocean-labs.com");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Xilinx Rio IP Core driver");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");
上面代碼中ioremap實(shí)現(xiàn)的就是物理地址的映射,該函數(shù)的第二個(gè)參數(shù)為映射的大小,由于模塊上DDR只有1G,所以實(shí)際最大的映射空間只有224M,能訪問IP核的實(shí)際地址空間為0x40000000-0x4e000000。驅(qū)動(dòng)中實(shí)現(xiàn)讀寫兩個(gè)函數(shù),對zynq FPGA地址的訪問可以直接調(diào)用ioread32()、iowrite32(),這兩個(gè)函數(shù)和xil_out32()、xil_in32()相對應(yīng)。
完成驅(qū)動(dòng)后修改Kconfig文件和Makefile文件,加入驅(qū)動(dòng)選項(xiàng),這里是合在了I2C總線驅(qū)動(dòng)里面:


4、 測試
對該驅(qū)動(dòng)的測試主要是通過調(diào)用讀函數(shù)訪問地址空間,判斷返回值是否符合預(yù)期。由于RapidIO IP核能夠訪問到CPS 1848,可以通過判斷返回值是否是1848的device ID加以驗(yàn)證。
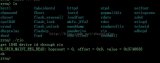
在probe中調(diào)用函數(shù)hlMaintRead(0xFF,0, 0, mtRdata),返回值如下:

Value和1848 datasheet中的一致,驗(yàn)證通過。

5、 總結(jié)
在對zynq PL部分IP核的驅(qū)動(dòng)開發(fā)過程中需要注意地址轉(zhuǎn)換問題,下面兩種異常都是屬于地址問題

這種異常是映射空間不夠大,對應(yīng)于ioremap第二個(gè)參數(shù)

 電子發(fā)燒友App
電子發(fā)燒友App























評論