Message Digest Algorithm MD5(中文名為消息摘要算法第五版)為計算機安全領域廣泛使用的一種散列函數,用以提供消息的完整性保護。該算法的文件號為RFC 1321(R.Rivest,MIT Laboratory for Computer Science and RSA Data Security Inc. April 1992)。
MD5即Message-Digest Algorithm 5(信息-摘要算法5),用于確保信息傳輸完整一致。是計算機廣泛使用的雜湊算法之一(又譯摘要算法、哈希算法),主流編程語言普遍已有MD5實現。將數據(如漢字)運算為另一固定長度值,是雜湊算法的基礎原理,MD5的前身有MD2、MD3和MD4。
MD5算法具有以下特點:
1、壓縮性:任意長度的數據,算出的MD5值長度都是固定的。
2、容易計算:從原數據計算出MD5值很容易。
3、抗修改性:對原數據進行任何改動,哪怕只修改1個字節,所得到的MD5值都有很大區別。
4、強抗碰撞:已知原數據和其MD5值,想找到一個具有相同MD5值的數據(即偽造數據)是非常困難的。
MD5的作用是讓大容量信息在用數字簽名軟件簽署私人密鑰前被“壓縮”成一種保密的格式(就是把一個任意長度的字節串變換成一定長的十六進制數字串)。除了MD5以外,其中比較有名的還有sha-1、RIPEMD以及Haval等。
MD5算法原理與實現
一、MD5概念
MD5,全名Message Digest Algorithm 5 ,中文名為消息摘要算法第五版,為計算機安全領域廣泛使用的一種散列函數,用以提供消息的完整性保護。上面這段話話引用自百度百科,我的理解MD5是一種信息摘要算法,主要是通過特定的hash散列方法將文本信息轉換成簡短的信息摘要,壓縮+加密+hash算法的結合體,是絕對不可逆的。
二、MD5計算步驟
MD5以512位分組來處理輸入的信息,且每一分組又被劃分為16個32位子分組,經過了一系列的處理后,算法的輸出由四個32位分組組成,將這四個32位分組級聯后將生成一個128位散列值。
第一步、填充
如果輸入信息的長度(bit)對512求余的結果不等于448,就需要填充使得對512求余的結果等于448。填充的方法是填充一個1和n個0。填充完后,信息的長度就為N*512+448(bit);
第二步、記錄信息長度
用64位來存儲填充前信息長度。這64位加在第一步結果的后面,這樣信息長度就變為N*512+448+64=(N+1)*512位。
第三步、裝入標準的幻數(四個整數)
標準的幻數(物理順序)是(A=(01234567)16,B=(89ABCDEF)16,C=(FEDCBA98)16,D=(76543210)16)。如果在程序中定義應該是(A=0X67452301L,B=0XEFCDAB89L,C=0X98BADCFEL,D=0X10325476L)。有點暈哈,其實想一想就明白了。
第四步、四輪循環運算
循環的次數是分組的個數(N+1)
1)將每一512字節細分成16個小組,每個小組64位(8個字節)
2)先認識四個線性函數(&是與,|是或,~是非,^是異或)
[cpp] view plain copyF(X,Y,Z)=(X&Y)|((~X)&Z)
G(X,Y,Z)=(X&Z)|(Y&(~Z))
H(X,Y,Z)=X^Y^Z
I(X,Y,Z)=Y^(X|(~Z))
3)設Mj表示消息的第j個子分組(從0到15),《《《s表示循環左移s位,則四種操作為:
[cpp] view plain copyFF(a,b,c,d,Mj,s,ti)表示a=b+((a+F(b,c,d)+Mj+ti)《《《s)
GG(a,b,c,d,Mj,s,ti)表示a=b+((a+G(b,c,d)+Mj+ti)《《《s)
HH(a,b,c,d,Mj,s,ti)表示a=b+((a+H(b,c,d)+Mj+ti)《《《s)
II(a,b,c,d,Mj,s,ti)表示a=b+((a+I(b,c,d)+Mj+ti)《《《s)
4)四輪運算
[cpp] view plain copy第一輪
a=FF(a,b,c,d,M0,7,0xd76aa478)
b=FF(d,a,b,c,M1,12,0xe8c7b756)
c=FF(c,d,a,b,M2,17,0x242070db)
d=FF(b,c,d,a,M3,22,0xc1bdceee)
a=FF(a,b,c,d,M4,7,0xf57c0faf)
b=FF(d,a,b,c,M5,12,0x4787c62a)
c=FF(c,d,a,b,M6,17,0xa8304613)
d=FF(b,c,d,a,M7,22,0xfd469501)
a=FF(a,b,c,d,M8,7,0x698098d8)
b=FF(d,a,b,c,M9,12,0x8b44f7af)
c=FF(c,d,a,b,M10,17,0xffff5bb1)
d=FF(b,c,d,a,M11,22,0x895cd7be)
a=FF(a,b,c,d,M12,7,0x6b901122)
b=FF(d,a,b,c,M13,12,0xfd987193)
c=FF(c,d,a,b,M14,17,0xa679438e)
d=FF(b,c,d,a,M15,22,0x49b40821)
第二輪
a=GG(a,b,c,d,M1,5,0xf61e2562)
b=GG(d,a,b,c,M6,9,0xc040b340)
c=GG(c,d,a,b,M11,14,0x265e5a51)
