資料介紹
A smarter grid with the Internet of Things
Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) will deliver a smarter grid to enable more information and connectivity throughout the infrastructure and to homes. Through the IoT, consum-ers, manufacturers and utility providers will uncover new ways to manage devices and ultimately conserve resources and save money by using smart meters, home gate-ways, smart plugs and connected appliances.
This white paper discusses the differ-ent approaches being taken worldwide to connect the smart grid. Examples are provided on how TI is developing full sys-tem solutions by combining hardware (analog and digital) and software to ad-dress some of the challenges in building a smarter and more connected smart grid.
Making the grid infrastructure, meters, homes and buildings more connected
The Internet of Things (IoT) is expected to grow to 50 billion connected devices by 2020 (Cisco, 2011) providing valuable information to consumers, manufacturers and utility provid-ers. Within the IoT, devices across a variety of industries will be interconnected through the Internet and peer-to-peer connections as well as closed networks like those used in the smart grid infrastructure.
With the global focus on energy and water management and conservation, the IoT will extend the connected benefits of the smart grid beyond the distribution, automation and monitoring being done by utility providers. Management systems for in-home and in-building use will help consumers monitor their own usage and adjust behaviors. These systems will eventually regulate automatically by operating during off-peak energy hours and connect to sensors to monitor occupancy, lighting conditions, and more. But it all starts with a smarter and more connected grid.
The grid needs to change to face today’s challenges
In the simplest terms, building a smart grid means securing the future of energy supply for everyone in a rapidly growing population with a limited power production capacity. A smart grid reduces the losses, increases efficiency, optimizes the energy demand distribution and also makes large-scale renewable energy such as solar and wind deployments a reality. With an aging infrastructure, the grid is facing severe challenges including recurring black-outs in major industrialized cities around the globe, more than 30 percent electrical energy lost from production to homes in countries like India, and 35 percent drinkable water wasted in leak-ages in France and Australia.
The grid topology needs to adapt and shift from a centralized source to a distributed topol-ogy that can absorb different energy sources in a dynamic way. There is a need to track real-time energy consumption and demand to the energy supply: this goes with the deployment of more remote sensing equipment capable of measuring, monitoring and communicating-
2 Texas Instruments
energy data that can be used to implement a self-healing grid, increase the overall efficiency, and increase the level of self-monitoring and decision making. The connected smart grid provides a communication network that will connect all the different energy-related equipment of the future. From the transmission and distribution power infrastructure, electrical, water, gas, and heat meters, to home and building automation, Texas Instruments (TI) is addressing global smart grid challenges and building system solutions to connect grid devices.
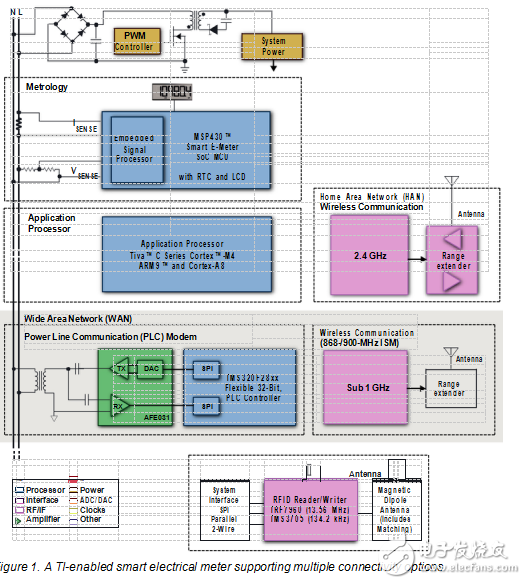
The first key step towards a smart grid that makes the IoT real is the mass deployment of smart meters.