d=GG(b,c,d,a,M0,20,0xe9b6c7aa)
a=GG(a,b,c,d,M5,5,0xd62f105d)
b=GG(d,a,b,c,M10,9,0x02441453)
c=GG(c,d,a,b,M15,14,0xd8a1e681)
d=GG(b,c,d,a,M4,20,0xe7d3fbc8)
a=GG(a,b,c,d,M9,5,0x21e1cde6)
b=GG(d,a,b,c,M14,9,0xc33707d6)
c=GG(c,d,a,b,M3,14,0xf4d50d87)
d=GG(b,c,d,a,M8,20,0x455a14ed)
a=GG(a,b,c,d,M13,5,0xa9e3e905)
b=GG(d,a,b,c,M2,9,0xfcefa3f8)
c=GG(c,d,a,b,M7,14,0x676f02d9)
d=GG(b,c,d,a,M12,20,0x8d2a4c8a)
第三輪
a=HH(a,b,c,d,M5,4,0xfffa3942)
b=HH(d,a,b,c,M8,11,0x8771f681)
c=HH(c,d,a,b,M11,16,0x6d9d6122)
d=HH(b,c,d,a,M14,23,0xfde5380c)
a=HH(a,b,c,d,M1,4,0xa4beea44)
b=HH(d,a,b,c,M4,11,0x4bdecfa9)
c=HH(c,d,a,b,M7,16,0xf6bb4b60)
d=HH(b,c,d,a,M10,23,0xbebfbc70)
a=HH(a,b,c,d,M13,4,0x289b7ec6)
b=HH(d,a,b,c,M0,11,0xeaa127fa)
c=HH(c,d,a,b,M3,16,0xd4ef3085)
d=HH(b,c,d,a,M6,23,0x04881d05)
a=HH(a,b,c,d,M9,4,0xd9d4d039)
b=HH(d,a,b,c,M12,11,0xe6db99e5)
c=HH(c,d,a,b,M15,16,0x1fa27cf8)
d=HH(b,c,d,a,M2,23,0xc4ac5665)
第四輪
a=II(a,b,c,d,M0,6,0xf4292244)
b=II(d,a,b,c,M7,10,0x432aff97)
c=II(c,d,a,b,M14,15,0xab9423a7)
d=II(b,c,d,a,M5,21,0xfc93a039)
a=II(a,b,c,d,M12,6,0x655b59c3)
b=II(d,a,b,c,M3,10,0x8f0ccc92)
c=II(c,d,a,b,M10,15,0xffeff47d)
d=II(b,c,d,a,M1,21,0x85845dd1)
a=II(a,b,c,d,M8,6,0x6fa87e4f)
b=II(d,a,b,c,M15,10,0xfe2ce6e0)
c=II(c,d,a,b,M6,15,0xa3014314)
d=II(b,c,d,a,M13,21,0x4e0811a1)
a=II(a,b,c,d,M4,6,0xf7537e82)
b=II(d,a,b,c,M11,10,0xbd3af235)
c=II(c,d,a,b,M2,15,0x2ad7d2bb)
d=II(b,c,d,a,M9,21,0xeb86d391)
5)每輪循環后,將A,B,C,D分別加上a,b,c,d,然后進入下一循環。
三、MD5應用
1、一致性驗證
MD5的典型應用是對一段文本信息產生信息摘要,以防止被篡改。常常在某些軟件下載站點的某軟件信息中看到其MD5值,它的作用就在于我們可以在下載該軟件后,對下載回來的文件用專門的軟件(如Windows MD5 Check等)做一次MD5校驗,以確保我們獲得的文件與該站點提供的文件為同一文件。
2、數字證書
如果有一個第三方的認證機構,用MD5還可以防止文件作者的“抵賴”,這就是所謂的數字簽名應用。
3、安全訪問認證
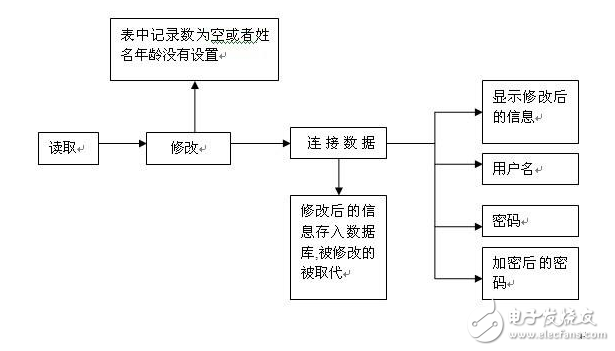
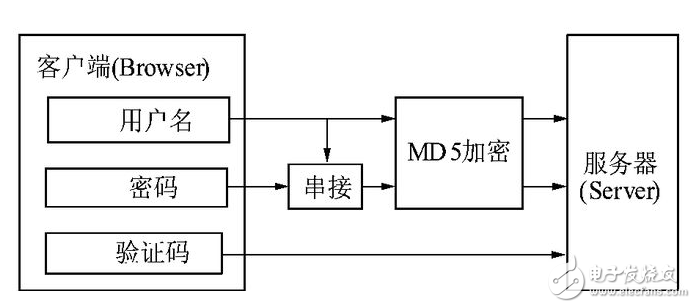
在Unix系統中用戶的密碼是以MD5(或其它類似的算法)經Hash運算后存儲在文件系統中。當用戶登錄的時候,系統把用戶輸入的密碼進行MD5 Hash運算,然后再去和保存在文件系統中的MD5值進行比較,進而確定輸入的密碼是否正確。通過這樣的步驟,系統在并不知道用戶密碼的明碼的情況下就可以確定用戶登錄系統的合法性。
四、源代碼
[cpp] view plain copy//MessageDigestAlgorithm5.h
#pragma once
#include《string》
#include《fstream》
#include《iostream》
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned char Byte;
class CMessageDigestAlgorithm5
{
public:
CMessageDigestAlgorithm5(void);
~CMessageDigestAlgorithm5(void);
//MD5算法主函數,對str加密
string Encode(string &str);
string Encode(ifstream& infile);
private:
unsigned int F(unsigned int x, unsigned int y,unsigned int z);
unsigned int G(unsigned int x, unsigned int y,unsigned int z);
unsigned int H(unsigned int x, unsigned int y,unsigned int z);
unsigned int I(unsigned int x, unsigned int y,unsigned int z);
void Initialize();
unsigned int LeftRotate(unsigned int opNumber,unsigned int opBit);
void FF(unsigned int &a, unsigned int b,unsigned int c,unsigned int d, unsigned int Mj,unsigned int s,unsigned int Ti);
void GG(unsigned int &a, unsigned int b,unsigned int c,unsigned int d, unsigned int Mj,unsigned int s,unsigned int Ti);
void HH(unsigned int &a, unsigned int b,unsigned int c,unsigned int d, unsigned int Mj,unsigned int s,unsigned int Ti);
void II(unsigned int &a, unsigned int b,unsigned int c,unsigned int d, unsigned int Mj,unsigned int s,unsigned int Ti);
void ByteToUnsignedInt(const Byte* input, unsigned int* output, size_t length);
string ByteToHexString(const Byte* input, size_t length);
void UnsignedIntToByte(const unsigned int * input, Byte* output, size_t length);
void ProcessOfMDA5(const Byte block[64]);
void EncodeByte(const Byte* input, size_t length);
void Final();
private:
unsigned int m_ChainingVariable[4];
unsigned int m_Count[2];
Byte m_Result[16];
Byte m_Buffer[64];
enum
{
S11 = 7,
S12 = 12,
S13 = 17,
S14 = 22,
S21 = 5,
S22 = 9,
S23 = 14,
S24 = 20,
S31 = 4,
S32 = 11,
S33 = 16,
S34 = 23,
S41 = 6,
S42 = 10,
S43 = 15,
S44 = 21,
};
static const Byte g_Padding[64];
};
[cpp] view plain copy//MessageDigestAlgorithm5.cpp
#include “stdafx.h”
#include “MessageDigestAlgorithm5.h”
const Byte CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::g_Padding[64] = { 0x80 };//第一位補1,其他補0
CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::CMessageDigestAlgorithm5(void)
{
}
CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::~CMessageDigestAlgorithm5(void)
{
}
unsigned int CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::F(unsigned int x, unsigned int y,unsigned int z)
{
return (x & y) | ((~ x) & z);
}
unsigned int CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::G(unsigned int x, unsigned int y,unsigned int z)
{
return (x & z) | (y & (~ z));
}
unsigned int CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::H(unsigned int x, unsigned int y,unsigned int z)
{
return x ^ y ^ z;
}
unsigned int CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::I(unsigned int x, unsigned int y,unsigned int z)