Millions of smart electrical meters are already connected
Around the world, electric meters are leading the way in smart meter deployments. For instance, the adoption rate of smart electrical meters (e-meters) in the United States is close to 50 percent with millions of electri-cal meters deployed today in the field, connected to the grid and regularly communicating data. Essentially,
- 智能柵極驅動白皮書 1次下載
- 2020物聯(lián)網白皮書(信通院)
- 物聯(lián)網_ZETA生態(tài)白皮書
- 物聯(lián)網白皮書分享(2020年) 1次下載
- LE audio白皮書
- 高通 Snapdragon Sound 技術白皮書
- 《人工智能標準化白皮書》2018版 0次下載
- 和利時工業(yè)信息安全白皮書下載 22次下載
- MiniGUI 技術白皮書 32次下載
- 微軟白皮書 屬于自己的全新物聯(lián)網 8次下載
- 【工信部】物聯(lián)網標識白皮書2013 17次下載
- IBM-Analytics工業(yè)4.0與物聯(lián)網白皮書 0次下載
- 物聯(lián)網白皮書(2015年) 14次下載
- 中國市場Wifi白皮書 18次下載
- 存儲基礎知識白皮書
- PLC在物聯(lián)網中的應用 836次閱讀
- 工控機在物聯(lián)網中的應用 542次閱讀
- 西門子發(fā)布工業(yè)5G全連接工廠白皮書(全文) 1863次閱讀
- 新型 GPU 云桌面的準確定義 5744次閱讀
- 《大規(guī)模光電集成賦能智能算力網絡白皮書》概述 1065次閱讀
- 白皮書上新 | Vishay 陶瓷電容快速選型指南,快接住! 1496次閱讀
- 突破物聯(lián)網界限,您準備好了嗎?(文末免費下載白皮書) 2027次閱讀
- 工業(yè)互聯(lián)網平臺創(chuàng)新發(fā)展白皮書你了解嗎全文PPT觀看 4489次閱讀
- 德勤首發(fā)《中國人工智能產業(yè)白皮書》:中國人工智能產業(yè)深度解析 5957次閱讀
- 大數(shù)據與人工智能技術如何幫助智能電網和能源互聯(lián)網的發(fā)展 9195次閱讀
- 通信技術對于物聯(lián)網意義重大,在物聯(lián)網產業(yè)中屬于核心技術 8302次閱讀
- 智能電網架構的目標原則和智能電網架構的演進路線探討 2984次閱讀
- 中本聰?shù)膭?chuàng)世紀之路如何開始的? 1448次閱讀
- Silicon Labs閱讀照明白皮書答題活動開獎! 4670次閱讀
- 物聯(lián)網中射頻技術的應用 2974次閱讀
下載排行
本周
- 1電子電路原理第七版PDF電子教材免費下載
- 0.00 MB | 1490次下載 | 免費
- 2單片機典型實例介紹
- 18.19 MB | 93次下載 | 1 積分
- 3S7-200PLC編程實例詳細資料
- 1.17 MB | 27次下載 | 1 積分
- 4筆記本電腦主板的元件識別和講解說明
- 4.28 MB | 18次下載 | 4 積分
- 5開關電源原理及各功能電路詳解
- 0.38 MB | 10次下載 | 免費
- 6基于AT89C2051/4051單片機編程器的實驗
- 0.11 MB | 4次下載 | 免費
- 7基于單片機和 SG3525的程控開關電源設計
- 0.23 MB | 3次下載 | 免費
- 8基于單片機的紅外風扇遙控
- 0.23 MB | 3次下載 | 免費
本月
- 1OrCAD10.5下載OrCAD10.5中文版軟件
- 0.00 MB | 234313次下載 | 免費
- 2PADS 9.0 2009最新版 -下載
- 0.00 MB | 66304次下載 | 免費
- 3protel99下載protel99軟件下載(中文版)
- 0.00 MB | 51209次下載 | 免費
- 4LabView 8.0 專業(yè)版下載 (3CD完整版)
- 0.00 MB | 51043次下載 | 免費
- 5555集成電路應用800例(新編版)
- 0.00 MB | 33562次下載 | 免費
- 6接口電路圖大全
- 未知 | 30320次下載 | 免費
- 7Multisim 10下載Multisim 10 中文版
- 0.00 MB | 28588次下載 | 免費
- 8開關電源設計實例指南
- 未知 | 21539次下載 | 免費
總榜
- 1matlab軟件下載入口
- 未知 | 935053次下載 | 免費
- 2protel99se軟件下載(可英文版轉中文版)
- 78.1 MB | 537791次下載 | 免費
- 3MATLAB 7.1 下載 (含軟件介紹)
- 未知 | 420026次下載 | 免費
- 4OrCAD10.5下載OrCAD10.5中文版軟件
- 0.00 MB | 234313次下載 | 免費
- 5Altium DXP2002下載入口
- 未知 | 233046次下載 | 免費
- 6電路仿真軟件multisim 10.0免費下載
- 340992 | 191183次下載 | 免費
- 7十天學會AVR單片機與C語言視頻教程 下載
- 158M | 183277次下載 | 免費
- 8proe5.0野火版下載(中文版免費下載)
- 未知 | 138039次下載 | 免費
 電子發(fā)燒友App
電子發(fā)燒友App

















 創(chuàng)作
創(chuàng)作 發(fā)文章
發(fā)文章 發(fā)帖
發(fā)帖  提問
提問  發(fā)資料
發(fā)資料 發(fā)視頻
發(fā)視頻 上傳資料賺積分
上傳資料賺積分









評論