{
return y ^ (x | (~ z));
}
/***************************************************
*參數:空
*功能:初始化鏈接變量
*返回值:空
****************************************************/
void CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::Initialize()
{
m_Count[0] = m_Count[1] = 0;
m_ChainingVariable[0] = 0x67452301;
m_ChainingVariable[1] = 0xefcdab89;
m_ChainingVariable[2] = 0x98badcfe;
m_ChainingVariable[3] = 0x10325476;
}
/***************************************************
*參數:opNumber表示待左移的數
opBit表示左移的位數
*功能:完成循環左移操作
*返回值:循環左移后值
****************************************************/
unsigned int CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::LeftRotate(unsigned int opNumber,unsigned int opBit)
{
unsigned int left = opNumber;
unsigned int right = opNumber;
return (left 《《 opBit) | (right 》》 (32 - opBit));
}
void CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::FF(unsigned int &a, unsigned int b,unsigned int c,unsigned int d, unsigned int Mj,unsigned int s,unsigned int Ti)
{
unsigned int temp = a + F(b,c,d) + Mj + Ti;
a = b + LeftRotate(temp,s);
}
void CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::GG(unsigned int &a, unsigned int b,unsigned int c,unsigned int d,unsigned int Mj,unsigned int s,unsigned int Ti)
{
unsigned int temp = a + G(b,c,d) + Mj + Ti;
a = b + LeftRotate(temp,s);
}
void CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::HH(unsigned int &a, unsigned int b,unsigned int c,unsigned int d, unsigned int Mj,unsigned int s,unsigned int Ti)
{
unsigned int temp = a + H(b,c,d) + Mj + Ti;
a = b + LeftRotate(temp,s);
}
void CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::II(unsigned int &a, unsigned int b,unsigned int c,unsigned int d, unsigned int Mj,unsigned int s,unsigned int Ti)
{
unsigned int temp = a + I(b,c,d) + Mj + Ti;
a = b + LeftRotate(temp,s);
}
/***************************************************
*參數:input表示輸入字節數組
output表示輸出unsigned int數組
length表示輸入字節長度
*功能:byte轉unsigned int(左低右高)
*返回值:空
****************************************************/
void CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::ByteToUnsignedInt(const Byte* input, unsigned int* output, size_t length)
{
for(size_t i = 0,j = 0;j 《 length;++ i, j += 4)
{
output[i] = ((static_cast《unsigned int》(input[j]))
|((static_cast《unsigned int》(input[j + 1])) 《《 8)
|((static_cast《unsigned int》(input[j + 2])) 《《 16)
|((static_cast《unsigned int》(input[j + 3])) 《《 24));
}
}
/***************************************************
*參數:input表示輸入unsigned int數組
output表示輸出字節數組
length表示輸入字節長度
*功能:unsigned int轉byte
*返回值:空
****************************************************/
void CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::UnsignedIntToByte(const unsigned int * input, Byte* output, size_t length)
{
for (size_t i = 0, j = 0; j 《 length; ++i, j += 4)
{
output[j] = static_cast《Byte》(input[i] & 0xff);
output[j + 1] = static_cast《Byte》((input[i]》》 8) & 0xff);
output[j + 2] = static_cast《Byte》((input[i]》》 16) & 0xff);
output[j + 3] = static_cast《Byte》((input[i]》》 24) & 0xff);
}
}
/***************************************************
*參數:groups[]表示一個512位(64字節)分組
*功能:四輪主要操作
*返回值:空
****************************************************/
void CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::ProcessOfMDA5(const Byte groups[64])
{
unsigned int a = m_ChainingVariable[0], b = m_ChainingVariable[1], c = m_ChainingVariable[2], d = m_ChainingVariable[3];
unsigned int M[16];
ByteToUnsignedInt( groups, M, 64);
FF(a, b, c, d, M[ 0], S11, 0xd76aa478);
FF(d, a, b, c, M[ 1], S12, 0xe8c7b756);
FF(c, d, a, b, M[ 2], S13, 0x242070db);
FF(b, c, d, a, M[ 3], S14, 0xc1bdceee);
FF(a, b, c, d, M[ 4], S11, 0xf57c0faf);
FF(d, a, b, c, M[ 5], S12, 0x4787c62a);
FF(c, d, a, b, M[ 6], S13, 0xa8304613);
FF(b, c, d, a, M[ 7], S14, 0xfd469501);
FF(a, b, c, d, M[ 8], S11, 0x698098d8);
FF(d, a, b, c, M[ 9], S12, 0x8b44f7af);
FF(c, d, a, b, M[10], S13, 0xffff5bb1);
FF(b, c, d, a, M[11], S14, 0x895cd7be);
FF(a, b, c, d, M[12], S11, 0x6b901122);
FF(d, a, b, c, M[13], S12, 0xfd987193);
FF(c, d, a, b, M[14], S13, 0xa679438e);
FF(b, c, d, a, M[15], S14, 0x49b40821);
GG(a, b, c, d, M[ 1], S21, 0xf61e2562);
GG(d, a, b, c, M[ 6], S22, 0xc040b340);
GG(c, d, a, b, M[11], S23, 0x265e5a51);
GG(b, c, d, a, M[ 0], S24, 0xe9b6c7aa);
GG(a, b, c, d, M[ 5], S21, 0xd62f105d);
GG(d, a, b, c, M[10], S22, 0x2441453);
GG(c, d, a, b, M[15], S23, 0xd8a1e681);
GG(b, c, d, a, M[ 4], S24, 0xe7d3fbc8);
GG(a, b, c, d, M[ 9], S21, 0x21e1cde6);
GG(d, a, b, c, M[14], S22, 0xc33707d6);
GG(c, d, a, b, M[ 3], S23, 0xf4d50d87);
GG(b, c, d, a, M[ 8], S24, 0x455a14ed);
GG(a, b, c, d, M[13], S21, 0xa9e3e905);
GG(d, a, b, c, M[ 2], S22, 0xfcefa3f8);
GG(c, d, a, b, M[ 7], S23, 0x676f02d9);
GG(b, c, d, a, M[12], S24, 0x8d2a4c8a);
HH(a, b, c, d, M[ 5], S31, 0xfffa3942);
HH(d, a, b, c, M[ 8], S32, 0x8771f681);
HH(c, d, a, b, M[11], S33, 0x6d9d6122);
HH(b, c, d, a, M[14], S34, 0xfde5380c);
HH(a, b, c, d, M[ 1], S31, 0xa4beea44);
HH(d, a, b, c, M[ 4], S32, 0x4bdecfa9);
HH(c, d, a, b, M[ 7], S33, 0xf6bb4b60);
HH(b, c, d, a, M[10], S34, 0xbebfbc70);
HH(a, b, c, d, M[13], S31, 0x289b7ec6);
HH(d, a, b, c, M[ 0], S32, 0xeaa127fa);
HH(c, d, a, b, M[ 3], S33, 0xd4ef3085);
HH(b, c, d, a, M[ 6], S34, 0x4881d05);
HH(a, b, c, d, M[ 9], S31, 0xd9d4d039);
HH(d, a, b, c, M[12], S32, 0xe6db99e5);
HH(c, d, a, b, M[15], S33, 0x1fa27cf8);
HH(b, c, d, a, M[ 2], S34, 0xc4ac5665);
II(a, b, c, d, M[ 0], S41, 0xf4292244);
II(d, a, b, c, M[ 7], S42, 0x432aff97);
II(c, d, a, b, M[14], S43, 0xab9423a7);
II(b, c, d, a, M[ 5], S44, 0xfc93a039);
II(a, b, c, d, M[12], S41, 0x655b59c3);
II(d, a, b, c, M[ 3], S42, 0x8f0ccc92);
II(c, d, a, b, M[10], S43, 0xffeff47d);
II(b, c, d, a, M[ 1], S44, 0x85845dd1);
II(a, b, c, d, M[ 8], S41, 0x6fa87e4f);
II(d, a, b, c, M[15], S42, 0xfe2ce6e0);
II(c, d, a, b, M[ 6], S43, 0xa3014314);
II(b, c, d, a, M[13], S44, 0x4e0811a1);
II(a, b, c, d, M[ 4], S41, 0xf7537e82);
II(d, a, b, c, M[11], S42, 0xbd3af235);
II(c, d, a, b, M[ 2], S43, 0x2ad7d2bb);
II(b, c, d, a, M[ 9], S44, 0xeb86d391);
m_ChainingVariable[0] += a;
m_ChainingVariable[1] += b;
m_ChainingVariable[2] += c;
m_ChainingVariable[3] += d;
}
/***************************************************
*參數:input表示輸入字節數組
length表示輸入字節長度=16(8*16=128位輸出)
*功能:byte轉16進制
*返回值:16進制字符串
****************************************************/
string CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::ByteToHexString(const Byte* input, size_t length)
{
const char MapByteToHex[16] =
{
‘0’, ‘1’, ‘2’, ‘3’,
‘4’, ‘5’, ‘6’, ‘7’,
‘8’, ‘9’, ‘A’, ‘B’,
‘C’, ‘D’, ‘E’, ‘F’
};
string str;
for (size_t i = 0; i 《 length; ++ i)
{
unsigned int temp = static_cast《unsigned int》(input[i]);
unsigned int a = temp / 16;
unsigned int b = temp % 16;
str.append(1, MapByteToHex[a]);
str.append(1, MapByteToHex[b]);
}
return str;
}
/***************************************************
*參數:str表示待加密文本
*功能:MD5算法主函數
*返回值:MD5加密后算列值
****************************************************/
string CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::Encode(string &str)
{
Initialize();
EncodeByte((const Byte * )(str.c_str()), str.length());
Final();
string strMD5 = ByteToHexString(m_Result,16);
return strMD5;
}
/***************************************************
*參數:infile表示待加密文件
*功能:MD5算法主函數
*返回值:MD5加密后算列值
****************************************************/
string CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::Encode(ifstream & infile)
{
if (!infile)
{
return “”;
}
Initialize();
streamsize length;
string str;
char buffer[1024];
while (! infile.eof())
{
infile.read(buffer, 1024);
length = infile.gcount();
if (length 》 0)
{
EncodeByte((const Byte* )buffer,length);
Final();
}
}
infile.close();
string strMD5 = ByteToHexString(m_Result,16);
return strMD5;
}
void CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::EncodeByte(const Byte* input, size_t length)
{
unsigned int index, partLen;
size_t i;
index = static_cast《unsigned int》((m_Count[0] 》》 3) & 0x3f);//轉換成字節mod64
m_Count[0] += (static_cast《unsigned int》(length) 《《 3);//bit數
if (m_Count[0] 《 (static_cast《unsigned int》(length) 《《 3))
{
++m_Count[1];
}
m_Count[1] += (static_cast《unsigned int》(length) 》》 29);//
partLen = 64 - index;
if (length 》= partLen)
{
memcpy(&m_Buffer[index], input, partLen);
ProcessOfMDA5(m_Buffer);
for (i = partLen; i + 63 《 length; i += 64)
{
ProcessOfMDA5(&input[i]);
}
index = 0;
}
else
{
i = 0;
}
memcpy(&m_Buffer[index], &input[i], length - i);
}
void CMessageDigestAlgorithm5::Final()
{
Byte bits[8];
unsigned int tempChainingVariable[4],tempCount[2];
unsigned int index, padLen;
memcpy(tempChainingVariable, m_ChainingVariable, 16);
memcpy(tempCount, m_Count, 8);
UnsignedIntToByte(m_Count, bits, 8);
index = static_cast《unsigned int》((m_Count[0] 》》 3) & 0x3f);
padLen = (index 《 56) ? (56 - index) : (120 - index);
EncodeByte(g_Padding, padLen);
EncodeByte(bits, 8);
UnsignedIntToByte(m_ChainingVariable,m_Result, 16);
memcpy(m_ChainingVariable, tempChainingVariable, 16);
memcpy(m_Count,tempCount, 8);
}
五、說明
對于MD5算法,不同的讀取格式產生的字節流是不一樣的,而且涉及計算可能需要數據格式轉換,如把bit轉換成一定的整型數據方便計算,因此,不同MD5算法實現版本算出的結果可能有很大不一樣。因此,我覺得最好多次計算的MD5算法版本一致。關于MD5算法,有一個比較好的在線計算工具,點擊MD5在線計算器。MD5算法是不可逆的,但是,基于鍵值對的字典關系原理,有一些收集海量MD5信息與摘要的數據庫,采用枚舉法能夠從MD5值找到原文本信息,提供一個類似的工具,點擊MD5在線破解。此外,在此提供MD5的討論社區,點擊MD5討論社區 。
 電子發燒友App
電子發燒友App




























評論